Pensioenleeftijd, een onderwerp dat de gemoederen bezighoudt. Verhogen of verlagen? Het is een lastige keuze met grote gevolgen. In dit artikel duiken we dieper in de materie en bespreken we de verschillende factoren die meespelen bij het bepalen van de pensioenleeftijd.
We onderzoeken de economische, sociale en politieke aspecten die van invloed zijn op de pensioenleeftijd. Ook kijken we naar internationale vergelijkingen en voorspellen we toekomstige trends. Door deze complexe kwestie vanuit verschillende invalshoeken te bekijken, hopen we een beter begrip te krijgen van de uitdagingen en kansen die gepaard gaan met het bepalen van de pensioenleeftijd.
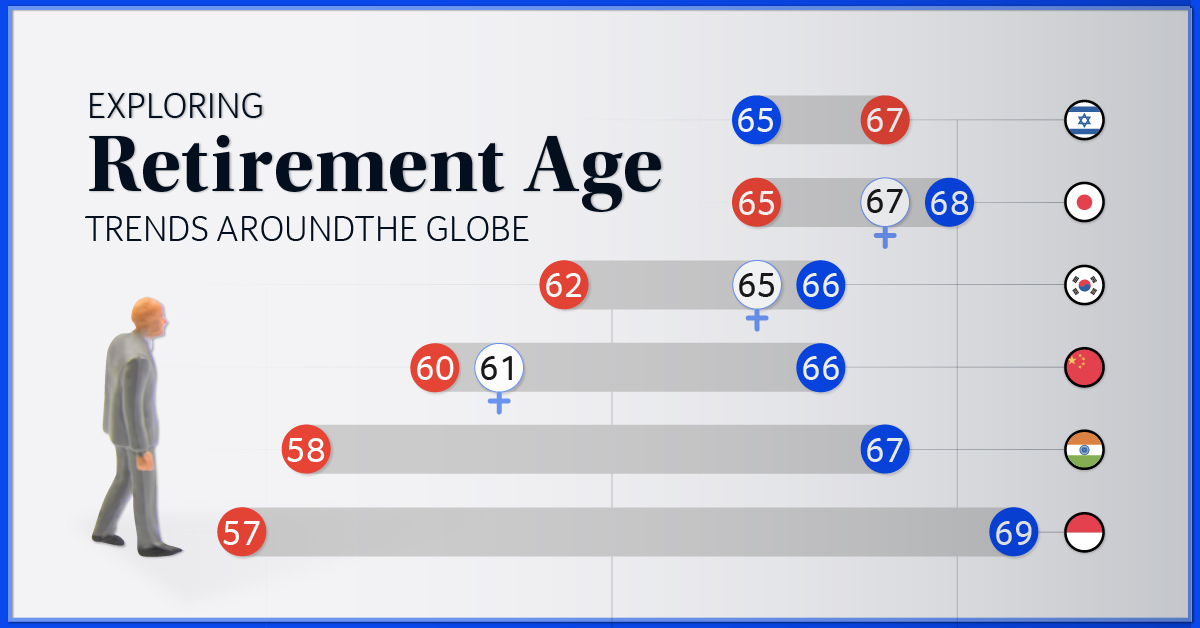
Pension Age in Different Countries
Pension age varies significantly across countries due to factors such as life expectancy, labor market conditions, and government policies. The table below compares the pension age in several countries:| Country | Pension Age ||—|—|| Netherlands | 67 || France | 62 || Germany | 65 || United States | 67 || Japan | 65 |Increasing life expectancy and aging populations have put pressure on pension systems, leading to discussions about raising the pension age in many countries.
However, this can have implications for labor market participation and the well-being of older workers.Policymakers need to consider the impact of demographic changes on the sustainability of pension systems and find ways to ensure adequate retirement income while maintaining labor market flexibility and social equity.
Historical Evolution of Pension Age
The pension age in the Netherlands has undergone significant changes over time, reflecting evolving societal and economic factors. Let’s explore the historical evolution of the pension age in the country.
Initially, the pension age in the Netherlands was set at 65 for both men and women. However, in the early 20th century, the government introduced a gradual increase in the pension age, starting with women. The reasoning behind this change was primarily driven by the increasing life expectancy and the need to ensure the sustainability of the pension system.
Gradual Increase in Pension Age
- In 1957, the pension age for women was raised to 62.
