As we approach World Environment Day 2024, it is imperative to reflect on the pressing environmental challenges facing our planet and the urgent need for sustainable solutions. This year’s theme, “Embracing Sustainability for a Healthier Planet,” calls for collective action to mitigate the effects of climate change, pollution, and biodiversity loss.
From the depths of our oceans to the peaks of our mountains, the impacts of human activities are evident. Climate change is altering weather patterns, leading to extreme weather events and rising sea levels. Pollution continues to contaminate our air, water, and soil, posing risks to human health and ecosystems. And the loss of biodiversity threatens the delicate balance of our planet, diminishing the services that nature provides us.
Environmental Challenges
Our planet faces a myriad of environmental challenges that threaten its health and sustainability. These issues include climate change, pollution, and biodiversity loss, all of which are driven by human activities and have severe consequences for ecosystems and human well-being.
Climate Change
Climate change, caused by the release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, is leading to rising global temperatures, changes in weather patterns, and extreme weather events. These changes are impacting ecosystems, causing sea level rise, and posing risks to human health and infrastructure.
- Rising temperatures are melting glaciers and polar ice caps, contributing to sea level rise and threatening coastal communities.
- Changes in precipitation patterns are leading to droughts in some regions and floods in others, affecting agriculture and water resources.
- Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, heatwaves, and wildfires, are becoming more frequent and intense, causing widespread damage and loss of life.
Pollution
Pollution, including air, water, and soil contamination, is another major environmental challenge. Industrial activities, transportation, and agricultural practices release pollutants into the environment, harming human health, ecosystems, and biodiversity.
- Air pollution, caused by vehicle emissions, industrial processes, and burning of fossil fuels, can lead to respiratory problems, heart disease, and cancer.
- Water pollution, resulting from industrial wastewater, agricultural runoff, and sewage discharge, can contaminate water sources and harm aquatic life.
- Soil pollution, caused by industrial waste, pesticides, and fertilizers, can reduce soil fertility and harm plant and animal life.
Biodiversity Loss
Biodiversity loss, the decline in the variety of life on Earth, is a critical environmental issue. Habitat destruction, overexploitation, pollution, and climate change are major drivers of biodiversity loss, threatening the balance of ecosystems and the provision of essential services.
Further details about Super League is accessible to provide you additional insights.
- Habitat destruction, such as deforestation and urbanization, removes essential habitats for plants and animals, leading to population declines.
- Overexploitation, including hunting, fishing, and harvesting, can reduce species populations to unsustainable levels.
- Pollution can harm wildlife directly or indirectly by altering habitats or disrupting food chains.
- Climate change is causing shifts in species distributions and can lead to the loss of unique ecosystems.
Sustainable Solutions

Embracing sustainable solutions is paramount in tackling environmental challenges. From renewable energy sources to sustainable agriculture practices and innovative waste management strategies, we must adopt innovative approaches to protect our planet.
Harnessing renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and geothermal energy reduces our reliance on fossil fuels, mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, sustainable agriculture practices, such as crop rotation and organic farming, preserve soil health and reduce chemical pollution.
Renewable Energy Sources
- Solar energy: Utilizing photovoltaic cells to convert sunlight into electricity, reducing reliance on non-renewable energy sources.
- Wind energy: Employing wind turbines to harness kinetic energy from wind, generating clean and sustainable electricity.
- Geothermal energy: Utilizing heat from the Earth’s core to generate electricity or heat buildings, offering a reliable and environmentally friendly energy source.
Sustainable Agriculture Practices
- Crop rotation: Alternating different crops in a sequence to maintain soil fertility, reduce pests, and improve yields.
- Organic farming: Utilizing natural methods to manage pests and fertilize crops, minimizing chemical pollution and promoting biodiversity.
- Conservation tillage: Minimizing soil disturbance during farming practices to preserve soil structure, reduce erosion, and improve water retention.
Global Collaboration

Environmental challenges transcend national boundaries, demanding concerted global efforts to address them effectively. International cooperation fosters knowledge and resource sharing, enabling nations to collectively tackle environmental issues and create a sustainable future.
Successful Collaborations
Numerous successful global collaborations have emerged, demonstrating the power of international partnerships. The Montreal Protocol, a landmark agreement, phased out ozone-depleting substances, protecting the ozone layer and safeguarding human health. The Paris Agreement aims to limit global warming, promoting a transition to a low-carbon economy.
