At the heart of the bustling energy landscape, the Little Gypsy Power Plant stands tall, a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of progress. Its rich history, technical prowess, and unwavering commitment to community make it a captivating subject that begs exploration.
From its inception to its current operations, the Little Gypsy Power Plant has played a pivotal role in shaping the local energy grid, providing a steady flow of electricity to homes and businesses alike. Over the years, it has undergone modernization and expansion, ensuring its continued relevance in an ever-evolving energy landscape.
Historical Overview of Little Gypsy Power Plant

The Little Gypsy Power Plant is a coal-fired power plant located in West Virginia. It was constructed in the 1950s and began operating in 1958. The plant has a capacity of 1,300 megawatts and is one of the largest coal-fired power plants in the United States.
The Little Gypsy power plant, also known as Tradescantia zebrina, is a vibrant creeper plant that adds a splash of color to any indoor or outdoor space. Its variegated leaves, featuring shades of green, purple, and silver, create a striking contrast that complements various decor styles.
Like other creeper plants ( types of creeper plants ), the Little Gypsy power plant is relatively easy to care for, making it a popular choice among plant enthusiasts.
The Little Gypsy Power Plant plays a significant role in the local energy grid. It provides electricity to over 1 million homes and businesses in the region. The plant also provides jobs for over 500 people.
Little gypsy power plant, also known as elephant ears, is a fast-growing, tropical plant that is often grown as an ornamental. The leaves of the little gypsy power plant are large and heart-shaped, and they can grow up to 3 feet long.
The leaves are a deep green color, but they can turn brown if they are not getting enough water or if they are exposed to too much sunlight. If you see that the leaves of your little gypsy power plant are turning brown, you can try to revive them by watering them more frequently or by moving them to a shadier location.
You can also read more about banana plant leaf brown for more information on how to care for your plant.
Environmental Impact
