Embark on a journey into the microscopic world with our comprehensive plant cell worksheet PDF. Delve into the intricate structure, function, and processes that govern these fundamental units of life.
Discover the secrets of the cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, vacuole, and chloroplasts. Witness the fascinating process of mitosis, comparing and contrasting it between plant and animal cells. Explore the mechanisms of transport across the plant cell membrane, unraveling the mysteries of passive and active transport.
Plant Cell Division: Plant Cell Worksheet Pdf

Plant cells, like all other eukaryotic cells, undergo cell division to produce new cells. The process of cell division in plant cells is called mitosis. Mitosis is a continuous process, but it can be divided into four distinct stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Stages of Mitosis in Plant Cells
| Stage | Key Events |
|---|---|
| Prophase |
|
| Metaphase |
|
| Anaphase |
|
| Telophase |
|
Comparison of Mitosis in Plant Cells to Mitosis in Animal Cells, Plant cell worksheet pdf
Mitosis in plant cells is similar to mitosis in animal cells, but there are a few key differences. One difference is that plant cells have a cell wall, while animal cells do not. The cell wall must be broken down during mitosis in order for the chromosomes to separate. Another difference is that plant cells have a large central vacuole, which takes up most of the cell’s volume. The vacuole must be displaced during mitosis in order for the chromosomes to line up in the center of the cell.
Plant Cell Transport
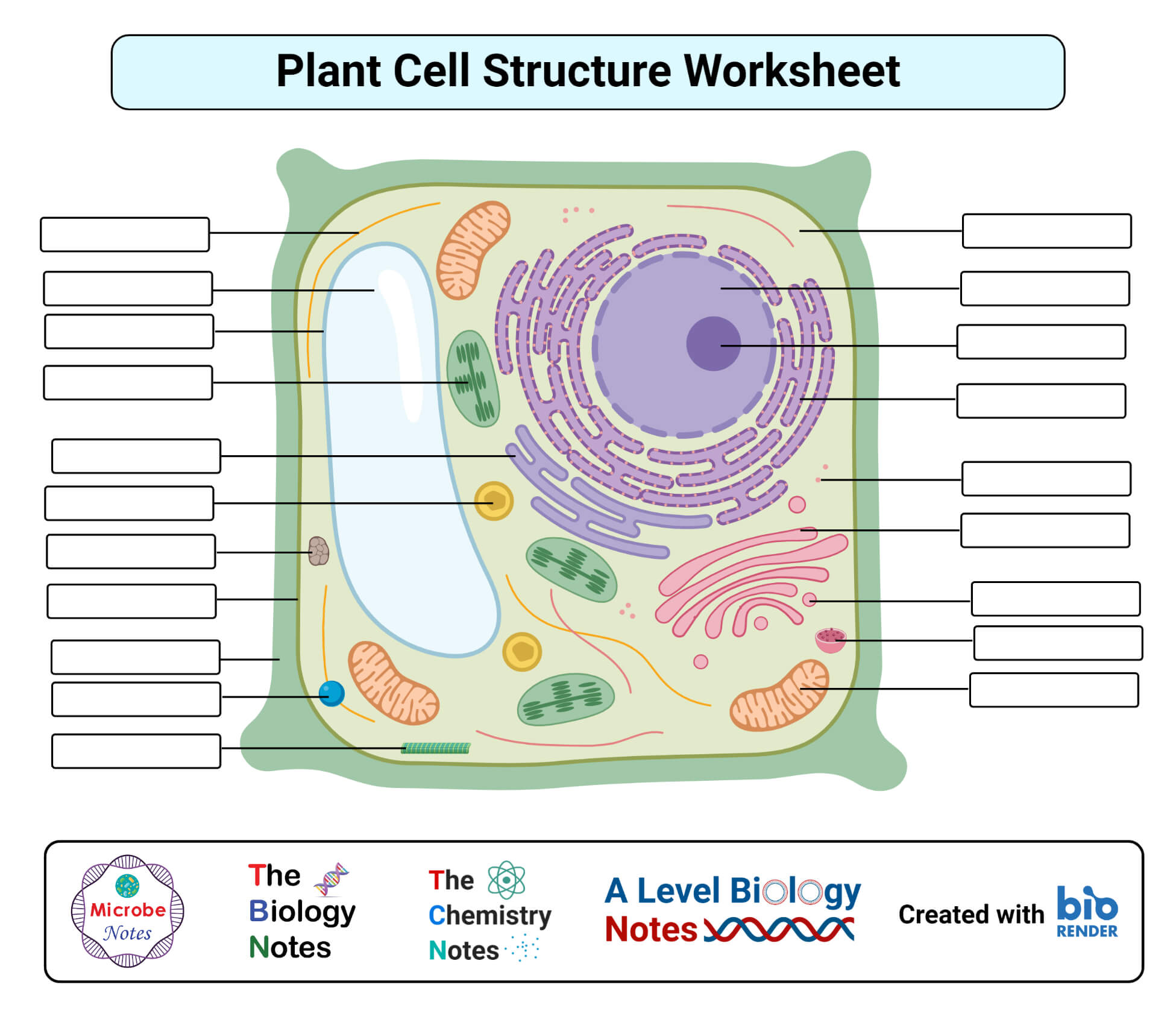
Plant cells rely on various mechanisms to transport molecules across their cell membranes, ensuring the uptake of essential nutrients and the removal of waste products. These mechanisms can be classified into two main categories: passive transport and active transport.
Passive Transport
Passive transport involves the movement of molecules across the cell membrane without the direct expenditure of cellular energy. It occurs when there is a concentration gradient or an electrochemical gradient across the membrane. There are three main types of passive transport:
- Diffusion: The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Small, nonpolar molecules like oxygen and carbon dioxide can easily diffuse across the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane.
- Osmosis: The movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration. Plant cells have a large central vacuole that stores water, and osmosis is crucial for maintaining the cell’s turgor pressure.
- Facilitated diffusion: The movement of molecules across the cell membrane with the assistance of specific transport proteins. These proteins provide a channel or carrier for molecules to pass through, increasing the rate of transport.
