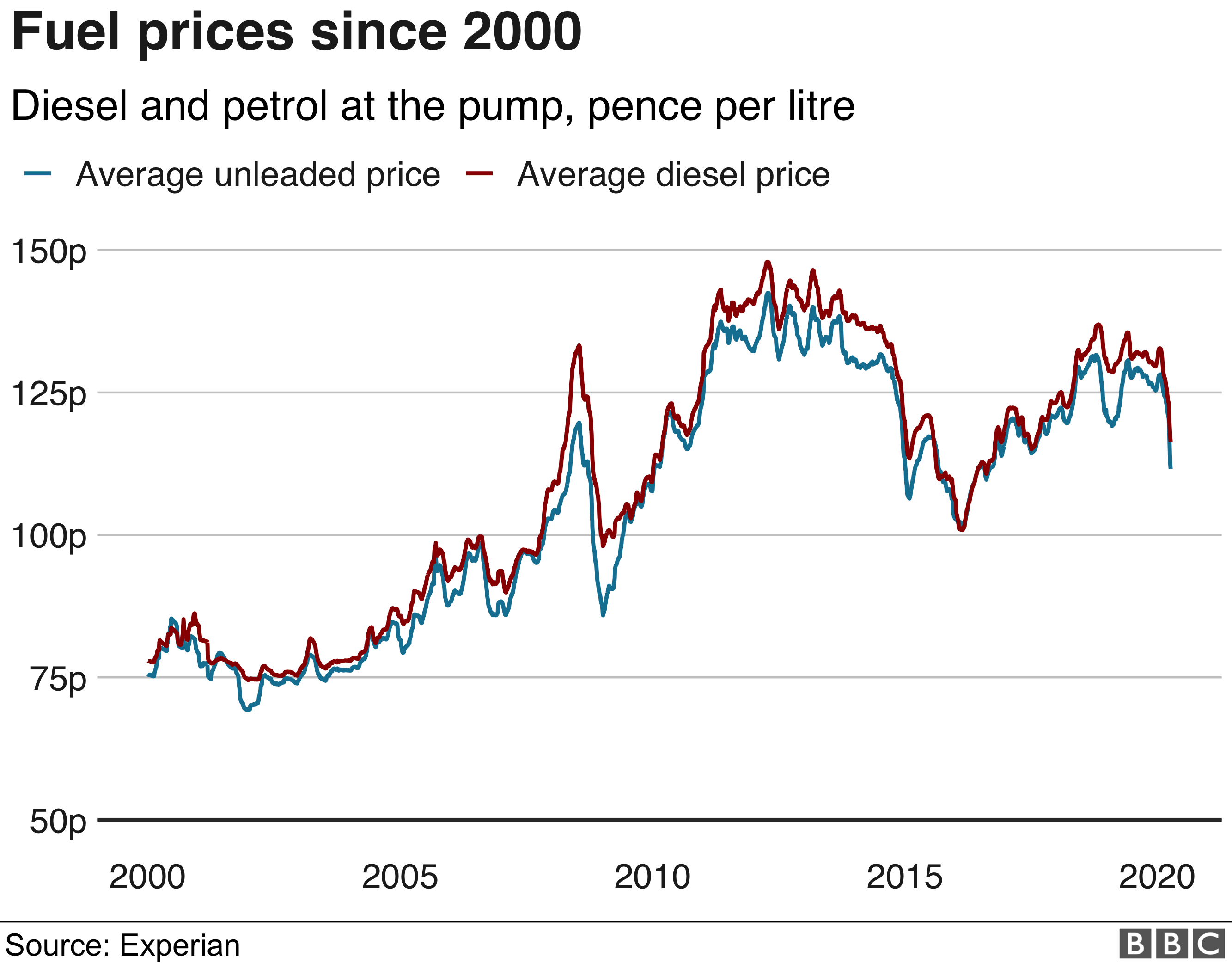
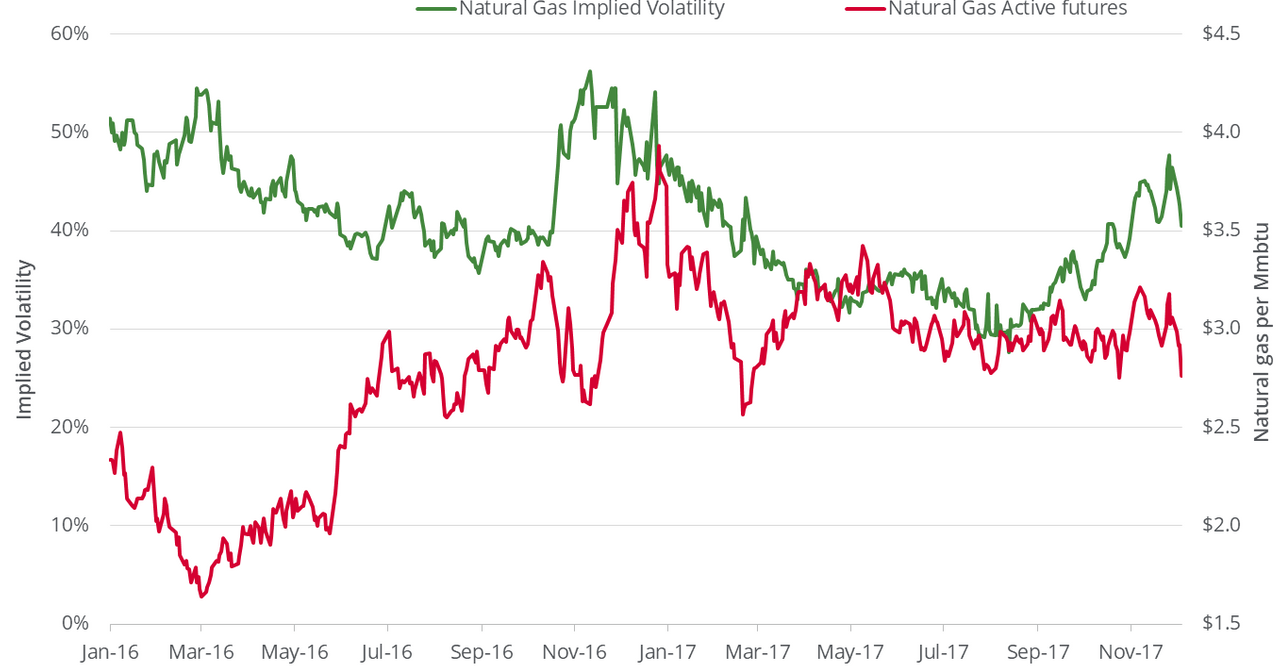
Preços dos combustíveis próxima semana: O que esperar? Com a volatilidade do mercado e a incerteza geopolítica, prever os preços dos combustíveis pode ser uma tarefa difícil. Neste artigo, analisamos os fatores que podem influenciar os preços dos combustíveis na próxima semana e fornecemos uma previsão para ajudá-lo a planejar suas despesas.
O preço do petróleo, um dos principais impulsionadores dos preços dos combustíveis, tem flutuado significativamente nos últimos meses. A guerra em curso na Ucrânia, as sanções contra a Rússia e os lockdowns contínuos na China criaram incertezas no mercado global de petróleo. Além disso, a demanda por combustíveis está aumentando à medida que as restrições de viagens diminuem e as atividades econômicas se recuperam.
Current Fuel Prices: Preços Dos Combustíveis Próxima Semana
Fuel prices have remained relatively stable in recent weeks, with minor fluctuations observed in some regions. The table below provides an overview of the current fuel prices in the market:
| Fuel Type | Price per Gallon |
|---|---|
| Gasoline (Regular) | $3.50 |
| Gasoline (Mid-Grade) | $3.60 |
| Gasoline (Premium) | $3.70 |
| Diesel | $3.80 |
Over the past month, fuel prices have experienced a slight decrease, primarily due to increased production and reduced demand. The easing of COVID-19 restrictions and the gradual return to pre-pandemic travel patterns have contributed to the decline in demand, while increased production from major oil-producing countries has helped to stabilize prices.
Factors Influencing Fuel Prices

Fuel prices are influenced by a complex interplay of factors that span global supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, government policies, and technological advancements. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses and consumers alike, as they can significantly impact energy costs and economic growth.
