Train strikes have become increasingly common in recent years, causing significant disruptions to commuters and businesses alike. This article examines the causes and impact of train strikes, exploring potential solutions to reduce their frequency and severity.
Strikes are often triggered by disputes over pay, working conditions, and job security, with unions playing a key role in organizing and negotiating with railway companies. The economic impact of strikes can be substantial, disrupting supply chains, reducing productivity, and affecting consumer spending.
Impact on Commuters
Train strikes have a significant impact on commuters, causing widespread disruptions and inconveniences. These strikes often result in the cancellation or delays of train services, leading to missed appointments, disrupted work schedules, and general inconvenience.
For commuters who rely on trains as their primary mode of transportation, strikes can have severe financial implications. They may have to resort to alternative modes of transport, such as taxis or ride-sharing services, which can be more expensive than train fares. Additionally, missed workdays due to transportation disruptions can lead to loss of income.
Travel Plans and Schedules
- Cancelled or delayed train services disrupt travel plans, causing commuters to miss important appointments, meetings, and social events.
- Unreliable train schedules make it difficult for commuters to plan their day effectively, leading to stress and frustration.
- Commuters may have to leave home much earlier than usual to avoid potential delays, resulting in wasted time and inconvenience.
Reasons for Strikes
Train strikes are typically caused by disputes between railway companies and unions representing their employees. These disputes can arise over a range of issues, including pay, working conditions, and job security.
Pay is a major factor in many train strikes. Unions argue that their members deserve fair pay for the work they do, while railway companies often cite financial constraints and the need to control costs.
Working conditions are another common source of conflict. Unions may seek improvements in areas such as hours of work, rest breaks, and safety measures. Railway companies, on the other hand, may prioritize efficiency and profitability.
Job security is a concern for many railway workers, especially in the face of technological advancements and changes in the industry. Unions may resist changes that they believe could lead to job losses or reduced benefits.
Historical Context
Train strikes have a long history in the United Kingdom. The first major strike occurred in 1919, when railway workers demanded better pay and working conditions. This strike lasted for three weeks and resulted in a wage increase and improved working conditions.
Subsequent train strikes have occurred over the years, with varying degrees of success. In 1955, a strike over pay and working conditions lasted for 26 days and resulted in a pay increase and reduced working hours.
In 1989, a strike over the privatization of British Rail lasted for two days. The strike was ultimately unsuccessful, but it did result in safeguards for workers.
More recently, a strike over pay and working conditions occurred in 2018. The strike lasted for one day and resulted in a pay increase and improved working conditions.
Role of Unions
Unions play a crucial role in organizing and negotiating with railway companies. They represent the interests of their members and seek to improve their pay, working conditions, and job security.
Unions use a variety of tactics to achieve their goals, including negotiation, mediation, and strikes. They also lobby the government for policies that support their members.
Impact of Strikes
Train strikes can have a significant impact on the economy, transportation, and the public.
Strikes can disrupt supply chains, delay deliveries, and cause economic losses. They can also make it difficult for people to get to work, school, or other appointments.
The public can be inconvenienced by train strikes, but they can also be sympathetic to the workers’ demands. Strikes can raise awareness of issues such as low pay and poor working conditions.
Alternative Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
There are a number of alternative dispute resolution mechanisms that can be used to prevent or resolve train strikes.
These mechanisms include mediation, arbitration, and fact-finding. Mediation involves a neutral third party who helps the two sides reach an agreement.
Arbitration involves a neutral third party who makes a binding decision on the dispute. Fact-finding involves a neutral third party who investigates the dispute and makes recommendations for a resolution.
Strategies for Preventing Future Strikes
There are a number of strategies that can be used to prevent future train strikes.
These strategies include:
- Improving communication between railway companies and unions
- Establishing clear and transparent procedures for negotiating and resolving disputes
- Providing fair pay and working conditions
- Investing in training and development for railway workers
- Promoting a culture of respect and trust between railway companies and unions
Government’s Response
The government has adopted a firm stance against train strikes, emphasizing the need to prioritize public interest and minimize disruption to essential services. It has actively sought to resolve disputes through negotiation and mediation, engaging with both unions and train operators to find common ground and prevent or shorten strikes.