- In 1989, the pension age for men was increased to 65, aligning it with the pension age for women.
- In 1999, the government announced a further increase in the pension age, gradually raising it to 67 for both men and women by 2021.
These changes were implemented to address the increasing longevity and the need to maintain the financial viability of the pension system. The gradual nature of the increases allowed individuals to adjust their retirement plans and financial arrangements accordingly.
Demographic Factors Affecting Pension Age
Demographic factors significantly influence the pension age by shaping the size and composition of the population that draws on pension funds. These factors include life expectancy, birth rates, and mortality rates.
Life Expectancy
As life expectancy increases, so does the period during which individuals receive pension benefits. This puts pressure on pension systems, as they must support a growing number of retirees for a longer duration. The rising life expectancy also extends the period of contributions, potentially increasing the overall financial burden on working individuals.
– Explain the economic factors that influence the determination of the pension age, such as life expectancy, labor market participation rates, and productivity.: Pensioenleeftijd
The determination of the pension age is influenced by a complex interplay of economic factors, including life expectancy, labor market participation rates, and productivity. These factors have a significant impact on the sustainability of pension systems and the financial security of retirees.
Life Expectancy
Life expectancy is a key factor in determining the pension age. As life expectancy increases, the number of years that retirees will receive pension benefits increases. This puts a strain on pension systems, as they must pay out benefits for a longer period of time.
As a result, many countries have raised the pension age in recent years to ensure the sustainability of their pension systems.
Labor Market Participation Rates, Pensioenleeftijd
The labor market participation rate is another important factor that influences the pension age. If the labor market participation rate is high, it means that more people are working and paying into the pension system. This can help to support a lower pension age, as there are more workers to support the retirees.
However, if the labor market participation rate is low, it can put a strain on the pension system, as there are fewer workers to support the retirees.
Productivity
Productivity is also a factor that can influence the pension age. If productivity is high, it means that workers are producing more goods and services. This can lead to higher wages and increased tax revenue, which can help to support a lower pension age.
However, if productivity is low, it can put a strain on the pension system, as there is less money available to support the retirees.
Social and Health Implications of Pension Age
The pension age significantly influences the social and health well-being of older adults. It affects their labor force participation, retirement planning, and overall quality of life.
Even if you’re not quite at retirement age, you can still enjoy the warmth and comfort of a cozy fireplace. With a few simple makeover ideas, you can transform your brick fireplace into a stunning focal point. From painting it a new color to adding decorative elements, there are endless possibilities.
Check out some brick fireplace makeover ideas and get inspired to create a fireplace that you’ll love for years to come. And when you’re finally ready to retire, you’ll have a beautiful fireplace to enjoy in your golden years.
Raising the pension age can lead to:
- Reduced labor force participation:Older workers may choose to retire earlier if the pension age is increased, resulting in a smaller labor force and potential labor shortages.
- Delayed retirement planning:Individuals may need to work longer to accumulate sufficient retirement savings, leading to delayed retirement plans and financial strain.
- Increased health risks:Staying in the workforce longer may expose older adults to physical and mental health risks associated with demanding jobs.
Impact on Well-being of Older Adults
The pension age also impacts the well-being of older adults in several ways:
- Financial security:A higher pension age can provide greater financial security in retirement, but it can also delay access to pension benefits.
- Health and longevity:Early retirement can allow individuals to pursue healthier lifestyles and activities, potentially leading to improved health outcomes and longevity.
- Social engagement:Retirement can provide opportunities for social engagement and activities, which can enhance the well-being of older adults.
Demographic and Economic Factors Driving the Need to Adjust Pension Age
Demographic and economic factors are driving the need to adjust the pension age in many countries. These factors include:
Increasing Life Expectancy
- People are living longer, which means they will need to support themselves for a longer period during retirement.
- This is putting a strain on pension systems, as they are required to pay out benefits for a longer period.
Aging Population
- The population is aging, which means there are more retirees relative to the number of working-age people.
- This is putting a strain on the economy, as there are fewer workers to support the growing number of retirees.
Low Birth Rates
- Birth rates are declining in many countries, which means there will be fewer working-age people in the future to support the growing number of retirees.
- This is putting a strain on pension systems, as there will be fewer workers to pay into the system.
Economic Growth
- Economic growth can help to offset the impact of demographic factors on pension systems.
- When the economy is growing, there are more jobs and higher wages, which means there is more money available to pay into pension systems.
