1 plant per sq ft yield – Embark on a journey to optimize your yield with our comprehensive guide to achieving 1 plant per square foot. Delve into the art of plant selection, spacing, and environmental manipulation to unlock the full potential of your growing space.
Discover the secrets of successful yield optimization techniques employed by seasoned growers worldwide, empowering you to maximize your harvest and elevate your gardening prowess.
Yield Optimization Techniques

Optimizing yield per square foot is crucial for maximizing productivity and profitability in indoor gardening. Employing effective strategies can significantly enhance plant growth, leading to increased harvests. This comprehensive guide delves into the techniques and factors that play a vital role in yield optimization, empowering growers with the knowledge to achieve exceptional results.
The “1 plant per sq ft yield” rule of thumb for container gardening ensures optimal growth and prevents overcrowding. For instance, a live elephant ear plant with its large, showy leaves thrives when given ample space to spread. Adhering to this rule allows each plant to receive adequate sunlight, nutrients, and water, resulting in a flourishing and productive garden.
Plant Selection and Spacing
Selecting the right plant varieties and optimizing spacing are essential for maximizing yield. Choose cultivars known for their high productivity and adaptability to indoor environments. Proper spacing ensures adequate light penetration, airflow, and nutrient availability for each plant. Research optimal spacing recommendations for specific species to prevent overcrowding and competition for resources.
The concept of “1 plant per sq ft yield” is an important factor in optimizing crop production. This strategy has been successfully implemented in various agricultural settings, including the Honda Anna Engine Plant . By carefully managing plant spacing and utilizing efficient growing techniques, farmers can maximize yields while ensuring optimal plant health and productivity.
This approach not only enhances crop quality but also promotes sustainable farming practices, leading to increased food security and economic growth.
Lighting
Light is the primary energy source for plants, and optimizing lighting conditions is critical for maximizing yield. Provide sufficient light intensity and duration to support photosynthesis and plant growth. Utilize high-quality LED grow lights or other efficient lighting systems that emit wavelengths beneficial for plant development. Consider factors such as light spectrum, intensity, and photoperiod to create an optimal lighting environment.
Nutrients
Providing essential nutrients is vital for plant growth and yield. Use a balanced fertilizer program that meets the specific nutritional requirements of your plants. Conduct regular soil or tissue testing to monitor nutrient levels and adjust fertilization accordingly. Ensure proper pH levels to facilitate nutrient uptake and avoid nutrient deficiencies or toxicities that can hinder yield.
Irrigation
Adequate and timely irrigation is essential for maintaining optimal soil moisture levels. Overwatering can lead to root rot and nutrient leaching, while underwatering can stunt growth and reduce yield. Use a reliable irrigation system that provides consistent moisture without waterlogging. Monitor soil moisture regularly and adjust watering schedules based on plant needs, environmental conditions, and the stage of growth.
Real-World Examples, 1 plant per sq ft yield
Numerous successful yield optimization techniques have been implemented in real-world scenarios. Commercial growers have achieved impressive yields by utilizing high-density planting techniques, advanced lighting systems, and precision nutrient management. In a study conducted by the University of California, Davis, researchers demonstrated a 30% increase in yield by optimizing light intensity and duration for cannabis plants.
The concept of 1 plant per sq ft yield is gaining popularity among urban gardeners seeking to maximize their harvests. By understanding the specific needs of each plant, growers can optimize growth and yields. For instance, the heavy metal grass plant , known for its ability to absorb and accumulate heavy metals, thrives in contaminated soils, demonstrating the adaptability of plants to various environmental conditions.
Returning to the concept of 1 plant per sq ft yield, careful plant selection and tailored care can significantly enhance yields in urban gardening settings.
