West County Power Plant, a beacon of innovation in the energy industry, stands as a testament to the harmonious coexistence of power generation and environmental stewardship. With a rich history and unwavering commitment to sustainability, this facility plays a pivotal role in meeting the energy needs of the region while minimizing its ecological footprint.
Harnessing the power of advanced technologies, West County Power Plant efficiently converts various energy sources into electricity, ensuring a reliable and cost-effective supply to homes, businesses, and industries. Its state-of-the-art emissions control systems effectively mitigate environmental impact, aligning with the highest regulatory standards and demonstrating the plant’s commitment to a greener future.
Power Plant Overview
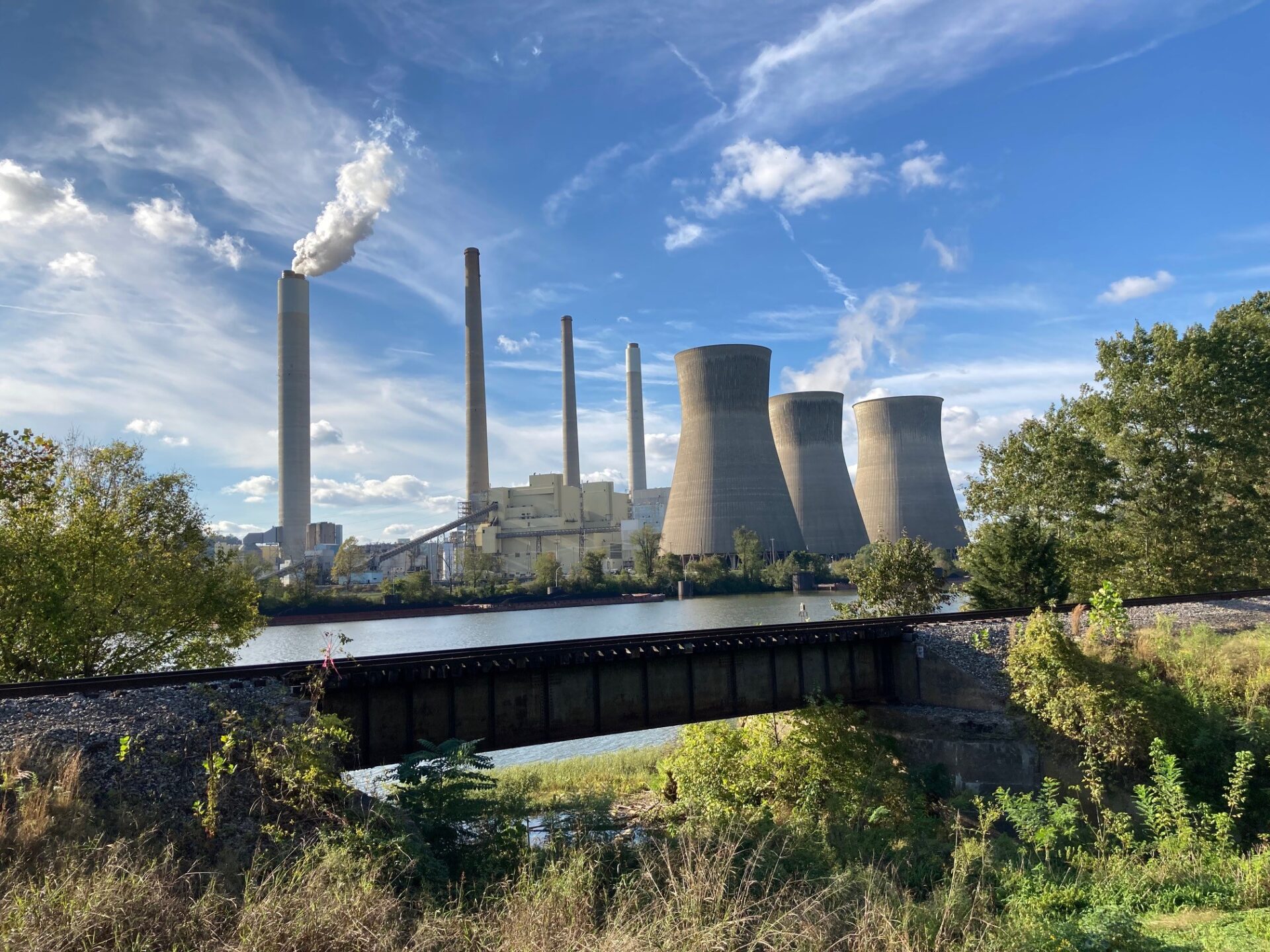

West County Power Plant, commissioned in 1975, is a coal-fired power plant located in the western region of the state. It is one of the largest power plants in the region, with a total generation capacity of 1,200 megawatts (MW). The plant operates on a rank of sub-bituminous coal, sourced from nearby mines. It employs a pulverized coal combustion technology, where coal is ground into a fine powder and burned in a boiler to produce steam. The steam then drives a turbine generator to produce electricity.