International Comparisons of Pension Systems

The Netherlands has a well-developed pension system compared to many other countries. The Dutch pension system is characterized by a three-pillar system, which includes a mandatory public pension scheme, mandatory occupational pension schemes, and voluntary private pension schemes.The public pension scheme provides a basic level of pension benefits for all Dutch citizens who have reached the retirement age.
The retirement age in the Netherlands is currently 67 years and is gradually increasing to 68 years by 2024. The mandatory occupational pension schemes are provided by employers and provide additional pension benefits on top of the public pension. The voluntary private pension schemes are provided by individuals and can be used to supplement the public and occupational pension benefits.The
Dutch pension system has been praised for its sustainability and its ability to provide a decent level of retirement income for Dutch citizens. However, the system is also facing some challenges, such as the increasing cost of providing pension benefits and the impact of the aging population.The
Netherlands can learn from the experiences of other countries in order to improve its own pension system. For example, the Netherlands could consider adopting a more flexible retirement age, which would allow individuals to choose when they want to retire.
The Netherlands could also consider increasing the contribution rates to the public pension scheme in order to ensure the sustainability of the system.
Best Practices from Other Countries
Some best practices that the Netherlands could learn from other countries include:
-
-*Automatic enrollment in pension schemes
Pension age can be a daunting topic, but it doesn’t have to be. With a little planning, you can make sure you’re financially secure in your retirement years. One way to do this is to invest in a home. A home is a great investment because it can provide you with a place to live, a source of income, and a tax break.
If you’re looking for a home in Berkeley, California, california closets berkeley can help you find the perfect place. They have a wide selection of homes to choose from, and they can help you find the right one for your needs and budget.
Plus, they can help you get the best possible price on your new home. So if you’re thinking about retiring, don’t forget to invest in a home. It’s one of the best ways to ensure you have a secure financial future.
This helps to ensure that all workers are saving for retirement.
-*Matching contributions from employers
This helps to make pension saving more affordable for workers.
Pensioenleeftijd is something that we all have to think about eventually, but it can be a daunting task. There are so many factors to consider, such as your financial situation, your health, and your desired lifestyle. If you’re looking for a way to make your retirement years more comfortable and enjoyable, I highly recommend investing in a heat surge roll n glow fireplace . These fireplaces are not only beautiful and stylish, but they can also help you save money on your energy bills.
Plus, they’re a great way to relax and unwind after a long day. So, if you’re thinking about retirement, be sure to add a heat surge roll n glow fireplace to your list of must-haves. You won’t regret it! As you plan for Pensioenleeftijd, remember to consider all your options and make choices that will help you live a happy and fulfilling life.
-*Tax incentives for pension saving
This can encourage workers to save more for retirement.
-*Flexible retirement ages
This allows individuals to choose when they want to retire, based on their individual circumstances.
Lessons Learned from Different Approaches
The Netherlands can also learn from the mistakes of other countries in order to avoid making the same mistakes. For example, the Netherlands could avoid raising the retirement age too quickly, which can lead to financial hardship for older workers.
The Netherlands could also avoid cutting pension benefits too deeply, which can lead to poverty in retirement.By learning from the experiences of other countries, the Netherlands can improve its own pension system and ensure that Dutch citizens have a secure retirement income.
Future Trends in Pension Age
The future of pension age is uncertain, as it is influenced by a complex interplay of demographic, economic, and social factors. However, based on current trends, we can make some predictions about what the future holds.
One of the most significant factors influencing the pension age is life expectancy. As people live longer, they will need to work longer to support themselves in retirement. This is already happening in many countries, where the pension age has been raised in recent years.
Another factor that will affect the pension age is the labor market participation rate. As more people work into their later years, the demand for workers will decrease, and this will put downward pressure on wages. This could make it more difficult for people to save for retirement, and it could also lead to a lower pension age.
Finally, the pension age will also be influenced by social and political factors. In some countries, there is a strong desire to protect the rights of older workers, and this could lead to a higher pension age. In other countries, there is a greater focus on reducing government spending, and this could lead to a lower pension age.
Implications of Future Trends in Pension Age
The future trends in pension age will have a significant impact on individuals and their retirement planning. People will need to start saving for retirement earlier and they will need to work longer to reach their retirement goals. They will also need to be more flexible in their retirement plans, as the traditional model of retiring at a fixed age may no longer be viable.