Plant Selection and Spacing
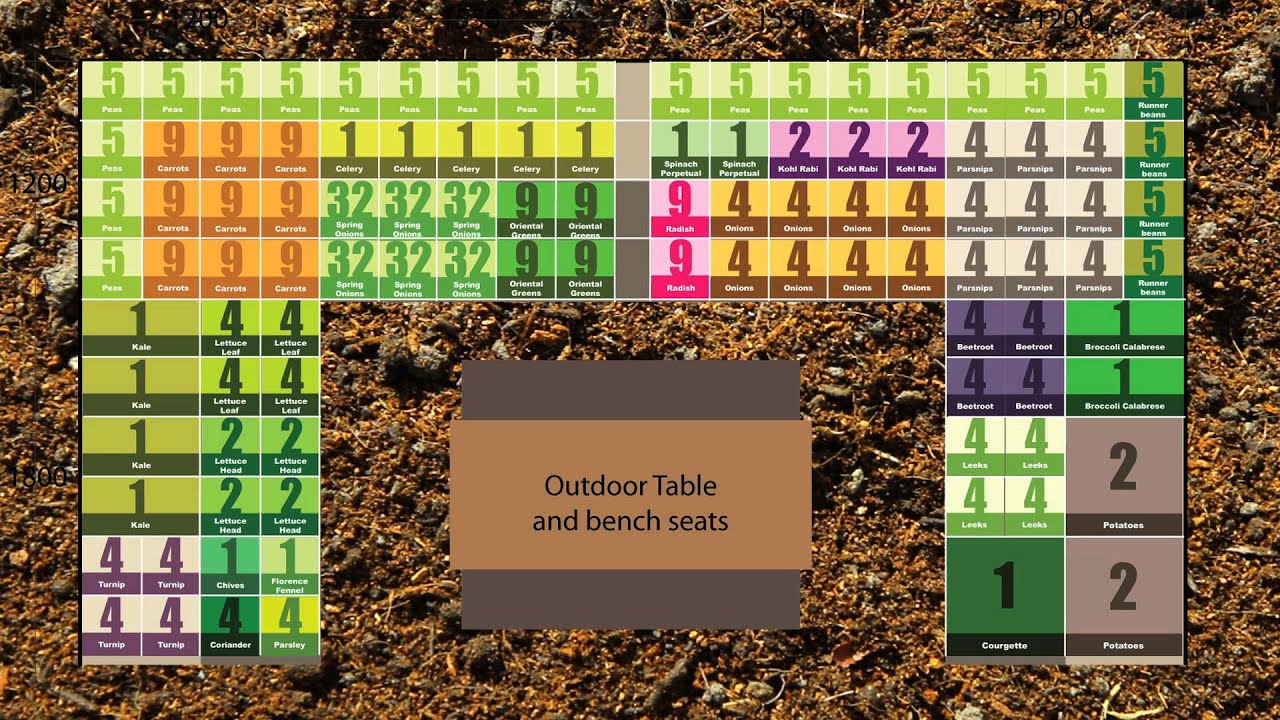
Maximizing yield per square foot requires careful consideration of plant selection and spacing. Choosing the right plant varieties and ensuring optimal spacing are crucial for achieving high yields.
Plant Selection
Selecting plant varieties that are well-suited to the growing conditions and have high yield potential is essential. Factors to consider include:
- Climate and hardiness zone
- Soil type and pH
- Sunlight availability
- Pest and disease resistance
Plant Spacing
Proper spacing between plants is critical for ensuring adequate light penetration and nutrient availability. Overcrowding can lead to competition for resources, reduced plant growth, and lower yields.
| Plant Species | Spacing (inches) |
|---|---|
| Tomatoes | 24-36 |
| Cucumbers | 18-24 |
| Peppers | 18-24 |
| Lettuce | 6-12 |
| Spinach | 4-6 |
By selecting the right plant varieties and adhering to optimal spacing recommendations, growers can maximize yield per square foot and achieve their desired production goals.
Environmental Factors: 1 Plant Per Sq Ft Yield
Environmental factors play a crucial role in determining the yield per square foot. Understanding the impact of temperature, humidity, and carbon dioxide levels on plant growth and development is essential for optimizing yields.
Creating an optimal environment involves monitoring and controlling these factors within specific ranges that promote plant health and productivity.
Temperature
- Optimal range: Most plants thrive in temperatures between 65-85°F (18-29°C).
- Impact of high temperatures: Excessive heat can cause heat stress, leading to reduced photosynthesis, wilting, and stunted growth.
- Impact of low temperatures: Cold temperatures slow down plant metabolism, inhibiting growth and development.
Humidity
- Optimal range: Relative humidity between 40-60% is generally ideal for most plants.
- Impact of high humidity: Excessive humidity can promote fungal growth and disease.
- Impact of low humidity: Low humidity can cause dehydration, wilting, and reduced transpiration.
Carbon Dioxide Levels
- Optimal range: The optimal CO2 concentration for plant growth is around 1,200-1,500 ppm.
- Impact of high CO2 levels: Elevated CO2 levels can increase photosynthesis and plant growth.
- Impact of low CO2 levels: Low CO2 levels limit photosynthesis and can result in reduced yields.