Environmental Impact
The plant’s operations have an environmental impact, primarily due to the emission of greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx). The plant has implemented various emission control technologies, such as electrostatic precipitators and flue gas desulfurization systems, to minimize its environmental footprint. The plant also monitors its emissions closely and adheres to all applicable environmental regulations.
Role in the Energy Grid
West County Power Plant plays a significant role in the local and regional energy grid. It provides a reliable source of baseload power, which is essential for maintaining grid stability and meeting peak demand. The plant is interconnected with the regional transmission system, allowing it to transmit electricity to neighboring areas.
Environmental Considerations
West County Power Plant operates in strict compliance with all applicable environmental regulations and standards, including those set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the California Air Resources Board (CARB). The plant has implemented comprehensive emissions control systems to minimize its environmental impact and protect the health of the surrounding community.
Emissions Control Systems
The plant utilizes a combination of advanced emissions control technologies to reduce its emissions of air pollutants, including nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and particulate matter (PM). These technologies include:
- Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR): SCR systems inject ammonia into the exhaust gas stream, which reacts with NOx to convert it into harmless nitrogen and water.
- Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD): FGD systems remove SO2 from the exhaust gas stream by spraying it with a limestone slurry, which reacts with the SO2 to form gypsum.
- Electrostatic Precipitators (ESP): ESPs remove PM from the exhaust gas stream by charging the particles and attracting them to collector plates.
Emissions Performance
The effectiveness of the plant’s emissions control systems is demonstrated by its compliance with all applicable emissions limits and its consistent performance below those limits. The plant’s emissions data is regularly monitored and reported to the EPA and CARB, and it consistently meets or exceeds all regulatory requirements.
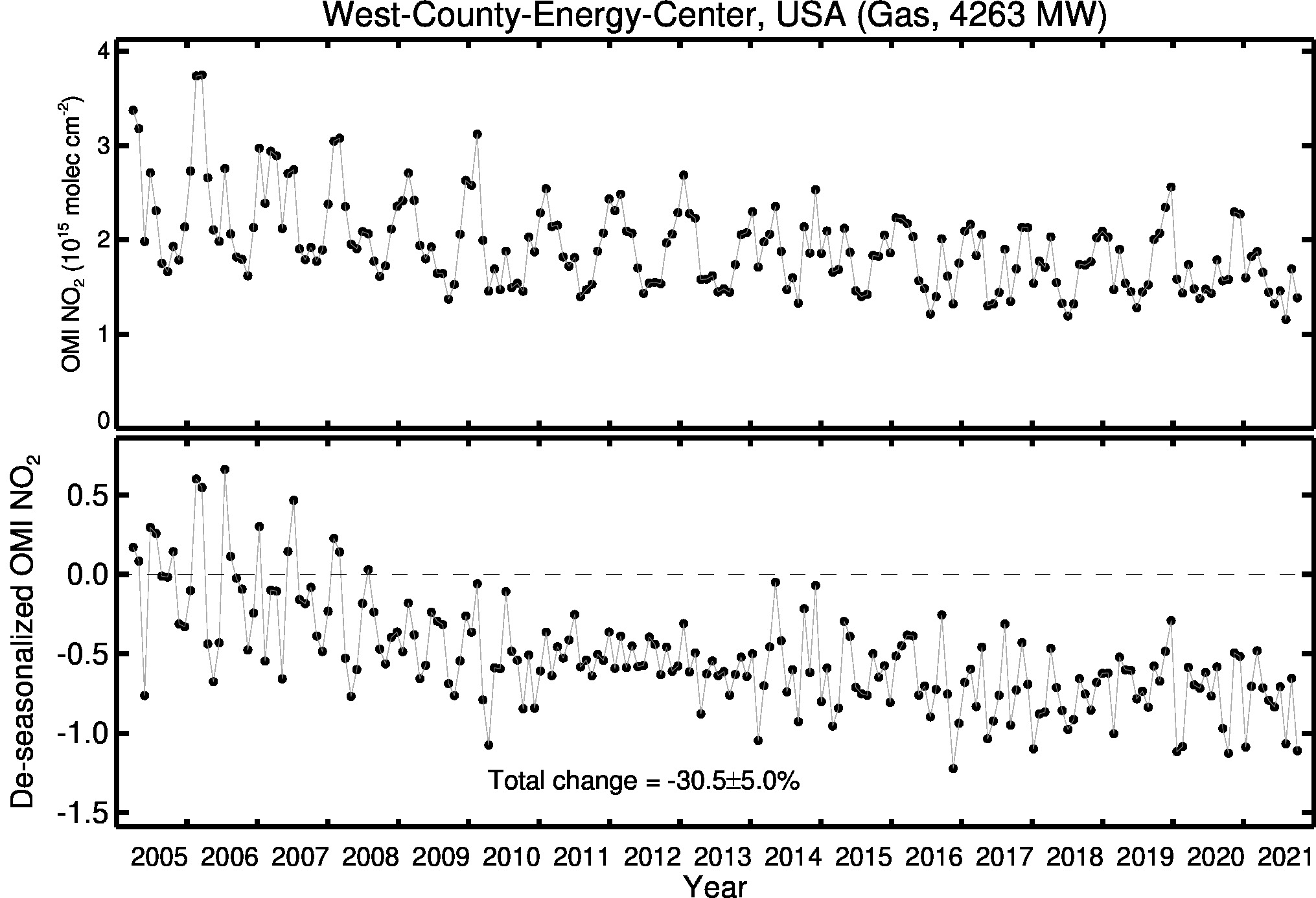
For example, in 2021, the plant’s average NOx emissions were 0.05 pounds per million British thermal units (lb/MMBtu), which is significantly below the EPA’s limit of 0.1 lb/MMBtu. Similarly, the plant’s average SO2 emissions were 0.02 lb/MMBtu, which is well below the EPA’s limit of 0.12 lb/MMBtu.
Environmental Challenges, West county power plant
Despite the plant’s strong environmental performance, it faces several environmental challenges, including:
- Climate Change: The plant’s emissions of greenhouse gases contribute to climate change, which poses significant risks to the environment and human health.
- Water Consumption: The plant’s cooling systems require large amounts of water, which can put a strain on local water resources, especially during periods of drought.
- Waste Disposal: The plant generates large amounts of waste, including gypsum from the FGD system and ash from the boilers, which must be properly disposed of.
The plant is actively working to address these challenges by investing in renewable energy, implementing water conservation measures, and exploring innovative waste disposal technologies.