Active Transport
Active transport requires the direct expenditure of cellular energy to move molecules across the cell membrane against a concentration gradient. It is used to transport molecules that are essential for the cell but are present at a lower concentration outside the cell. Active transport is carried out by membrane proteins called pumps or carriers:
- Ion pumps: These proteins use ATP hydrolysis to pump ions across the cell membrane, establishing an electrochemical gradient that drives other transport processes.
- Carrier proteins: These proteins bind to specific molecules and use ATP hydrolysis to change their conformation, transporting the molecules across the membrane.
The structure of the plant cell membrane facilitates transport by providing a selectively permeable barrier that allows the passage of specific molecules while blocking others. The lipid bilayer forms the main barrier, while embedded proteins provide channels or carriers for specific molecules.
Understanding the structure and function of plant cells is essential for students of biology. A plant cell worksheet pdf can provide a comprehensive overview of the topic, including diagrams, definitions, and review questions. The south tempe water plant is a great example of a facility that utilizes plant cells in its water purification process.
By integrating this real-world application into the study of plant cell worksheets, students can gain a deeper understanding of the importance of these cells in the environment and beyond.
Plant cell worksheets are a great way to learn about the structure and function of plant cells. They can be used by students of all ages to learn about the different parts of a plant cell, how they work together, and how they are different from animal cells.
For example, the african milk plant is a succulent plant that is native to Africa. It is a popular houseplant because it is easy to care for and can tolerate a wide range of conditions. To learn more about the african milk plant, visit african milk plant care . You can also find many other resources on plant cells and plant biology online.
Plant cell worksheet pdfs are an excellent resource for students learning about the structure and function of plant cells. They provide detailed diagrams and explanations of the different organelles found in plant cells, including the nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria. For a practical example of a plant cell, consider the cordyline red star plant , known for its vibrant foliage and adaptability to various environments.
Its cells exhibit the same fundamental structures described in plant cell worksheet pdfs, making it an ideal specimen for further exploration.