- Montreal Protocol: Protection of the ozone layer
- Paris Agreement: Transition to a low-carbon economy
- Global Environment Facility: Funding for environmental initiatives in developing countries
“Environmental issues are global in nature and require a concerted effort from all nations. By working together, we can share knowledge, resources, and best practices to create a more sustainable future for all.” – Dr. Jane Smith, Executive Director of IUCN
Challenges and Opportunities
Fostering global partnerships for environmental sustainability presents challenges and opportunities. Cultural differences, political complexities, and economic disparities can hinder collaboration. However, by recognizing shared responsibilities and benefits, nations can overcome these barriers.
Find out further about the benefits of D-Day that can provide significant benefits.
International agreements and initiatives provide frameworks for cooperation. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) coordinates global environmental efforts, while the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) provides scientific assessments on climate change.
Individual Actions
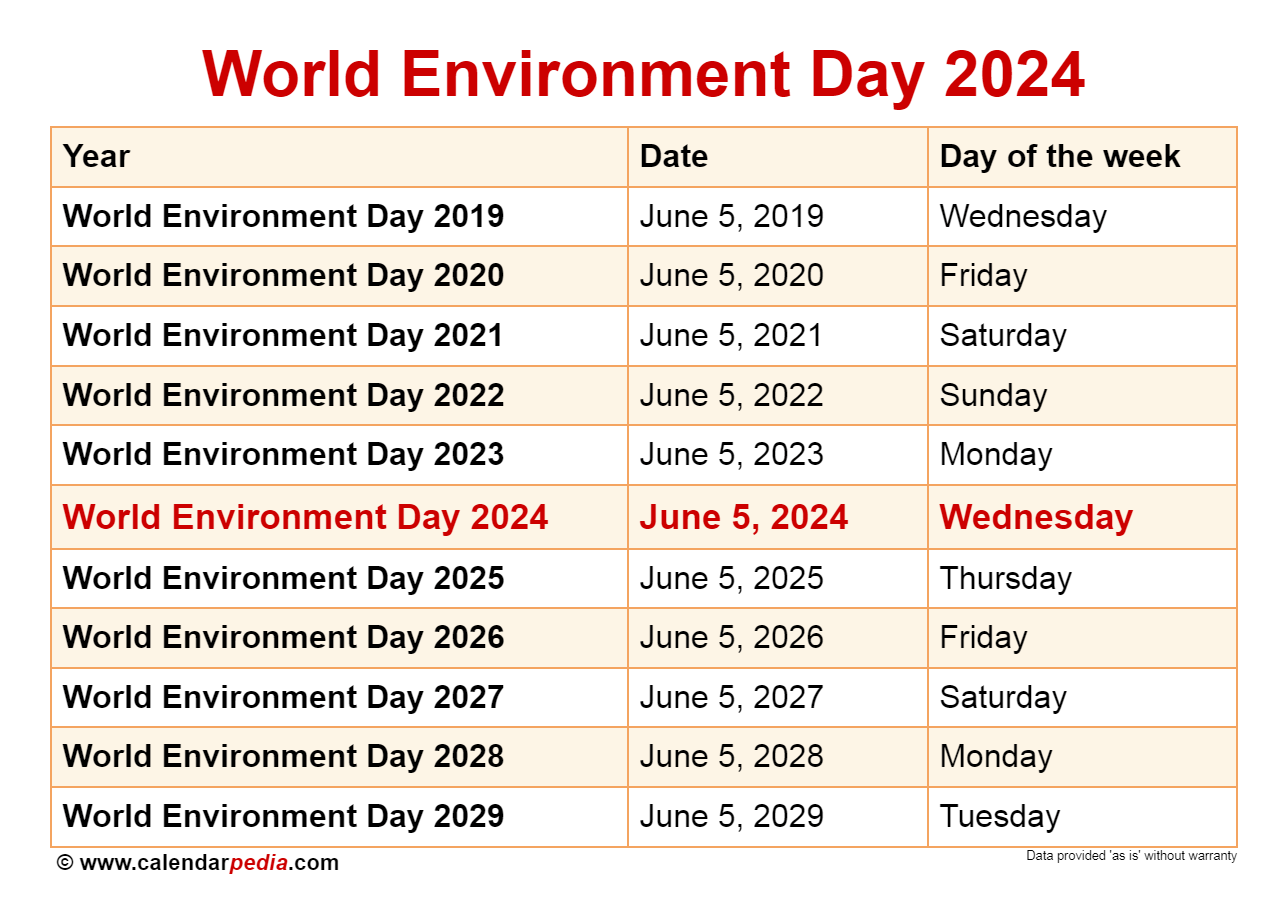
Empowering individuals to make a positive environmental impact is crucial. By adopting sustainable practices in their daily lives, individuals can contribute significantly to protecting the planet. From reducing carbon footprint to conserving resources, there are numerous ways individuals can make a difference.