Legislation and Regulations
The government has implemented legislation and regulations to regulate industrial action, including the use of injunctions and the imposition of minimum service levels. Injunctions can be sought by employers to prevent or limit strikes deemed unlawful or causing excessive disruption. Minimum service levels require a certain number of trains to operate during strike periods, ensuring essential travel and mitigating the impact on commuters.
Impact on the Economy
Train strikes can have significant economic consequences, disrupting supply chains, reducing productivity, and dampening consumer spending. The financial losses incurred by businesses and the government can be substantial.
Disruptions to Supply Chains
Strikes can severely disrupt supply chains, leading to delays in the delivery of goods and services. This can result in production losses, increased costs, and shortages of essential commodities.
Do not overlook explore the latest data about VfB.
Losses to Businesses
Businesses across various sectors, including manufacturing, retail, and tourism, face significant financial losses due to train strikes. Disruptions to transportation and supply chains can lead to reduced sales, lost revenue, and increased operating costs.
Long-term Economic Implications
Prolonged strikes can have long-term implications for economic growth and productivity. Reduced investment, innovation, and consumer confidence can hinder economic recovery and development.
Economic Costs
| Economic Cost | Description |
|---|---|
| Job Losses | Strikes can lead to temporary or permanent job losses in affected industries. |
| Decreased Tax Revenue | Reduced economic activity and business revenue can result in lower tax revenue for the government. |
| Consumer Spending | Disruptions to transportation and supply chains can reduce consumer spending, impacting retail and hospitality sectors. |
“Train strikes can have a devastating impact on the economy, causing billions of dollars in losses and disrupting businesses and consumers alike.” – Economist, National Institute of Economic and Social Research
Alternative Transportation Options
When train services are disrupted due to strikes, commuters are forced to seek alternative modes of transportation. This section explores the available options, their advantages and disadvantages, and their capacity to meet the increased demand during strikes.
Buses
- Pros:
- Widely available and accessible
- Relatively affordable
- Cons:
- Can be slow and unreliable
- Crowded during peak hours
Taxis
- Pros:
- Convenient and door-to-door service
- Available 24/7
- Cons:
- Expensive, especially during high demand
- Limited availability during strikes
Ride-Sharing Services
- Pros:
- Convenient and often cheaper than taxis
- Widely available through mobile apps
- Cons:
- Surge pricing during peak hours
- Reliability can be affected by driver availability
The capacity of alternative transportation systems to meet the demand during strikes is a concern. Buses often experience overcrowding, leading to delays and discomfort for passengers. Taxis and ride-sharing services may face increased fares and limited availability, making them less accessible for many commuters. Therefore, it is crucial for transportation authorities to plan for and implement measures to enhance the capacity and reliability of alternative transportation options during strike periods.
Public Perception

Public perception of train strikes is complex and multifaceted, influenced by a range of factors. Generally, support for train strikes tends to be lower than opposition, with the public often expressing frustration and inconvenience during periods of industrial action.
Factors Influencing Public Sentiment
* Reasons for strikes: The public’s perception of train strikes is heavily influenced by the reasons behind them. Strikes that are perceived as being for legitimate reasons, such as fair pay or working conditions, tend to garner more support.
* Impact on commuters: The inconvenience caused by train strikes is a major factor in shaping public sentiment. Strikes that cause significant disruption to daily life, such as those during peak commuting hours, are more likely to be met with opposition.
* Media coverage: The media plays a significant role in shaping public opinion on train strikes. Negative media coverage, which focuses on the disruption caused by strikes, can contribute to a more negative public perception.
* Demographic and regional variations: Public sentiment towards train strikes can vary depending on demographic and regional factors. For example, commuters who rely heavily on trains for their daily commute may be more likely to oppose strikes.
Role of Social Media
Social media has become an increasingly important platform for shaping public perception of train strikes. It allows individuals to share their experiences and opinions, and can amplify both support and opposition to industrial action.