The Little Gypsy Power Plant has a significant environmental impact. The plant emits large amounts of carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides. These pollutants contribute to air pollution and climate change.
The plant also produces large amounts of waste. The waste is stored in a landfill, which can contaminate groundwater and surface water.
Little gypsy power plant, a vibrant addition to any garden, is known for its captivating blooms and adaptability. It thrives in warm climates, particularly in USDA hardiness zone 9, where it complements a wide range of zone 9 flowering plants . Its low maintenance nature and ability to attract pollinators make it a popular choice for gardeners seeking colorful and sustainable landscaping options.
Despite its modest size, little gypsy power plant packs a punch with its bold foliage and cheerful flowers, adding a touch of vibrancy to any garden.
In recent years, the Little Gypsy Power Plant has been under increasing pressure to reduce its environmental impact. The plant has installed pollution control equipment and has switched to cleaner-burning coal.
Technical Specifications and Operations: Little Gypsy Power Plant
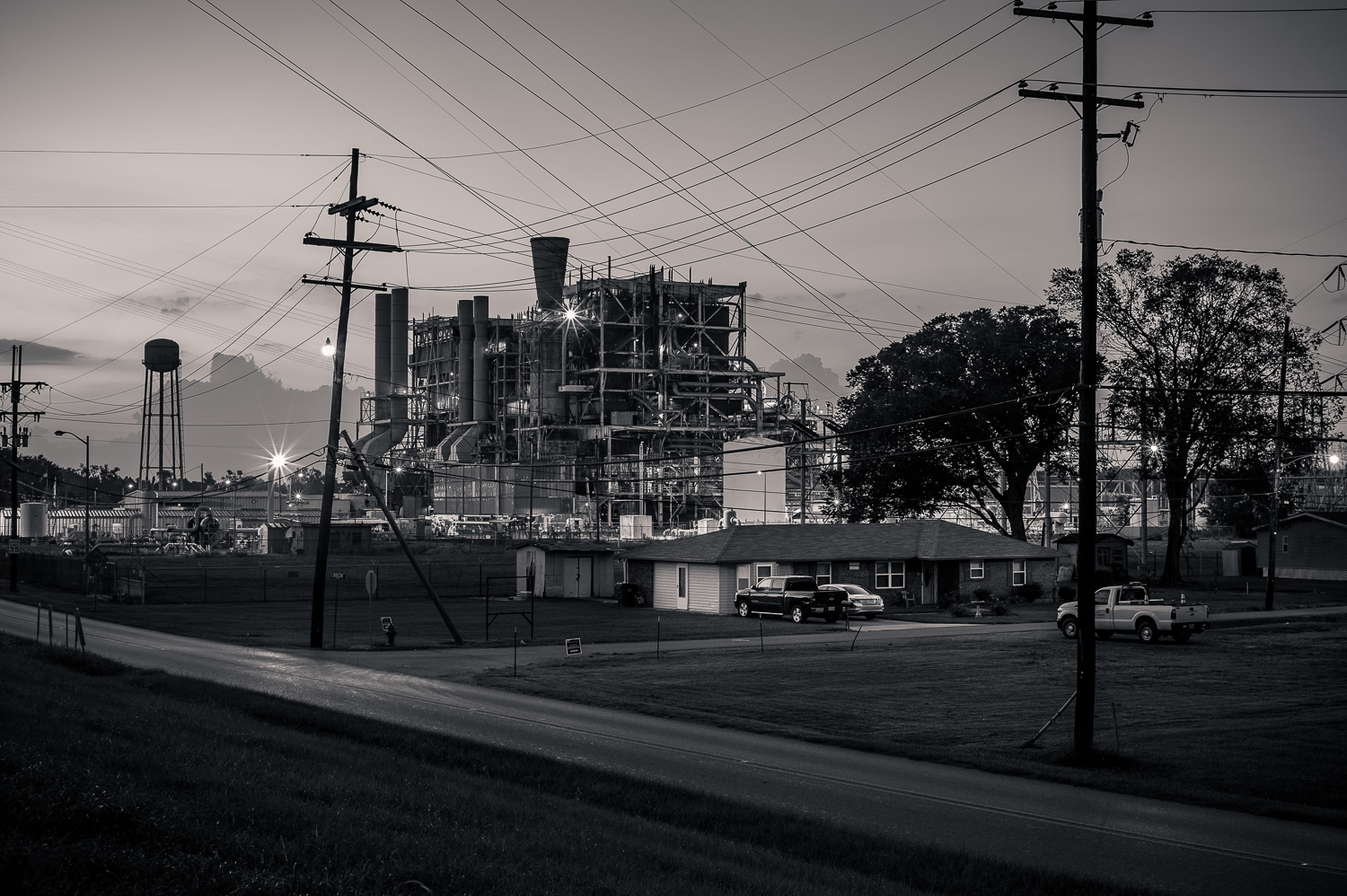

The Little Gypsy Power Plant operates using pulverized coal as its primary fuel source. The plant’s total generating capacity is 1,150 megawatts (MW), with each of its two units capable of producing 575 MW. The plant achieves an efficiency of approximately 38%, which is considered relatively low compared to modern coal-fired power plants.
Fuel Handling and Combustion, Little gypsy power plant
Coal is delivered to the plant via rail and stored in a large coal yard. The coal is then crushed and pulverized into a fine powder, which is then mixed with air and burned in the plant’s boilers. The heat generated by the combustion of coal turns water into steam, which is then used to drive the plant’s turbines.
Steam Turbine and Generator
The steam produced in the boilers is directed to the plant’s steam turbines. The turbines convert the thermal energy of the steam into mechanical energy, which is then used to rotate the generators. The generators convert the mechanical energy into electrical energy, which is then distributed to the power grid.