The future trends in pension age will also have a significant impact on pension systems. Governments will need to find ways to make pension systems more sustainable, and they will need to ensure that people have adequate retirement income.
Recommendations for Policymakers and Pension Providers
Policymakers and pension providers need to take steps to address the challenges and opportunities presented by future trends in pension age. They should consider the following recommendations:
- Raise the pension age gradually to give people time to adjust.
- Encourage people to save for retirement earlier and more aggressively.
- Make pension systems more flexible so that people can retire at different ages.
- Provide incentives for people to work longer.
- Increase government spending on retirement benefits.
By taking these steps, policymakers and pension providers can help to ensure that people have a secure retirement.
Role of Technology in Pension Age
Technology is transforming the labor market and retirement patterns, potentially impacting the pension age. Advancements in automation, artificial intelligence, and robotics are creating new job opportunities while displacing others.
This technological shift may lead to:
Labor Market Participation
- Increased Labor Market Participation:Automation can free up workers from repetitive tasks, allowing them to focus on higher-value activities, potentially extending their working lives.
- New Job Opportunities:Technology creates new industries and job roles, providing employment opportunities for older workers with specialized skills.
Retirement Patterns
- Flexible Retirement:Technology enables remote work and flexible schedules, allowing workers to gradually transition into retirement while remaining partially employed.
- Delayed Retirement:Increased longevity and healthier lifestyles may encourage individuals to work longer to maintain their financial security.
– Consider the potential impact of pension age adjustments on different demographic groups, such as women, minorities, and low-income earners.
Adjustments to the pension age can have a significant impact on different demographic groups, particularly those who face systemic barriers and economic disparities. It is crucial to consider the unique challenges and circumstances faced by these groups to ensure equitable outcomes.
Impact on Women
Women often have lower pension savings due to factors such as career interruptions for childcare, lower wages, and part-time work. Increasing the pension age can disproportionately affect women, as they may have to work longer to accumulate the same level of retirement savings as men.
Impact on Minorities
Minorities may face systemic barriers in the labor market, such as discrimination and limited access to higher-paying jobs. This can result in lower pension contributions and a greater reliance on government pension benefits. Raising the pension age could exacerbate these disparities.
Impact on Low-Income Earners
Low-income earners often have physically demanding jobs and may not be able to work until the increased pension age without experiencing health issues. Additionally, they may have limited access to private pension schemes and rely heavily on government benefits, making pension age adjustments particularly impactful.
Communication and Public Engagement on Pension Age
Clear and effective communication is crucial for informing the public about pension age changes. It helps build understanding, address concerns, and foster support for necessary adjustments. Public engagement is equally important, allowing diverse perspectives to shape pension age policies and ensure they align with societal values and needs.
Importance of Clear Communication
- Provides accurate information about pension age changes and their rationale.
- Addresses misconceptions and concerns, building trust and reducing anxiety.
- Facilitates informed decision-making by individuals and policymakers.
Role of Public Engagement
- Gathers input from a wide range of stakeholders, including workers, retirees, employers, and community organizations.
- Identifies potential impacts and explores alternative solutions.
- Promotes transparency and accountability in pension age policymaking.
– Analyze the impact of pension age on labor market participation rates by gender, age group, and industry.
The impact of pension age on labor market participation rates is a complex issue that depends on a variety of factors, including gender, age group, and industry. In general, raising the pension age can lead to a decrease in labor market participation rates, as older workers are more likely to retire.
However, this effect can be offset by other factors, such as increased life expectancy and improved health among older workers.
There is a significant body of research that has examined the impact of pension age on labor market participation rates. One study, conducted by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), found that raising the pension age by one year can lead to a decrease in labor market participation rates of 0.5% to 1%. However, the study also found that this effect is smaller for women than for men, and for older workers than for younger workers.
Another study, conducted by the National Bureau of Economic Research, found that raising the pension age can lead to a decrease in labor force participation rates, but that this effect is smaller for workers in high-paying jobs than for workers in low-paying jobs.
This suggests that the impact of pension age on labor market participation rates may be more pronounced for low-income workers.
Impact on labor supply
Raising the pension age can have a significant impact on the supply of labor. In the short term, it can lead to a decrease in the labor force participation rate, as older workers are more likely to retire. However, in the long term, it can lead to an increase in the labor force participation rate, as younger workers enter the labor market and older workers remain in the labor force for longer.