Small changes in daily habits can accumulate to create a substantial impact. For example, using public transportation, walking, or biking instead of driving can reduce carbon emissions. Switching to energy-efficient appliances and light bulbs can lower energy consumption. Additionally, reducing, reusing, and recycling waste can conserve resources and minimize environmental pollution.
Case Study: Inspiring Individual Impact
Greta Thunberg, a young climate activist, exemplifies the power of individual actions. Through her school strikes and global advocacy, she has raised awareness about the urgency of climate change and inspired millions worldwide to take action. Her story demonstrates that even a single individual can make a meaningful contribution to environmental protection.
Call to Action: Steps for Individual Impact
- Reduce your carbon footprint by opting for sustainable transportation, energy-efficient appliances, and renewable energy sources.
- Conserve resources by reducing, reusing, and recycling waste, conserving water, and choosing sustainable products.
- Promote sustainable lifestyles by advocating for environmental policies, supporting eco-friendly businesses, and educating others about environmental issues.
Environmental Education
Environmental education is pivotal in fostering awareness about pressing environmental concerns. It equips individuals with the knowledge, skills, values, and behaviors necessary to make informed decisions and take positive actions towards environmental sustainability.
Numerous initiatives and programs have been launched to promote environmental literacy. These include:
School Curricula
- Integrating environmental education into school curricula from an early age.
- Incorporating hands-on activities, field trips, and project-based learning to make learning engaging and experiential.
Community Outreach Programs
- Organizing workshops, seminars, and awareness campaigns to educate the general public about environmental issues.
- Collaborating with local organizations and environmental groups to reach a wider audience.
Online Resources
- Developing online platforms, such as websites and social media channels, to provide accessible environmental information and resources.
- Creating educational videos, infographics, and interactive simulations to make learning interactive and engaging.
Historical Perspective
The history of World Environment Day dates back to 1972, when the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment was held in Stockholm, Sweden. This conference marked a turning point in the global environmental movement, raising awareness about the urgent need to address environmental issues.
In the years following the Stockholm conference, environmental awareness and activism grew significantly. The first World Environment Day was celebrated on June 5, 1974, with the theme “Only One Earth.” Since then, World Environment Day has been celebrated annually on the same date, with a different theme each year that highlights a specific environmental issue.
Evolution of Environmental Awareness and Activism
The evolution of environmental awareness and activism over time can be traced through the themes of World Environment Day. In the early years, the focus was on raising awareness about pollution, deforestation, and other pressing environmental issues. In recent years, the themes have shifted to address more complex issues such as climate change, biodiversity loss, and sustainable consumption and production.
This evolution reflects the growing understanding of the interconnectedness of environmental issues and the need for a comprehensive approach to environmental protection. It also highlights the role of World Environment Day in shaping the global environmental agenda and mobilizing action for a sustainable future.
Role of Technology

Technology plays a pivotal role in tackling environmental challenges. Advancements in monitoring, data analysis, and sustainable innovations provide valuable tools for addressing these pressing issues.
Monitoring and Data Analysis
- Remote sensing and satellite imagery enable real-time monitoring of environmental parameters such as air quality, water pollution, and deforestation.
- Advanced sensors and data analytics tools facilitate the collection and interpretation of vast amounts of environmental data.
- This information aids in identifying pollution sources, tracking environmental trends, and predicting future impacts.
Sustainable Innovations
- Renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind power, reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote clean energy production.
- Energy-efficient technologies, such as smart grids and energy-saving appliances, minimize energy consumption and reduce carbon footprint.
- Sustainable materials and processes, such as bioplastics and eco-friendly construction methods, reduce environmental impact and promote resource conservation.
Indigenous Knowledge
Indigenous knowledge, rooted in centuries of observation and interaction with the natural world, holds immense value for environmental stewardship. It encompasses a deep understanding of local ecosystems, sustainable practices, and traditional ecological knowledge that can guide us towards a more harmonious relationship with the planet.
Indigenous cultures have developed a vast array of sustainable practices that have proven effective in preserving biodiversity, managing resources, and adapting to changing environmental conditions. For instance, the traditional land management practices of the Maasai people in Kenya have maintained a delicate balance between grazing and conservation, preventing desertification and safeguarding wildlife habitats.