Role of Public Figures and Organizations
Public figures and organizations can also influence public opinion on train strikes. Trade unions, for example, play a key role in communicating the reasons for strikes and advocating for workers’ rights. Politicians and government officials can also shape public perception through their statements and actions.
Recommendations for Improving Public Communication and Engagement
* Clear and timely communication: Governments and train operators should provide clear and timely information to the public about the reasons for strikes and the potential impact on services.
* Engagement with stakeholders: Governments and train operators should engage with stakeholders, including trade unions, passenger groups, and local communities, to understand their concerns and find ways to mitigate the impact of strikes.
* Use of social media: Governments and train operators should use social media to provide updates and engage with the public during periods of industrial action.
* Independent reporting: The media should provide balanced and objective reporting on train strikes, giving voice to both sides of the debate and focusing on the impact on the public.
Historical Context
Train strikes have a long and complex history in the country. The first major strike occurred in 1877, when railroad workers walked off the job in protest of low wages and poor working conditions. The strike was eventually broken by federal troops, but it marked the beginning of a long period of labor unrest in the railroad industry.
In the early 20th century, train strikes became more frequent and more violent. In 1922, a nationwide strike by railroad shopmen led to the deaths of several strikers and the destruction of railroad property. The strike was eventually settled by government intervention, but it left a lasting legacy of bitterness and distrust between railroad workers and management.
In the post-World War II era, train strikes became less frequent, but they continued to occur periodically. In 1981, a strike by air traffic controllers led to the firing of 11,000 workers and the grounding of all commercial flights in the United States. The strike was eventually broken by President Ronald Reagan, but it had a significant impact on the airline industry and the economy as a whole.
In recent years, train strikes have become less common, but they have not disappeared entirely. In 2018, a strike by conductors on the Long Island Rail Road led to the cancellation of hundreds of trains and caused major disruptions for commuters. The strike was eventually settled after several days of negotiations.
Factors Contributing to Train Strikes
There are a number of factors that have contributed to the occurrence of train strikes in the past. These include:
- Low wages and poor working conditions: Railroad workers have historically been paid less than workers in other industries, and they have often worked in dangerous and unhealthy conditions.
- Lack of union representation: In the early days of the railroad industry, many railroad workers were not represented by unions. This made it difficult for them to negotiate with management and improve their working conditions.
- Government intervention: The government has often intervened in train strikes, sometimes in favor of the workers and sometimes in favor of management. This has made it difficult for the two sides to reach a settlement on their own.
International Comparisons: Train Strikes
Train strikes are a global phenomenon, with varying patterns and outcomes across different countries and regions. By examining international experiences, we can identify best practices and lessons learned to improve strike prevention, negotiation strategies, and public communication.
Enhance your insight with the methods and methods of Eintracht Frankfurt.
Strike Causes
Common strike causes across countries include:
- Wages and working conditions
- Pension reforms
- Job security concerns
- Modernization and automation
Government Responses
Government responses vary widely, ranging from:
- Direct intervention and negotiation
- Imposition of minimum service levels
- Legal restrictions on strike action
- Financial penalties for striking workers
Public Reactions
Public reactions to train strikes can differ based on factors such as:
- Level of public sympathy for strikers
- Perception of strike impact on daily life
- Government’s communication and handling of the situation
Best Practices and Lessons Learned
International experiences offer valuable insights into effective strike prevention and management:
- Early intervention and dialogue: Engaging with unions early on can help prevent disputes from escalating into strikes.
- Transparent negotiation processes: Clear and open communication between parties builds trust and facilitates compromise.
- Public education campaigns: Informing the public about the reasons for strikes and their potential impact can garner understanding and support.
