The steam plant photos – Immerse yourself in the captivating world of steam plants through our exclusive collection of photographs. These images not only showcase the architectural grandeur of these industrial giants but also provide a glimpse into the intricate processes that power our world. Join us on a visual journey that unravels the fascinating story of steam plants.
From towering chimneys and cooling towers to the humming turbines within, each element of a steam plant plays a crucial role in harnessing the energy of steam. Our detailed descriptions and comprehensive table will guide you through the various sections of these complex facilities, revealing the inner workings that generate electricity.
Visual Exploration of Steam Plant Architecture
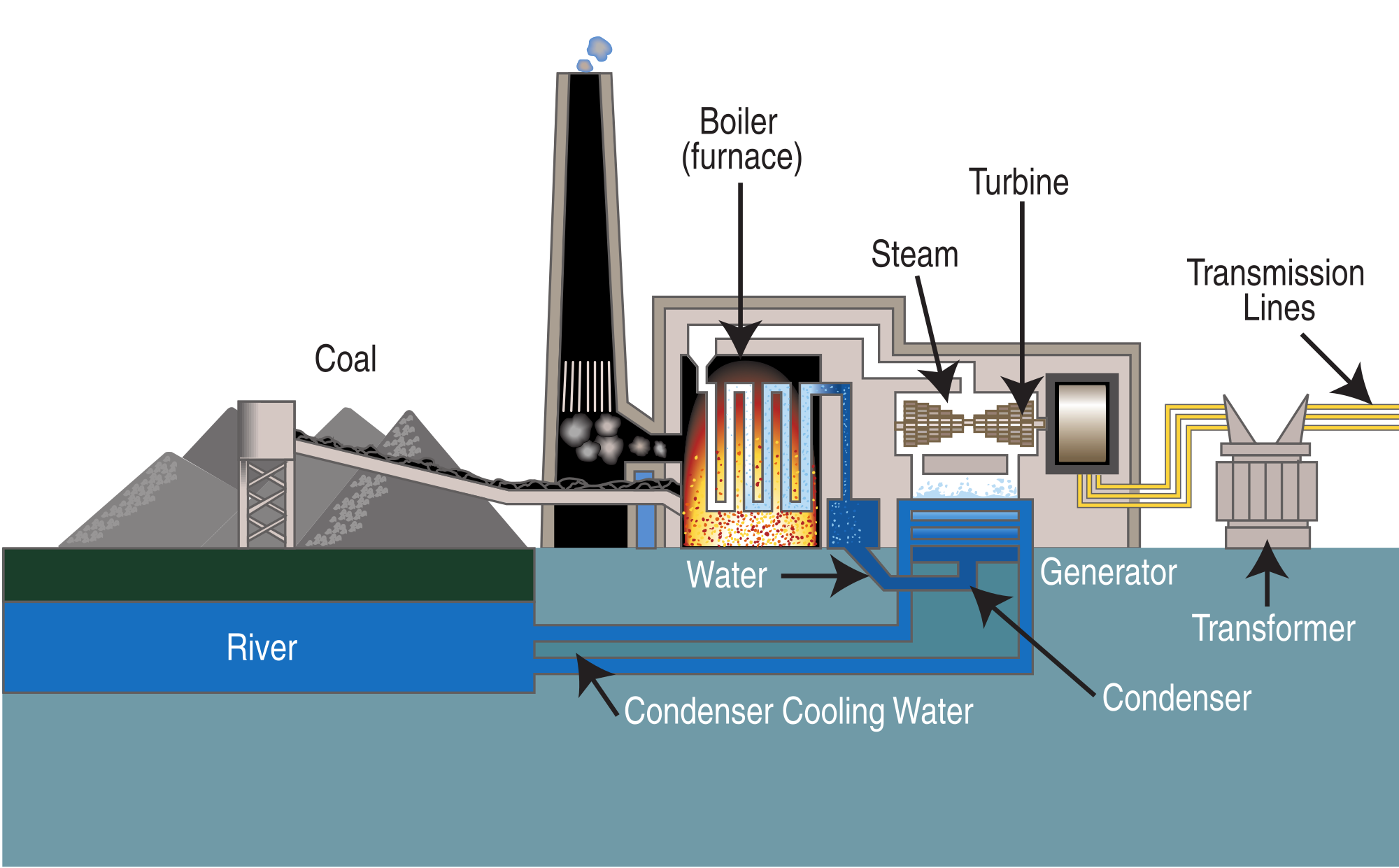
Steam plants, with their imposing structures and intricate systems, stand as testaments to human ingenuity and the pursuit of efficient energy production. These industrial giants are characterized by their distinct architectural features, each playing a crucial role in the conversion of fuel into electricity.