The impact of raising the pension age on the labor supply is also likely to vary depending on the specific circumstances of each country. For example, in countries with a high life expectancy and a strong social safety net, the impact of raising the pension age is likely to be smaller than in countries with a low life expectancy and a weak social safety net.
Pension Age and Retirement Planning
Pension age has a profound impact on retirement planning and financial security. Understanding how these factors interact is crucial for individuals to make informed decisions about their future.
Early planning is essential as it allows individuals to assess their financial needs, adjust their savings strategies, and make informed decisions about the timing of their retirement.
Impact of Different Pension Age Scenarios
Different pension age scenarios can significantly affect retirement savings and income. For example, a higher pension age may require individuals to save more during their working years to maintain a comfortable retirement lifestyle.
Conversely, a lower pension age may allow individuals to retire earlier but could result in reduced retirement income and increased financial risk.
Flexibility in Retirement Age Policies
Flexible retirement age policies provide individuals with greater control over their retirement planning. They allow individuals to choose a retirement age that aligns with their personal circumstances and financial goals.
For example, some countries offer a phased retirement option, allowing individuals to gradually reduce their working hours and transition into retirement.
Policy Recommendations
To improve the alignment between pension age and retirement planning needs, policymakers can consider:
- Encouraging early retirement planning through financial education and awareness campaigns.
- Providing flexible retirement age policies that allow individuals to choose a retirement age that meets their needs.
- Adjusting pension age gradually over time to mitigate the impact on individuals and the economy.
Pension Age and Gender

Women and men often have different experiences in the labor market, leading to disparities in pension outcomes. This is influenced by factors such as the gender pay gap, time spent out of the workforce for caregiving responsibilities, and occupational segregation.
The gender pension gap refers to the difference in pension wealth and retirement income between women and men. It is a complex issue with multiple contributing factors. On average, women have lower pension savings than men due to lower earnings, career interruptions, and part-time work.
Contributing Factors
- Gender Pay Gap:Women generally earn less than men for the same work, which affects their pension contributions and overall pension wealth.
- Career Interruptions:Women are more likely to take time off work for childcare or eldercare, which can impact their pension contributions and accrual rates.
- Part-Time Work:Women are more likely to work part-time, which often means lower earnings and reduced pension contributions.
- Occupational Segregation:Women are often concentrated in lower-paying occupations with fewer pension benefits, such as in the service sector or caregiving roles.
Addressing Disparities
- Closing the Gender Pay Gap:Addressing the gender pay gap would reduce the disparity in pension wealth and retirement income.
- Supporting Caregivers:Providing affordable childcare and eldercare support can help women stay in the workforce and maintain their pension contributions.
- Encouraging Part-Time Pension Contributions:Making it easier for part-time workers to contribute to pension schemes can help reduce the gender pension gap.
- Raising Awareness:Educating women about the importance of pension saving and planning can help them make informed decisions about their retirement.
Pension Age and Disability
Individuals with disabilities face unique challenges and opportunities in relation to pension age adjustments. They may have different retirement needs and preferences, and their ability to work and earn a pension may be affected by their disability.
There are a number of factors that can affect the impact of disability on pension age. These include the severity of the disability, the age of onset, and the availability of support services. Individuals with severe disabilities may need to retire earlier than those with less severe disabilities.
Those who develop disabilities later in life may have a shorter period of time to build up a pension. And those who lack access to support services may find it more difficult to work and earn a pension.
Challenges
- Individuals with disabilities may have difficulty finding and keeping a job.
- They may be more likely to experience discrimination and prejudice in the workplace.
- They may have higher healthcare costs, which can reduce their ability to save for retirement.
- They may be more likely to experience poverty and homelessness.
Opportunities
- Individuals with disabilities may be eligible for government benefits and programs that can help them to offset the costs of retirement.
- They may be able to find work in sheltered workshops or other supported employment settings.
- They may be able to access training and education programs that can help them to develop new skills and qualifications.
- They may be able to find support from family, friends, and community organizations.
Last Word
De pensioenleeftijd is een onderwerp dat voortdurend in beweging is. Naarmate de bevolking vergrijst en de economie verandert, moeten we de pensioenleeftijd blijven herzien om ervoor te zorgen dat deze duurzaam en rechtvaardig blijft. Door de verschillende factoren die we in dit artikel hebben besproken te overwegen, kunnen we weloverwogen beslissingen nemen over de toekomst van de pensioenleeftijd.