Comparative Table
| Country | Number of Strike Days per Year | Average Duration of Strikes | Government Response Time | Public Support for Strikes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom | 10-20 | 5-7 days | Immediate intervention | Mixed |
| France | 15-25 | 3-5 days | Mediation and negotiation | High |
| Germany | 5-10 | 1-3 days | Legal restrictions on strikes | Low |
| United States | 2-5 | 1-2 days | Imposition of minimum service levels | Mixed |
| Japan | <5 | <1 day | Cultural norms and consensus-building | Very low |
Key Findings and Recommendations
By comparing international experiences, we observe:
- The number of strike days varies significantly across countries, influenced by factors such as labor laws and union strength.
- Early intervention and transparent negotiations can reduce the likelihood and duration of strikes.
- Public education and communication play a crucial role in shaping public perception and support for strikes.
Recommendations for policymakers include:
- Establish clear and fair negotiation frameworks to prevent disputes from escalating into strikes.
- Engage in proactive dialogue with unions and other stakeholders to build trust and understanding.
- Implement effective public communication strategies to inform the public about strike causes and their potential impact.
Case Study: 2022 United Kingdom Rail Strikes

The 2022 United Kingdom rail strikes were a series of industrial actions undertaken by members of the Rail, Maritime and Transport (RMT) union in response to a dispute with Network Rail and train operating companies over pay, working conditions, and job security.
The strikes caused significant disruption to rail services across the country, with many lines being closed or operating with reduced services. The strikes had a major impact on commuters, businesses, and the economy.
Government Intervention
The government intervened in the dispute on several occasions, but was unable to prevent the strikes from taking place. The government’s main focus was on minimizing the impact of the strikes on the public and the economy.
The government provided financial support to train operating companies to help them cope with the loss of revenue caused by the strikes. The government also worked with employers to encourage them to allow their employees to work from home or take other forms of leave during the strikes.
Impact on the Economy, Train strikes
The strikes had a significant impact on the economy. The Centre for Economics and Business Research (CEBR) estimated that the strikes cost the UK economy £1.5 billion in lost output.
The strikes also had a negative impact on businesses. Many businesses reported a loss of revenue due to the strikes, and some businesses were forced to close temporarily.
Public Perception
The public was generally supportive of the strikers. A poll conducted by YouGov found that 53% of Britons supported the strikes, while only 27% opposed them.
The public’s support for the strikes was likely due to the fact that many people sympathized with the strikers’ demands for better pay and working conditions.
Lessons Learned
The 2022 United Kingdom rail strikes provide a number of lessons for the future.
- First, the strikes highlight the importance of effective communication between employers and employees.
- Second, the strikes show that the government can play a role in resolving industrial disputes, but that it is important for the government to remain impartial.
- Third, the strikes demonstrate the importance of public support for industrial action.
The lessons learned from the 2022 United Kingdom rail strikes can help to prevent or manage similar strikes in the future.
Recommendations
In order to prevent or manage similar strikes in the future, the following recommendations should be considered:
- Employers and employees should engage in early and meaningful dialogue to address concerns and prevent disputes from escalating.
- The government should establish an independent body to mediate industrial disputes and help to resolve them before they reach the point of strike action.
- The public should be informed about the issues involved in industrial disputes and the reasons why workers are taking strike action.
By following these recommendations, it is possible to reduce the likelihood of strikes and to minimize their impact on the public and the economy.
Long-Term Solutions
To reduce the frequency and impact of train strikes, long-term solutions must be explored. These solutions aim to address the root causes of industrial disputes and improve labor relations within the rail industry.