Environmental Controls
The Little Gypsy Power Plant employs various environmental control systems to minimize its impact on the environment. These systems include:
– Electrostatic precipitators to remove particulate matter from the flue gas
– Scrubbers to remove sulfur dioxide from the flue gas
– Selective catalytic reduction systems to reduce nitrogen oxide emissions
Safety Measures and Regulations
The Little Gypsy Power Plant operates under strict safety measures and regulations to ensure the safety of its employees and the surrounding community. These measures include:
– Regular inspections and maintenance of all plant equipment
– Emergency response plans and procedures
– Training programs for employees on safety protocols
– Compliance with all applicable environmental and safety regulations
Community Impact and Future Plans
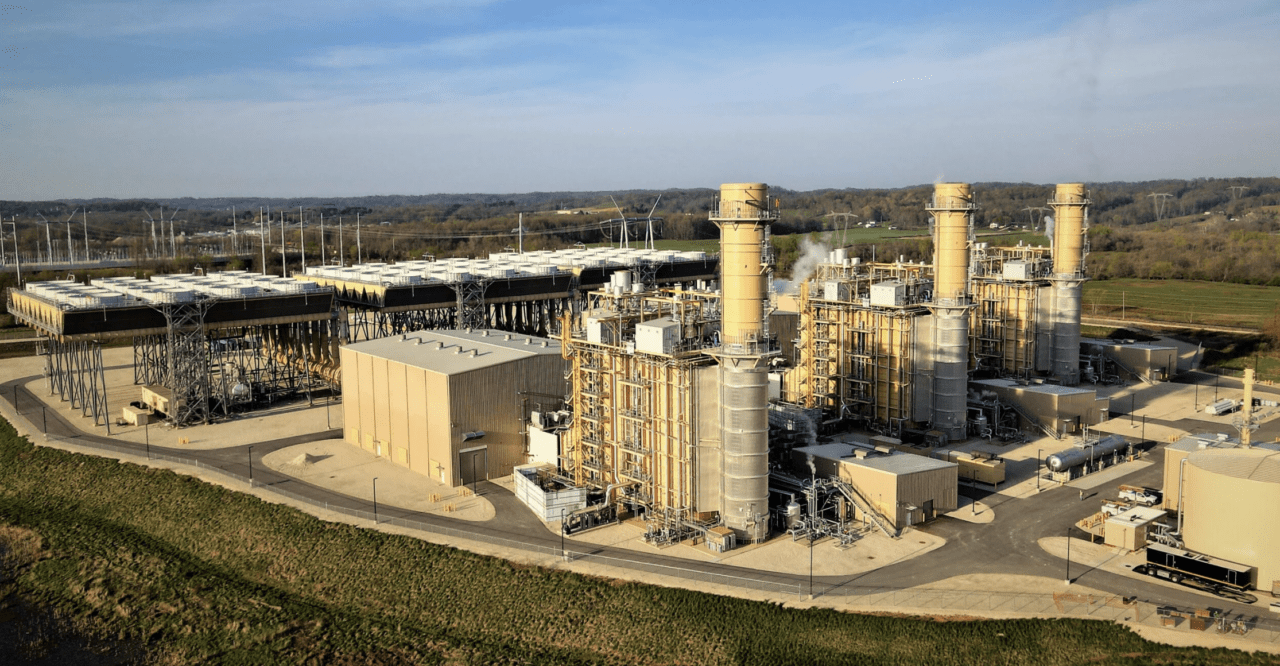
Little Gypsy Power Plant has played a significant role in the economic and social development of the surrounding community. The plant has provided jobs, stimulated local businesses, and supported community initiatives.
Economic Impact
- Job Creation: The plant employs over 200 people, providing stable and well-paying jobs for the local workforce.
- Local Business Stimulation: The plant’s operations have led to increased demand for goods and services from local businesses, such as construction companies, suppliers, and transportation providers.
- Tax Revenue: The plant contributes significantly to local tax revenues, which are used to fund essential public services such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure.
Social Impact
- Community Support: The plant actively supports community initiatives, including scholarships, educational programs, and environmental conservation efforts.
- Improved Infrastructure: The plant has invested in upgrading local infrastructure, such as roads and bridges, benefiting the entire community.
- Educational Opportunities: The plant collaborates with local schools and colleges to provide educational opportunities and training programs for students interested in the energy industry.
Future Plans
Little Gypsy Power Plant is committed to continued operations and modernization to meet future energy needs while minimizing environmental impact.
Expansion and Modernization
- Capacity Expansion: The plant is exploring options to increase its generating capacity to meet growing electricity demand in the region.
- Technology Upgrades: The plant plans to invest in new technologies to improve efficiency and reduce emissions.
- Fuel Diversification: The plant is investigating the use of alternative fuels, such as natural gas or biomass, to reduce its reliance on coal.
Renewable Energy Development
The plant recognizes the importance of renewable energy development and is actively exploring opportunities to integrate renewable sources into its operations.
- Solar Power: The plant is considering the installation of solar panels to generate clean and sustainable electricity.
- Wind Power: The plant is assessing the feasibility of constructing wind turbines to harness the region’s wind resources.
- Battery Storage: The plant is evaluating the use of battery storage systems to store excess energy generated from renewable sources.