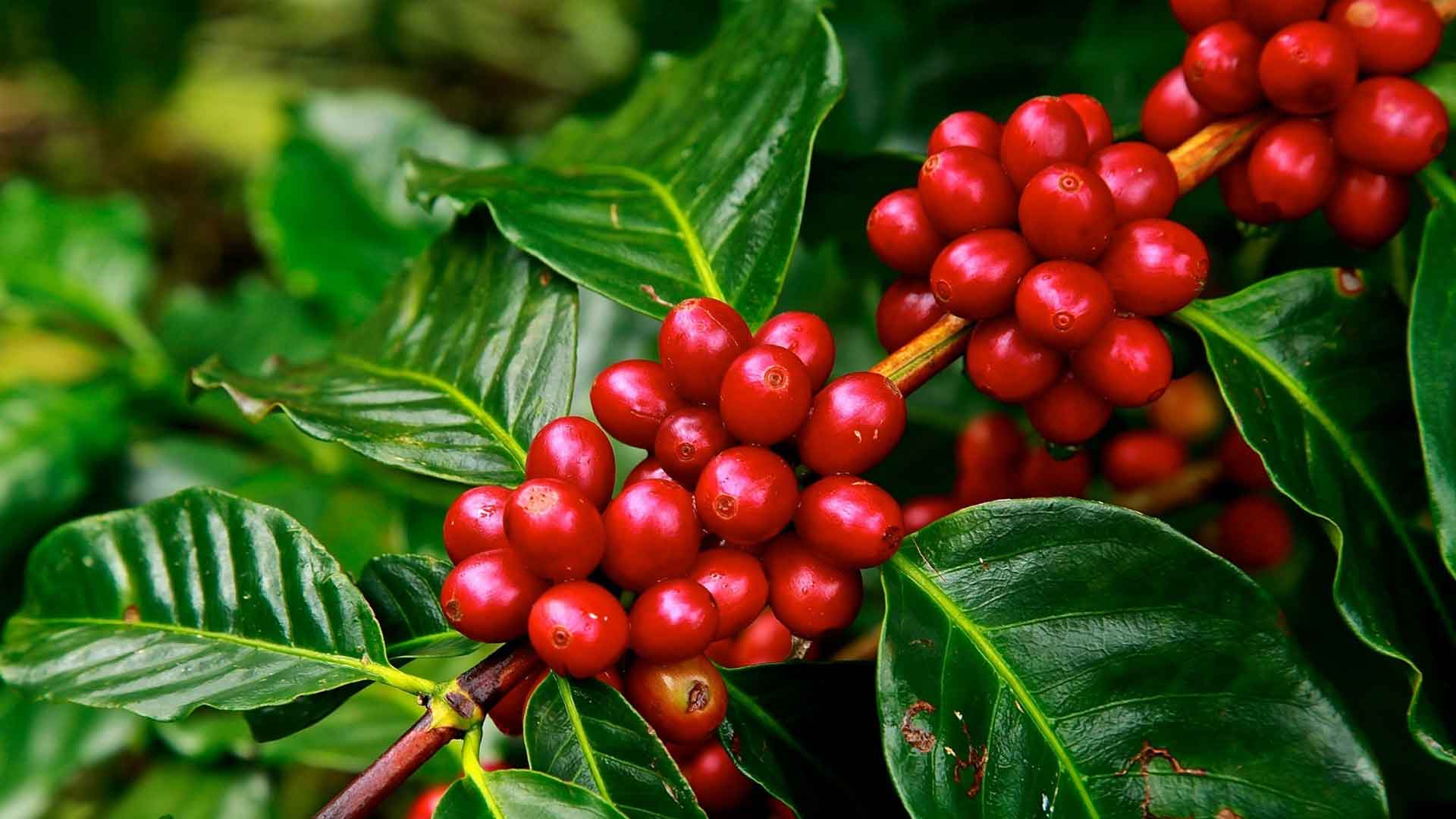
Planta de cafe robusta – Planta de café robusta, a cornerstone of the coffee industry, offers a distinct flavor profile and robust characteristics that have captivated coffee enthusiasts worldwide. Its cultivation, processing, and brewing techniques hold the key to unlocking the full potential of this extraordinary bean.