Improved Labor Relations
Improved labor relations are crucial for reducing the likelihood of strikes. This can be achieved through:
- Open and transparent communication between unions and management
- Regular consultation and negotiation to address concerns and grievances
- Establishment of joint working groups to foster cooperation and understanding
Alternative Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
Alternative dispute resolution mechanisms provide alternative avenues for resolving conflicts without resorting to strikes. These mechanisms include:
- Mediation and conciliation services
- Independent arbitration tribunals
- Early intervention and dispute prevention programs
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements can also play a role in reducing the impact of strikes. These advancements include:
- Automated train operations to reduce reliance on manual labor
- Real-time passenger information systems to minimize disruption during strikes
- Improved communication and collaboration tools to facilitate negotiations
Illustrations/Images
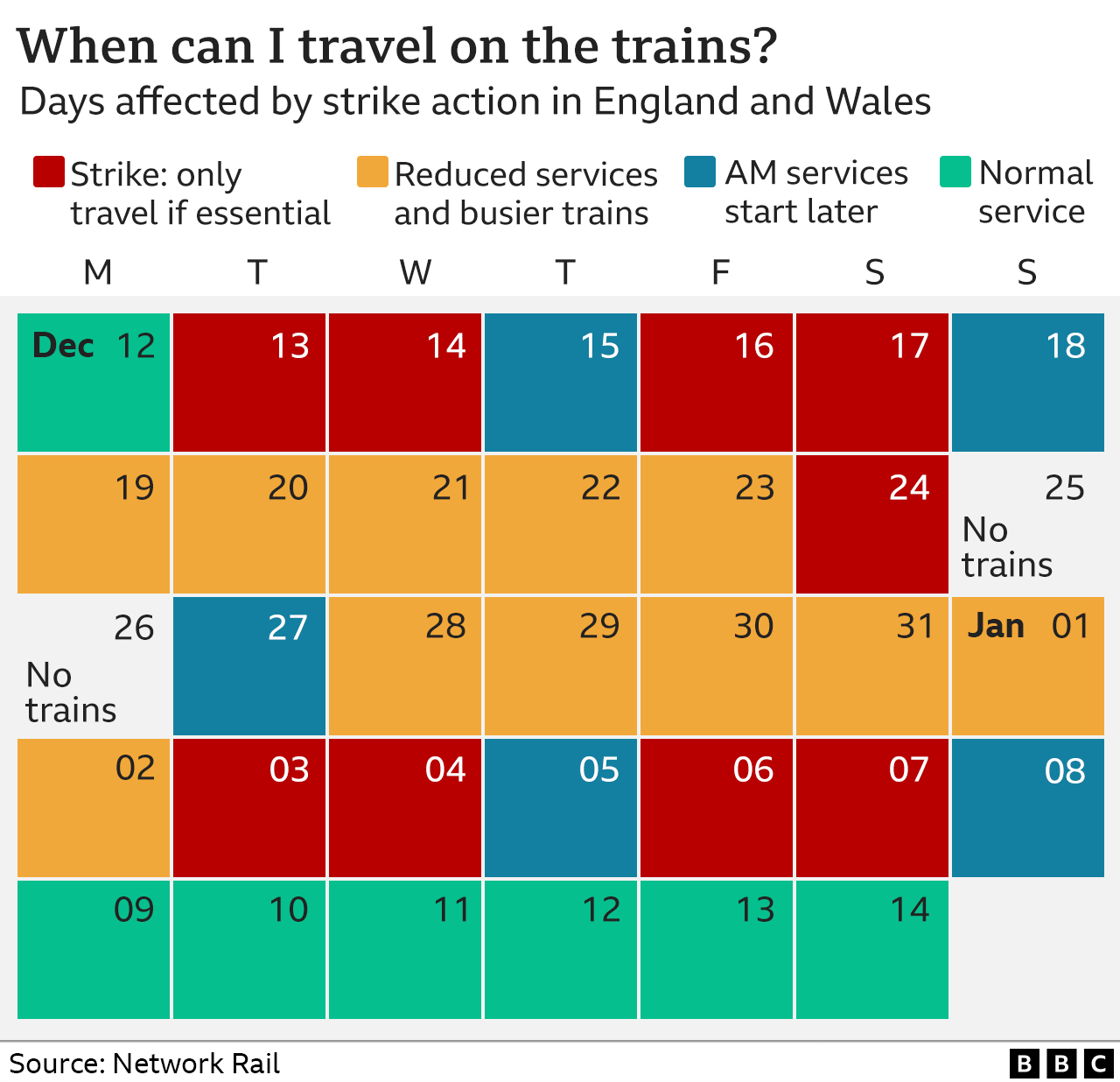
Visual representations can powerfully convey the impact of train strikes on commuters, businesses, and the economy.