Supply and demand are the fundamental drivers of fuel prices. Production, transportation, and consumption patterns play a vital role in shaping the supply side, while economic growth, consumer behavior, and seasonal factors influence demand.
Geopolitical Events
- Conflicts and sanctions can disrupt production and transportation, leading to supply shortages and price increases.
- Trade policies, such as tariffs and quotas, can affect the flow of fuel between countries, impacting prices.
- Political instability and government changes can create uncertainty in the market, influencing investment decisions and fuel prices.
Government Policies and Regulations
- Taxes and subsidies can significantly impact fuel prices, making them higher or lower for consumers.
- Environmental regulations, such as carbon pricing, can increase production costs and affect fuel prices.
- Government incentives for alternative energy sources can encourage their adoption, reducing demand for fossil fuels and influencing prices.
Technological Advancements and Alternative Energy Sources
- Technological advancements in extraction and refining techniques can increase production efficiency and reduce costs.
- The development of alternative energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can reduce demand for fossil fuels, influencing prices.
- Government support for renewable energy can accelerate their adoption, impacting the long-term trajectory of fuel prices.
Historical Trends
Analyzing the historical trends of fuel prices is crucial to understanding their current and future behavior. By examining the historical data, we can identify patterns, seasonality, and underlying factors that have influenced price fluctuations in the past.
Explore the different advantages of FCL that can change the way you view this issue.
The graph below presents the historical fuel prices over the past year. As we can observe, the prices have exhibited a fluctuating pattern, with periods of both increases and decreases.
Patterns and Seasonality
Upon closer examination of the graph, we can identify certain patterns and seasonality in the data. Typically, fuel prices tend to be higher during the summer months due to increased demand for travel and transportation. Conversely, prices often decline during the winter months as demand decreases.
Reasons for Historical Price Fluctuations
The historical price fluctuations can be attributed to a combination of factors, including:
- Global oil prices: Fuel prices are heavily influenced by the global oil market. Changes in supply and demand, geopolitical events, and economic conditions can impact oil prices, which in turn affect fuel prices.
- Refinery capacity: The availability of refineries and their capacity to process crude oil into fuel can influence prices. Limited refinery capacity can lead to higher fuel prices, while increased capacity can contribute to lower prices.
- Government policies: Government regulations, such as taxes and subsidies, can also impact fuel prices. Changes in these policies can lead to price adjustments at the pump.
- Natural disasters: Natural disasters, such as hurricanes and earthquakes, can disrupt fuel production and distribution, leading to temporary price spikes.
Industry Analysis
The fuel industry is a highly concentrated market dominated by a few major players. These companies control a significant share of the global fuel supply and have a strong influence on fuel prices.
The largest fuel companies in the world include ExxonMobil, Shell, BP, Chevron, and TotalEnergies. These companies have a combined market share of over 50% of the global fuel market.
Market Share and Competitive Strategies
The major fuel companies compete fiercely for market share. They use a variety of competitive strategies, including:
- Price competition: The major fuel companies often compete on price, offering discounts and promotions to attract customers.
- Product differentiation: The major fuel companies also compete by differentiating their products. For example, some companies offer premium fuels that are designed to improve engine performance.
- Customer service: The major fuel companies also compete on customer service. They offer a variety of services, such as loyalty programs and roadside assistance, to attract and retain customers.
Potential Mergers and Acquisitions
The fuel industry is constantly evolving, and there is a potential for mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in the future. M&A can be a way for companies to increase their market share, gain access to new markets, or reduce costs.
Some potential M&A targets in the fuel industry include:
- Smaller fuel companies that are struggling to compete with the major players
- Companies that have access to new markets, such as emerging markets
- Companies that have expertise in new technologies, such as renewable fuels
Key Financial Metrics
The following table compares the key financial metrics of the major fuel companies:
| Company | Revenue (USD billions) | Net income (USD billions) | Market capitalization (USD billions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ExxonMobil | 361.4 | 46.4 | 450.1 |
| Shell | 332.8 | 42.3 | 406.7 |
| BP | 303.6 | 37.2 | 353.4 |
| Chevron | 285.6 | 36.5 | 342.9 |
| TotalEnergies | 281.8 | 36.2 | 339.1 |
Executive Summary
The fuel industry is a highly concentrated market dominated by a few major players. These companies control a significant share of the global fuel supply and have a strong influence on fuel prices.