From its origins in the African rainforests to its global distribution, Robusta coffee has become an indispensable part of the coffee landscape. Its economic significance and global production contribute to the livelihoods of countless farmers and the enjoyment of millions of coffee lovers.
Overview of Coffea Robusta: Planta De Cafe Robusta
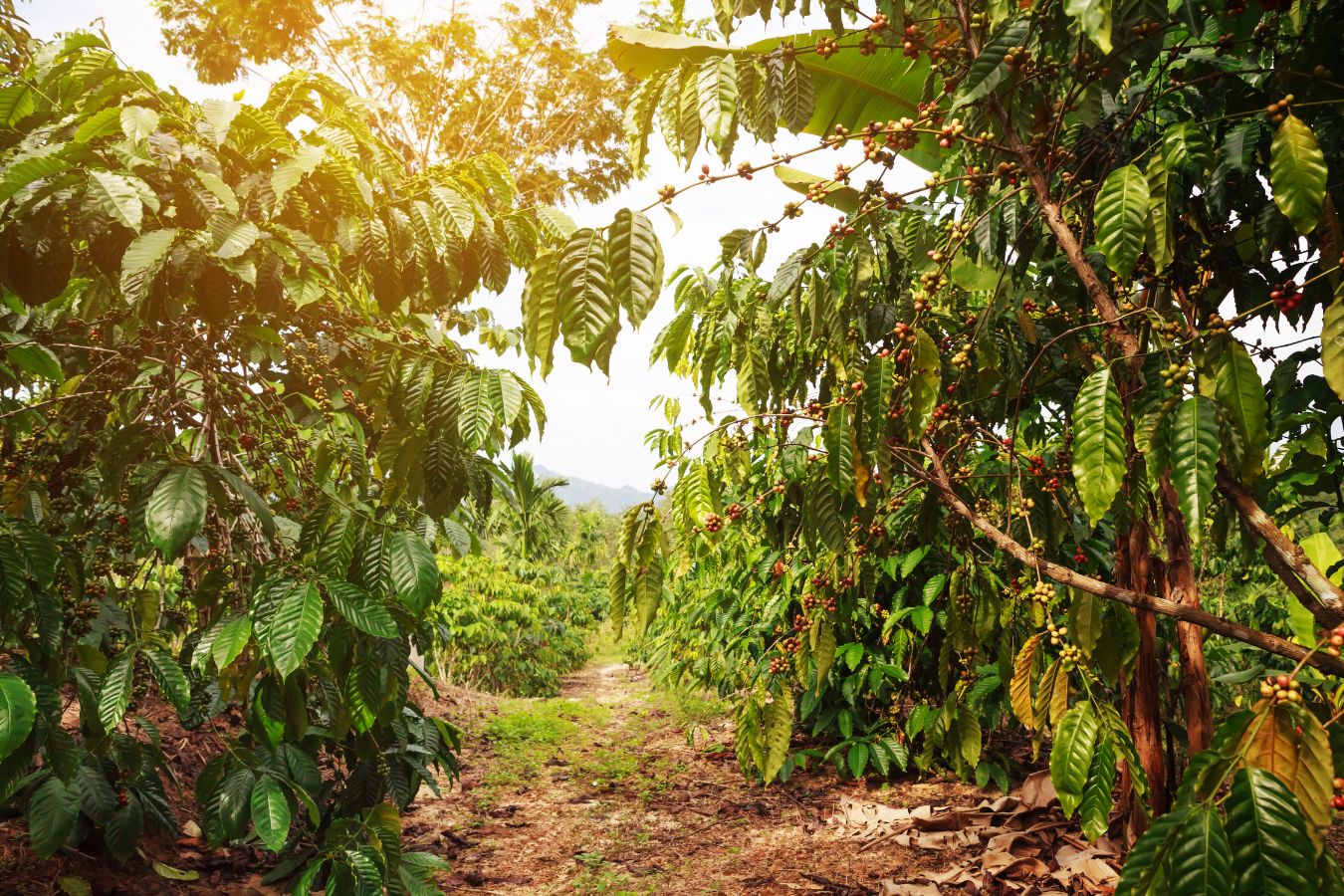

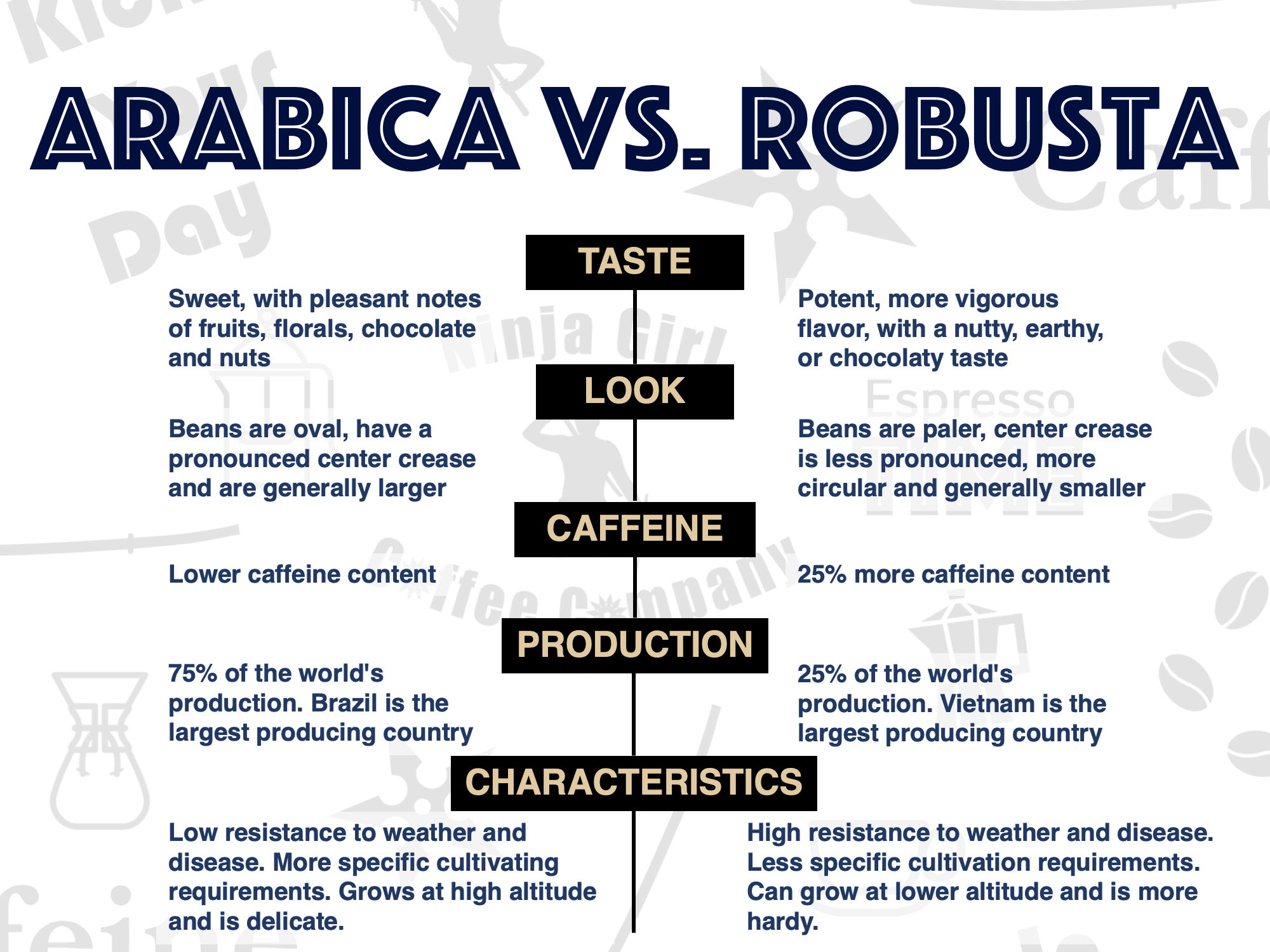
Coffea Robusta, also known as Robusta coffee, is a species of coffee originating from the tropical regions of Central and Western Africa. It is known for its distinct flavor profile, characterized by strong bitterness, earthy notes, and a lower acidity compared to Arabica coffee. Robusta plants are typically more robust and easier to cultivate, making them widely cultivated in various parts of the world.