At the heart of a steam plant lies the boiler room, where towering boilers generate steam by heating water using various fuels such as coal, natural gas, or biomass. This steam, carrying immense energy, is then directed to the turbine hall, where massive turbines convert its thermal energy into mechanical energy.
Chimneys
Chimneys, towering over the plant, serve as the primary means of releasing exhaust gases and particulate matter into the atmosphere. These tall structures create a draft, drawing combustion gases upward and away from the plant’s surroundings.
Cooling Towers
Cooling towers, often seen as iconic symbols of steam plants, play a vital role in the cooling process. These structures use evaporation to dissipate heat from the steam used in the turbines. By releasing water vapor into the atmosphere, cooling towers condense the steam back into water, allowing it to be reused in the plant’s cycle.
Turbines
Turbines, the workhorses of steam plants, convert the thermal energy of steam into mechanical energy. These rotating machines consist of a series of blades mounted on a shaft. As high-pressure steam flows through the turbine, it impinges on the blades, causing them to rotate. This rotational motion is then used to generate electricity.
Steam Plant Equipment and Processes

Steam plants utilize an array of specialized equipment to generate electricity. The core components include boilers, condensers, and generators. Boilers are responsible for converting water into high-pressure steam by burning fuel, typically coal or natural gas. Condensers cool the steam back into water, creating a vacuum that draws more steam from the boiler. Generators convert the mechanical energy of the steam turbine into electrical energy.
Fuel Combustion
Combustion is the chemical reaction between fuel and oxygen, releasing heat energy. In steam plants, pulverized coal or natural gas is mixed with air and ignited in the boiler’s combustion chamber. The heat generated by combustion is transferred to water circulating through tubes within the boiler, converting it into steam.
Heat Transfer
The boiler’s tubes facilitate heat transfer from the combustion gases to the water. As the water absorbs heat, it undergoes a phase change from liquid to steam. The high-pressure steam is then directed to the steam turbine.
Steam Turbine Operation, The steam plant photos
The steam turbine is a rotary engine that converts the thermal energy of steam into mechanical energy. High-pressure steam enters the turbine through nozzles, causing the turbine blades to rotate. As the steam expands and cools, it loses pressure and exits the turbine. The mechanical energy of the rotating turbine is used to drive the generator, producing electricity.
Flowchart of Steam Power Generation
[Flowchart diagram illustrating the step-by-step process of steam power generation in a steam plant, from fuel combustion to electricity generation.]
Environmental Impact of Steam Plants: The Steam Plant Photos

Steam plants have a significant impact on the environment, primarily through air pollution, water usage, and waste generation.
Air pollution from steam plants results from the combustion of fossil fuels, which releases pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter (PM). These pollutants contribute to smog, acid rain, and respiratory problems. To mitigate these impacts, steam plants employ technologies such as scrubbers, which remove SO2 and NOx from exhaust gases, and electrostatic precipitators, which capture particulate matter.
Water usage is another environmental concern associated with steam plants. The cooling process requires large amounts of water, which can deplete local water resources. To reduce water usage, steam plants use cooling towers or closed-loop cooling systems, which recycle water for cooling purposes.
Waste generation is also an issue for steam plants. The combustion of fossil fuels produces solid waste, such as ash and slag, which must be disposed of properly. Steam plants often implement waste management programs to minimize the environmental impact of waste disposal.