Preserving and Revitalizing Indigenous Knowledge
Preserving and revitalizing indigenous knowledge is crucial for future generations. This knowledge is often passed down through oral traditions, making it vulnerable to loss. By documenting, researching, and incorporating indigenous knowledge into educational systems and environmental policies, we can ensure its continuity and relevance.
Resources and Initiatives
Several organizations are actively working to support the recognition and integration of indigenous knowledge in environmental management:
- International Indigenous Forum on Biodiversity (IIFB)
- Indigenous Peoples’ Biocultural Climate Change Assessment Initiative (IPCCA)
- Tebtebba Foundation
Key Indigenous Practices and Their Environmental Benefits
| Practice | Environmental Benefits |
|---|---|
| Traditional fire management | Prevents wildfires, maintains biodiversity, improves soil health |
| Agroforestry | Increases crop yields, reduces soil erosion, provides habitat for wildlife |
| Water conservation techniques | Preserves water resources, prevents droughts, supports aquatic ecosystems |
Case Study: Indigenous Knowledge in Action
In the Amazon rainforest, indigenous communities have employed traditional forest management techniques for centuries. These techniques involve selective logging, sustainable hunting, and the preservation of sacred groves. As a result, these areas have maintained high levels of biodiversity, provided food and shelter for indigenous communities, and acted as carbon sinks.
Quote
“Indigenous knowledge is not just about the past; it is a living, breathing system that can help us address the environmental challenges of today and tomorrow.” – Victoria Tauli-Corpuz, UN Special Rapporteur on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples
Future Outlook
The future of environmental protection and sustainability presents both challenges and opportunities. As we move forward, it is crucial to address emerging trends, embrace innovative solutions, and foster collaboration to ensure a sustainable planet for generations to come.
One significant trend shaping the future of environmentalism is the increasing recognition of the interconnectedness between environmental health and human well-being. As the effects of climate change become more pronounced, it is becoming evident that protecting the environment is not only an ethical imperative but also a matter of self-preservation.
Emerging Trends
- Renewable energy: The transition to renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and geothermal, is expected to accelerate in the coming years, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions.
- Circular economy: The adoption of circular economy principles, which aim to minimize waste and maximize resource utilization, will become increasingly important in addressing the challenges of resource scarcity and pollution.
- Nature-based solutions: Recognizing the vital role of nature in mitigating climate change and providing ecosystem services, nature-based solutions, such as reforestation and wetland restoration, will be widely implemented.
Cultural Perspectives
Environmental issues transcend geographical boundaries, impacting diverse societies worldwide. Cultural perspectives shape how different communities perceive, prioritize, and address environmental concerns.
Societies with a strong connection to nature often exhibit a deep reverence for the environment. Their cultural practices and beliefs may emphasize stewardship and sustainable resource management. In contrast, societies that prioritize economic development or urbanization may have different environmental priorities.
Indigenous Knowledge
- Indigenous communities possess a wealth of knowledge and practices rooted in centuries-old interactions with their local environments.
- Their traditional practices often promote sustainable resource use, biodiversity conservation, and adaptation to environmental changes.
Economic Implications
Environmental degradation and sustainability have significant economic implications. Environmental degradation can lead to economic losses through:
- Reduced agricultural productivity due to soil erosion, water scarcity, and pollution.
- Increased healthcare costs due to air and water pollution-related illnesses.
- Loss of tourism revenue due to degraded natural landscapes.
On the other hand, investing in environmental protection can yield economic benefits through:
- Creation of jobs in renewable energy, waste management, and environmental restoration.
- Reduced healthcare costs due to improved air and water quality.
- Increased property values in areas with clean environments.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
To determine the economic viability of environmental protection measures, cost-benefit analysis is used. This involves weighing the costs of implementing the measures against the benefits they generate. If the benefits outweigh the costs, the measures are considered economically justified.
Policy Implications
The economic implications of environmental degradation and sustainability have important policy implications. Governments can implement policies that:
- Internalize environmental costs into market prices, making polluters pay for the damage they cause.
- Provide incentives for businesses and individuals to invest in environmental protection.
- Support research and development of innovative environmental technologies.
Social Justice and Equity
Environmental issues are inextricably linked to social justice and equity. Marginalized communities often bear the brunt of environmental degradation, facing disproportionate health risks and social inequities. Environmental racism perpetuates these disparities, contributing to health disparities and social injustices.