Origins and Characteristics
Coffea Robusta was first discovered in the Congo Basin of Central Africa in the late 19th century. It is a member of the Rubiaceae family, which includes other plants such as quinine and gardenia. Robusta plants are characterized by their large, oval-shaped leaves, which are typically dark green in color. The flowers are white and fragrant, and the fruits are small, round berries that turn red when ripe.
Cultivation and Distribution
Coffea Robusta is a relatively easy-to-grow plant that can thrive in a wide range of climatic conditions. It is typically cultivated in tropical regions with high rainfall and warm temperatures. The main growing areas for Robusta coffee include Southeast Asia, particularly Vietnam and Indonesia, as well as Central and Western Africa. Robusta plants are generally more resistant to pests and diseases compared to Arabica coffee, making them a more suitable option for large-scale cultivation.
Economic Importance and Global Production
Robusta coffee is a significant contributor to the global coffee industry. It accounts for approximately 30-40% of the world’s coffee production, making it the second most cultivated coffee species after Arabica. Robusta coffee is primarily used in the production of instant coffee, espresso blends, and lower-grade coffee products due to its strong flavor and high caffeine content. The global demand for Robusta coffee continues to grow, particularly in emerging markets where consumers prefer stronger and more affordable coffee options.
Agronomic Considerations for Robusta Cultivation
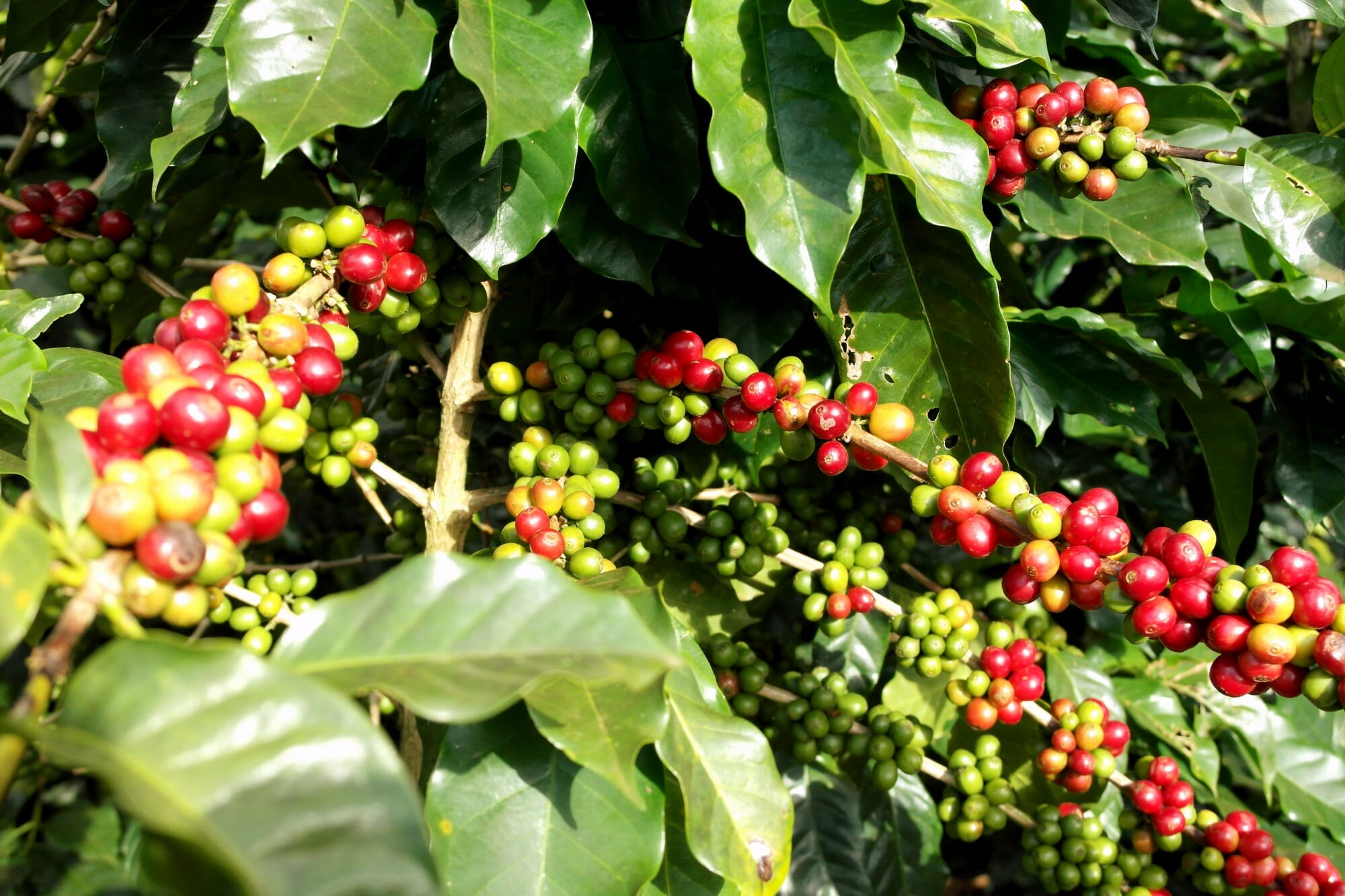
Robusta coffee, known for its hardiness and high caffeine content, requires specific agronomic practices to thrive. Understanding the optimal growing conditions, planting, pruning, harvesting techniques, and disease and pest management is crucial for successful Robusta cultivation.
Growing Conditions
Robusta plants prefer well-drained soils with a pH between 5.5 and 6.5. They can tolerate a wide range of altitudes, from sea level to 1,000 meters above sea level, and require ample sunlight and rainfall. The ideal temperature range for Robusta cultivation is between 20-28 degrees Celsius.
Planting
Robusta seedlings are typically planted at a spacing of 2.5-3 meters apart in rows that are 3-4 meters apart. The planting holes should be dug deep enough to accommodate the entire root system, and the soil should be well-drained and amended with organic matter.