Images should capture the disruption, inconvenience, and economic consequences caused by strikes. They could depict:
Commuters
- Long queues at train stations, with commuters struggling to find alternative transportation.
- Crowded buses and roads, as commuters switch to alternative modes of transport.
- Frustrated commuters facing delays and cancellations, leading to stress and lost productivity.
Businesses
- Empty storefronts and reduced foot traffic in areas heavily reliant on train commuters.
- Supply chain disruptions, as businesses struggle to receive goods and deliver products due to transportation delays.
- Financial losses for businesses, particularly in sectors like retail, hospitality, and tourism.
Economy
- Reduced economic activity, as businesses and consumers are affected by transportation disruptions.
- Slowed down economic growth, as strikes impact productivity and supply chains.
- Negative impact on investor confidence, as uncertainty and disruption create concerns about the stability of the economy.
12. Tables
Tables can be an effective way to present comparative data in a clear and concise manner. In the context of train strikes, a table can be used to compare the causes and outcomes of strikes in different countries or regions.
Country-wise Comparison of Train Strikes
The following table compares the causes and outcomes of train strikes in three different countries:
| Country | Strike Date | Cause | Duration | Resolution |
|—|—|—|—|—|
| United Kingdom | 2022 | Pay and working conditions | 2 days | Agreement on pay increase and improved working conditions |
| France | 2018 | Pension reform | 3 weeks | Government withdrew pension reform proposal |
| India | 2021 | Privatization of railways | 1 week | Government agreed to suspend privatization plans |
As can be seen from the table, the causes and outcomes of train strikes can vary significantly from country to country. In some cases, strikes are successful in achieving their objectives, while in other cases they are not. The duration of strikes can also vary significantly, from a few days to several weeks or even months.
Blockquotes
Blockquotes are a powerful tool for highlighting key quotes or statements from experts, government officials, or union representatives. They can help to add credibility and authority to your writing, and they can also make your content more engaging and interesting to read.
When using blockquotes, it is important to include attribution and context. This means that you should provide the name of the person who said the quote, as well as the source of the quote. You should also provide a brief explanation of the context in which the quote was made.
Using Blockquotes Effectively
Here are a few tips for using blockquotes effectively:
- Use blockquotes sparingly. Too many blockquotes can make your writing look cluttered and overwhelming.
- Choose quotes that are relevant to your topic and that support your argument.
- Make sure that the quotes are accurate and that you have attributed them correctly.
- Use blockquotes to break up your text and make it more visually appealing.
Conclusion

Train strikes are a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. Understanding their causes, impact, and potential solutions is crucial for mitigating their effects and improving the rail system. This analysis has explored various aspects of train strikes, providing a comprehensive overview of the topic.
Causes of Train Strikes
Train strikes are primarily driven by disputes between railway operators and unions representing train workers. These disputes often center around issues such as pay, working conditions, and job security. In some cases, strikes may also be politically motivated or related to broader social or economic issues.
Impact of Train Strikes
Train strikes have a significant impact on commuters, businesses, and the economy as a whole. Commuters face disruption and delays, leading to lost productivity and inconvenience. Businesses may experience supply chain disruptions and lost revenue. The economy suffers from reduced economic activity and decreased consumer spending.
Potential Solutions for Train Strikes
Addressing train strikes requires a multifaceted approach involving both short-term and long-term solutions. Short-term measures include mediation, negotiation, and compromise between railway operators and unions. Long-term solutions focus on improving communication, fostering trust, and addressing underlying issues that contribute to industrial disputes.
Recommendations for Further Research and Policy Action
Further research is needed to explore the underlying causes of train strikes and develop effective prevention strategies. Policymakers should consider implementing measures that promote fair labor practices, foster dialogue between stakeholders, and ensure the long-term sustainability of the rail system.
Wrap-Up
Addressing the underlying causes of train strikes requires a collaborative approach involving governments, railway companies, and unions. Alternative dispute resolution mechanisms and long-term solutions, such as improved labor relations and technological advancements, can help prevent or mitigate strikes and ensure a reliable and efficient rail network.