Do not overlook explore the latest data about OMR.
The major fuel companies compete fiercely for market share. They use a variety of competitive strategies, including price competition, product differentiation, and customer service.
There is potential for M&A in the fuel industry in the future. M&A can be a way for companies to increase their market share, gain access to new markets, or reduce costs.
Government Regulations
Government regulations play a significant role in shaping fuel prices. These regulations aim to ensure fair competition, protect consumers, and promote environmental sustainability.
One of the most direct ways governments influence fuel prices is through taxes and subsidies. Taxes on fuel, such as excise duties and value-added tax (VAT), can increase the final price paid by consumers. Conversely, subsidies can reduce the cost of fuel, making it more affordable for consumers.
Environmental Regulations
Governments are increasingly implementing environmental regulations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change. These regulations can impact fuel prices by increasing the cost of production for fossil fuels and promoting the development of alternative energy sources.
Economic Indicators

Economic indicators play a crucial role in shaping fuel prices. They provide insights into the overall health of the economy, which in turn influences the demand for fuel.
One of the most important economic indicators is economic growth. When the economy grows, businesses and consumers tend to increase their spending, leading to a higher demand for fuel. Conversely, during economic downturns, fuel demand may decline as businesses reduce operations and consumers cut back on discretionary spending.
Inflation and Interest Rates
Inflation and interest rates are two other key economic indicators that can affect fuel prices. Inflation measures the rate at which prices for goods and services are rising. When inflation is high, the purchasing power of consumers decreases, which can lead to a decrease in fuel demand. Interest rates, set by central banks, influence the cost of borrowing money. Higher interest rates make it more expensive for businesses to invest and expand, which can slow economic growth and reduce fuel demand.
Global Supply and Demand

The global supply and demand for fuel play a crucial role in determining fuel prices. The world’s major oil producers, such as OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries), have a significant influence on the supply side. OPEC members control a large portion of the world’s oil reserves and can impact prices by adjusting their production levels. On the demand side, factors such as economic growth, population growth, and industrialization drive the demand for fuel.
OPEC and Major Oil Producers
OPEC, established in 1960, is a cartel of 13 oil-producing countries. It controls over 40% of the world’s oil production and has a significant influence on global oil prices. OPEC members can collectively decide to increase or decrease production, affecting the supply and ultimately the price of oil. Other major oil producers, such as Russia, the United States, and Canada, also play a role in shaping global supply and demand dynamics.
Impact of Global Events
Global events, such as political instability, economic crises, and natural disasters, can impact fuel prices. Political instability in oil-producing regions can disrupt production and lead to supply shortages. Economic crises can reduce demand for fuel, resulting in lower prices. Natural disasters, such as hurricanes or earthquakes, can also disrupt production and distribution, affecting fuel availability and prices.
Alternative Fuels
Alternative fuels are playing an increasingly important role in the energy sector, driven by concerns over climate change, energy security, and air pollution. Electric vehicles, renewable energy sources, and government incentives are accelerating the adoption of alternative fuels, transforming the automotive industry and energy landscape.
Electric Vehicles and Renewable Energy
Electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining popularity due to their environmental benefits and lower operating costs. EVs use electricity instead of fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. The growth of EVs is supported by the development of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, which provide clean and sustainable electricity.
Government Incentives for Alternative Fuels
Governments worldwide are offering incentives to promote the adoption of alternative fuels. These incentives include tax credits, rebates, and infrastructure investments. Tax credits reduce the cost of purchasing EVs and installing charging stations. Rebates provide direct financial assistance to consumers who purchase alternative fuel vehicles. Infrastructure investments support the development of charging stations and other infrastructure necessary for the widespread adoption of EVs.
Comparison of Alternative Fuels
| Fuel | Environmental Impact | Cost-Effectiveness | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biofuels | Reduced greenhouse gas emissions | Comparable to fossil fuels | Limited availability |
| Hydrogen | Zero emissions | High production costs | Developing infrastructure |
| Natural Gas | Lower greenhouse gas emissions than gasoline | Cost-effective | Widely available |