Pruning
Pruning is essential to maintain the shape and health of Robusta trees. Regular pruning removes dead, diseased, or unproductive branches and encourages the growth of new shoots. Pruning should be done during the dry season, and the cuts should be made cleanly to prevent infection.
Harvesting
Robusta coffee cherries ripen in 9-11 months after flowering. They are typically harvested by hand, and the ripe cherries are picked and separated from the unripe ones. The harvested cherries are then processed to remove the pulp and seeds.
Disease and Pest Management
Robusta coffee is susceptible to various diseases and pests, including leaf rust, coffee berry disease, and nematodes. Proper sanitation, disease-resistant varieties, and timely application of pesticides are essential for effective disease and pest management.
Processing and Brewing Techniques

The processing and brewing techniques employed for Robusta coffee beans significantly influence their flavor profile. Let’s delve into the various methods used and their impact on the final cup.
Processing Methods
Robusta beans undergo different processing methods that shape their flavor characteristics:
- Dry Processing: Beans are sun-dried with the fruit still attached. This traditional method imparts a rustic, earthy flavor with a higher caffeine content.
- Wet Processing: Beans are pulped to remove the fruit and fermented in water tanks. This process results in a cleaner, more balanced flavor with lower caffeine levels.
Roasting Techniques, Planta de cafe robusta
Roasting techniques play a crucial role in developing the flavor profile of Robusta coffee:
- Light Roast: Preserves the natural flavors and aromas of the beans, resulting in a bright, acidic cup with hints of fruitiness.
- Medium Roast: Enhances the body and sweetness of the beans, balancing acidity and bitterness.
- Dark Roast: Caramelizes the beans, creating a full-bodied, intense flavor with low acidity and a smoky undertone.
Brewing Methods
Robusta coffee can be brewed using various methods, each extracting different flavor nuances:
- Espresso: A concentrated brew with a thick crema, highlighting the intensity and bitterness of Robusta beans.
- Pour Over: A gentle extraction method that produces a clean, balanced cup with subtle acidity and sweetness.
- French Press: A full-bodied brew that captures the earthy notes and higher caffeine content of Robusta beans.