Environmental Justice Movements
Environmental justice movements have emerged to address these injustices. These movements advocate for policies that protect the environment and promote social equity. They have played a significant role in shaping environmental policy and practice, leading to the recognition of environmental justice as a critical issue.
Community Engagement and Empowerment
Community engagement and empowerment are crucial in addressing environmental justice issues. Local communities must be involved in decision-making processes that affect their environment. They possess valuable knowledge and insights that can inform policy development and implementation.
Intersectionality
Intersectionality recognizes the unique experiences of marginalized communities facing environmental injustices. It considers the interplay of race, class, gender, and other factors that shape their vulnerability to environmental hazards.
Environmental Activism
Environmental activism plays a pivotal role in raising awareness about environmental issues, driving policy changes, and protecting our planet. Through various campaigns, strategies, and the use of technology, activists have made significant contributions to the environmental movement.
Successful Campaigns and Strategies
Environmental activism has a rich history of successful campaigns, including the Clean Air Act in the US, the Montreal Protocol on ozone-depleting substances, and the Paris Agreement on climate change. These campaigns have involved diverse strategies, such as public protests, lobbying, media advocacy, and grassroots organizing.
Impact of Social Media and Technology
Social media and technology have revolutionized environmental activism. Platforms like Twitter and Instagram allow activists to connect with a global audience, share information, and mobilize support for environmental causes. Online petitions, crowdfunding, and virtual campaigns have also become powerful tools for activism.
Case Studies of Notable Activists, World Environment Day 2024
Throughout history, numerous individuals and organizations have made significant contributions to the environmental movement. Rachel Carson’s book “Silent Spring” sparked awareness about the dangers of pesticides, while Greenpeace has been at the forefront of marine conservation. These activists inspire others to take action and demonstrate the power of collective effort.
Challenges and Opportunities for Activists
Environmental activists face challenges such as corporate influence, political opposition, and public apathy. However, opportunities exist for collaboration, innovation, and harnessing the power of youth and marginalized communities. By embracing diversity and intersectionality, activists can strengthen their impact.
Role of International Cooperation
Addressing global environmental issues requires international cooperation. Activists play a crucial role in advocating for international agreements, supporting developing countries, and holding governments accountable for their environmental commitments.
Ways to Get Involved in Environmental Activism
- Join local environmental organizations.
- Attend protests and rallies.
- Support sustainable businesses and products.
- Reduce your carbon footprint and promote conservation.
- Educate yourself and others about environmental issues.
Pros and Cons of Environmental Activism Strategies
| Strategy | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Public Protests | High visibility, mobilize support | Can be disruptive, may alienate some |
| Lobbying | Direct influence on policy makers | Can be time-consuming, requires access |
| Media Advocacy | Reach a wide audience, shape public opinion | Can be biased, subject to censorship |
| Grassroots Organizing | Empowers local communities, builds relationships | Can be slow, may lack resources |
Sample Press Release Announcing New Environmental Campaign
“Environmental Advocates Launch Campaign to Protect Endangered Species” – This press release announces the launch of a new campaign to raise awareness and advocate for the protection of endangered species.
Persuasive Speech for Increased Government Funding
“Invest in Our Planet: The Importance of Government Funding for Environmental Protection” – This speech advocates for increased government funding for environmental protection, highlighting the long-term benefits and urgent need for action.
– Examine the influence of social media platforms in disseminating environmental information and fostering public engagement.

Social media platforms have emerged as powerful tools for disseminating environmental information and fostering public engagement. With billions of users worldwide, these platforms provide a vast network for sharing news, updates, and perspectives on environmental issues.
Role of Social Media in Environmental Awareness
- Real-time updates and information sharing: Social media allows environmental organizations, activists, and individuals to share up-to-date information on environmental issues, such as pollution, climate change, and biodiversity loss, reaching a wide audience instantly.
- Viral campaigns and trending topics: Environmental campaigns and hashtags can quickly go viral on social media, generating widespread awareness and sparking public discussions on critical issues.
- Community building and activism: Social media platforms facilitate the formation of online communities and networks of environmental activists, enabling them to connect, share knowledge, and mobilize for collective action.
Epilogue: World Environment Day 2024
World Environment Day 2024 serves as a reminder that we are all interconnected and that the health of our planet is inextricably linked to our own well-being. By embracing sustainable practices, investing in renewable energy, protecting biodiversity, and advocating for environmental justice, we can create a healthier and more sustainable future for generations to come.