Economic Impact: West County Power Plant

The West County Power Plant plays a pivotal role in driving economic growth and prosperity within the local community and the broader region.
Its operations generate substantial economic benefits, including job creation, tax revenue, and support for various businesses and industries.
Job Creation
The plant is a major employer in the area, providing direct employment to hundreds of skilled workers.
These jobs cover a range of fields, including engineering, operations, maintenance, and administration.
Tax Revenue
The plant contributes significantly to local and regional tax revenues through property taxes, sales taxes, and other levies.
These revenues support essential public services, such as education, infrastructure, and healthcare.
Business and Industry Support
The reliable and affordable electricity generated by the plant powers numerous businesses and industries in the area.
- Manufacturing facilities rely on the plant’s electricity to operate their machinery and production lines.
- Commercial establishments, such as offices, retail stores, and restaurants, depend on the plant’s electricity for lighting, heating, and cooling.
- Local farms utilize the plant’s electricity for irrigation, lighting, and other agricultural operations.
Economic Development and Investment
The presence of a reliable and cost-effective power source makes the region more attractive to businesses and investors.
This has led to the establishment of new businesses and the expansion of existing ones, creating additional employment opportunities and boosting the local economy.
The West County Power Plant, a massive energy facility located in the outskirts of the city, stood as a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of progress. Its towering smokestacks pierced the heavens, releasing plumes of steam that curled lazily into the atmosphere.
Yet, amidst the industrial grandeur, a touch of elegance could be found in the form of an exquisite urn planter on pedestal , its intricate carvings adorned with vibrant blooms. This unexpected juxtaposition served as a poignant reminder that even in the most utilitarian of settings, beauty and nature could find a way to coexist with the relentless march of technology.
West County Power Plant has a complex cooling system that uses water from the nearby river. The water is used to cool the plant’s generators and is then discharged back into the river. The discharged water is often warmer than the river water, which can have a negative impact on the river’s ecosystem.
To mitigate this impact, the power plant has planted wiri wiri pepper plants along the riverbank. These plants help to cool the water and provide habitat for fish and other aquatic life. The power plant’s use of wiri wiri pepper plants is an example of how industry can work with nature to protect the environment.
The West County Power Plant, a cutting-edge facility that utilizes advanced technology to generate electricity, has implemented sustainable practices to minimize its environmental impact. One such practice is the utilization of John Deere 1745 planters for precision farming. These planters optimize seed placement and minimize soil disturbance, resulting in increased crop yields and reduced erosion.
The West County Power Plant’s commitment to sustainability extends beyond its operations, as it actively supports initiatives that promote environmental stewardship in the surrounding community.