New plant life top soil – New plant life holds the key to unlocking the transformative potential of topsoil, offering a wealth of benefits for soil health and overall ecosystem vitality. From enhancing soil structure to promoting moisture retention, the introduction of new plant species can revitalize topsoil, setting the stage for a thriving and resilient environment.
The intricate root systems of new plants play a crucial role in stabilizing topsoil, preventing erosion and safeguarding the integrity of the soil profile. Moreover, specific plant species possess unique abilities to improve soil fertility, adding essential nutrients and organic matter that enrich the soil’s composition.
Impact of New Plant Life on Topsoil Quality: New Plant Life Top Soil
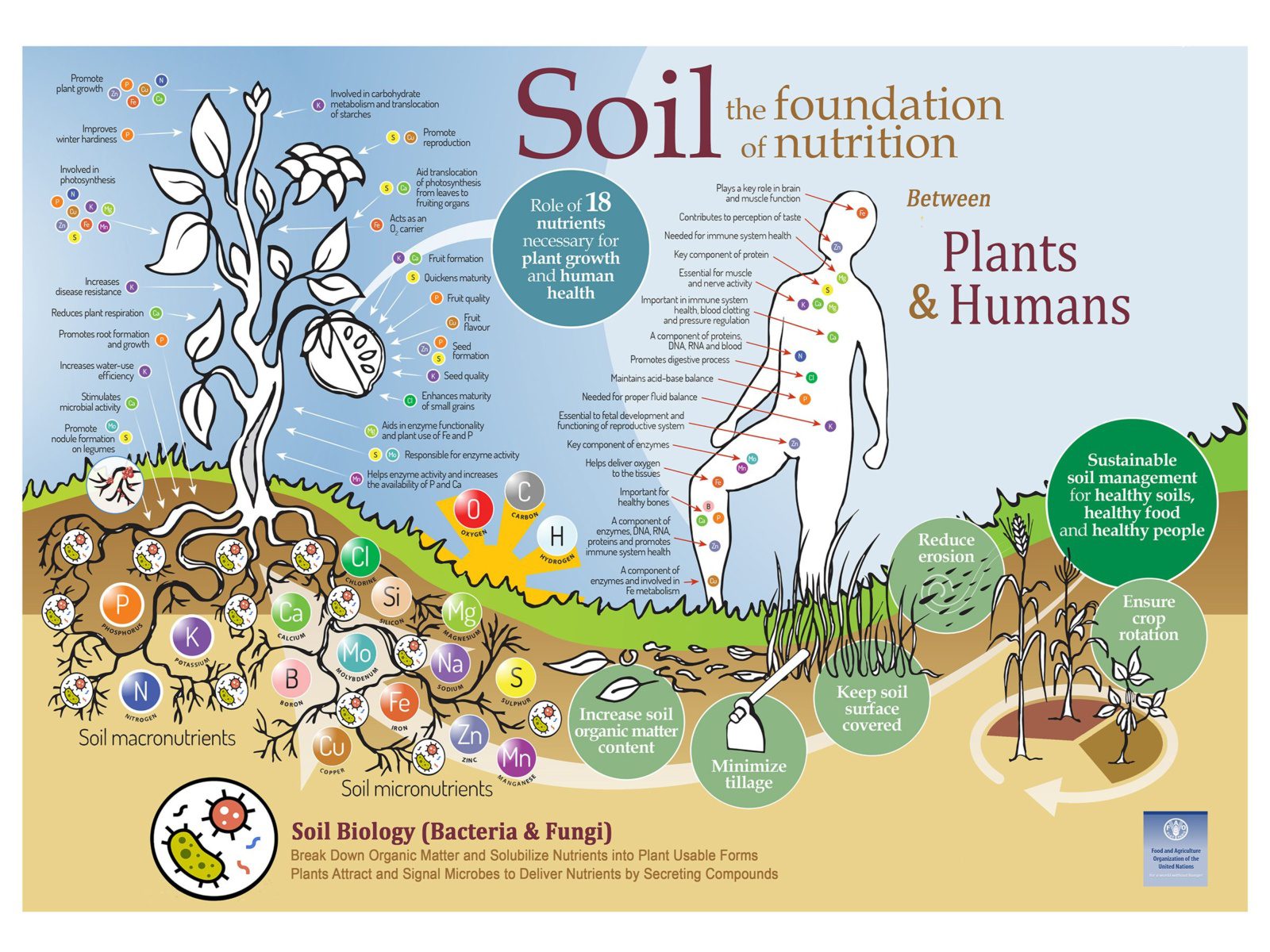
Introducing new plant life to an area can have profound benefits for topsoil health. Plants play a crucial role in maintaining and improving soil quality by:
Enhancing Soil Structure
The root systems of plants help to create a stable soil structure. As roots penetrate the soil, they create channels that allow water and air to penetrate deeper into the ground. This improves drainage and aeration, which are essential for healthy plant growth. Additionally, the organic matter produced by plant roots helps to bind soil particles together, creating a more stable structure.
Improving Soil Fertility
Plants help to improve soil fertility by adding organic matter to the soil. Organic matter is a rich source of nutrients that can be used by plants for growth. Additionally, plants help to cycle nutrients through the soil, making them more available to other plants.
Increasing Moisture Retention
The leaves of plants help to shade the soil, which reduces evaporation. Additionally, the organic matter produced by plant roots helps to hold water in the soil. This can help to prevent drought and improve plant growth.
Topsoil Management Practices for New Plant Life

Establishing a thriving new plant life begins with nurturing the foundation – the topsoil. Proper topsoil management practices are essential for providing optimal conditions for plant growth and ensuring long-term soil health.
Before planting, it is crucial to prepare the topsoil by loosening and aerating it. This can be achieved through tilling or digging, which improves drainage and allows roots to penetrate more easily. Additionally, removing weeds and debris from the topsoil ensures a clean slate for new plant life.
Amending Topsoil
Amending topsoil with organic matter, nutrients, and soil conditioners enhances its fertility and structure. Organic matter, such as compost or manure, adds essential nutrients and improves water retention. Nutrients, like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, can be added through fertilizers based on soil testing results.
Soil conditioners, such as gypsum or lime, can improve soil structure and pH levels. Gypsum helps break up compacted soil, while lime raises the pH of acidic soils, making them more suitable for plant growth.
Soil Testing, New plant life top soil
Soil testing is a valuable tool for determining the specific needs of new plant life. It provides insights into the soil’s pH, nutrient levels, and organic matter content. Based on the test results, you can tailor your topsoil management practices to address any deficiencies or imbalances.
By following these topsoil management practices, you can create an optimal environment for new plant life to flourish and thrive.
Case Studies and Examples of Successful Plant-Topsoil Interactions

The positive impact of new plant life on topsoil quality is well-documented. Several successful examples demonstrate the benefits of sustainable topsoil management practices.
Successful Examples of Plant-Topsoil Interactions
One notable example is the restoration of degraded grasslands in the Great Plains region of the United States. By introducing native plant species and implementing grazing management practices, landowners have significantly improved soil health and increased carbon sequestration. The restoration efforts have led to increased soil organic matter, reduced erosion, and improved water infiltration.
Another example is the use of cover crops in agricultural systems. Cover crops are plants grown primarily to cover the soil and improve its health. By preventing erosion, adding organic matter, and enhancing soil structure, cover crops have proven effective in improving topsoil quality and crop yields.