Welcome to the captivating world of advertising, where creativity meets strategy to persuade, inform, and inspire. Ad takes center stage in this comprehensive guide, unraveling the secrets of effective advertising campaigns and empowering you to harness its transformative potential.
From understanding the nuances of different ad types to crafting compelling ad copy and measuring campaign success, this guide equips you with the knowledge and tools to navigate the ever-evolving advertising landscape with confidence.
Ad Definition and Types
An advertisement, often shortened to ad, is a form of marketing communication used to promote a product, service, or idea. Ads can appear in various media, including print, digital, social media, and broadcast.
The primary purpose of an advertisement is to persuade the audience to take a specific action, such as making a purchase, visiting a website, or signing up for a service. Ads can also be used to build brand awareness, create a positive image, or educate the audience about a particular topic.
Print Ads
Print ads are advertisements that appear in printed publications such as newspapers, magazines, and brochures. Print ads can be used to reach a specific target audience based on the publication’s readership.
Strengths of print ads include their credibility and ability to provide detailed information. However, print ads can be expensive to produce and have a limited reach compared to digital ads.
Digital Ads
Digital ads are advertisements that appear on electronic devices such as computers, smartphones, and tablets. Digital ads can be displayed on websites, social media platforms, and search engines.
Strengths of digital ads include their ability to reach a large audience, target specific demographics, and track results. However, digital ads can be intrusive and may not be effective for all target audiences.
Social Media Ads
Social media ads are advertisements that appear on social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. Social media ads can be used to reach a specific target audience based on their interests, demographics, and behavior.
Strengths of social media ads include their ability to target specific demographics, build relationships with customers, and drive traffic to a website. However, social media ads can be expensive and may not be effective for all target audiences.
Ad Structure and Components
An ad is a message designed to persuade people to buy a product or service. It has a specific structure and components that work together to create an effective message.
Headline
The headline is the first thing people see in an ad. It should be short, catchy, and attention-grabbing. The headline should summarize the main message of the ad and make people want to read more.
Body Copy
The body copy is the main text of the ad. It provides more detail about the product or service and explains why people should buy it. The body copy should be clear, concise, and persuasive.
Call-to-Action
The call-to-action is the last thing people see in an ad. It tells people what they should do next, such as visiting a website or making a purchase. The call-to-action should be clear and easy to follow.
Ad Objectives and Target Audience
Advertising campaigns aim to achieve specific goals, ranging from increasing brand awareness to driving sales. Identifying and targeting specific audiences is crucial for effective advertising, ensuring that messages resonate with the right individuals.
Types of Advertising Objectives
- Brand Awareness: Aiming to increase the visibility and recognition of a brand among the target audience.
- Lead Generation: Gathering potential customer information (leads) through advertising efforts.
- Sales Conversion: Encouraging customers to make purchases or take desired actions.
- Customer Engagement: Building relationships with customers by fostering interaction and engagement.
Target Audience Identification
Identifying the target audience involves understanding their demographics, interests, behaviors, and media consumption habits. This enables advertisers to tailor messages and channels that align with the audience’s specific needs and preferences.
Importance of Target Audience
- Relevance: Ensuring that advertising messages are relevant and meaningful to the intended audience.
- Efficiency: Directing advertising efforts towards individuals most likely to be interested in the product or service.
- Cost-effectiveness: Optimizing advertising budgets by focusing on audiences with a higher probability of conversion.
Ad Media and Channels
Advertising can take place through various media and channels, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
The choice of media and channels depends on factors such as the target audience, the advertising objectives, and the budget available.
Traditional Media
- Print advertising: Includes newspapers, magazines, and billboards. Print advertising is a traditional form of advertising that has been used for centuries. It is still effective for reaching specific target audiences, such as local consumers or readers of particular publications.
- Broadcast advertising: Includes television and radio. Broadcast advertising is a mass-reach medium that can be used to reach a large audience quickly and effectively. However, it can be expensive, and it can be difficult to target specific audiences.
- Outdoor advertising: Includes billboards, posters, and street furniture. Outdoor advertising is a highly visible form of advertising that can be used to reach people on the go. However, it can be expensive, and it can be difficult to measure the effectiveness of outdoor advertising campaigns.
Digital Media, Ad
- Online advertising: Includes search engine marketing, display advertising, and social media advertising. Online advertising is a cost-effective way to reach a large audience, and it can be targeted to specific demographics and interests. However, it can be difficult to stand out from the competition, and it can be challenging to measure the effectiveness of online advertising campaigns.
- Mobile advertising: Includes in-app advertising, mobile search advertising, and SMS advertising. Mobile advertising is a growing channel that can be used to reach people on their smartphones and tablets. However, it can be difficult to create mobile ads that are engaging and effective.
- Social media advertising: Includes paid advertising on social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. Social media advertising can be used to reach a large audience, and it can be targeted to specific demographics and interests. However, it can be difficult to create social media ads that are engaging and effective.
Ad Measurement and Metrics
Measuring the effectiveness of advertising campaigns is crucial to optimize ROI and ensure successful results. Various metrics and techniques are employed to track and analyze the performance of ads, providing valuable insights for improvement and optimization.
Key metrics include:
- Impressions: Number of times an ad is displayed
- Reach: Number of unique individuals who saw the ad
- Click-through rate (CTR): Percentage of people who clicked on the ad after seeing it
- Conversion rate: Percentage of people who completed a desired action, such as making a purchase or signing up for a service
- Return on investment (ROI): Ratio of revenue generated to the cost of advertising
Tracking and Analyzing Metrics
Tracking and analyzing these metrics involves using various tools and techniques, such as:
- Google Analytics: Provides detailed insights into website traffic, including ad performance
- Social media analytics: Tracks engagement and performance of ads on social media platforms
- Email marketing analytics: Monitors email campaign performance, including open rates and click-through rates
Regularly monitoring and analyzing these metrics enables marketers to identify what’s working well and what needs improvement, allowing them to make data-driven decisions to optimize their advertising campaigns.
Ad Creative and Design
In the realm of advertising, creativity reigns supreme. It’s the spark that ignites the fire of memorability and drives results. Effective ad creative is a symphony of visual elements, messaging, and tone of voice, orchestrated to captivate attention, convey a message, and evoke a desired response.
Visual elements are the canvas upon which the ad’s story unfolds. Striking images, vibrant colors, and eye-catching designs create an instant visual connection with the audience. Whether it’s a breathtaking photograph or an animated masterpiece, the visuals should align seamlessly with the brand’s identity and the message being conveyed.
Messaging and Tone of Voice
The messaging is the heart and soul of an ad. It articulates the brand’s value proposition, tells a compelling story, and persuades the audience to take action. The tone of voice, whether humorous, serious, or aspirational, should resonate with the target audience and reinforce the brand’s personality.
Examples of Creative Excellence
History is replete with ad campaigns that have showcased creative brilliance and achieved remarkable success. The “Just Do It” campaign for Nike became an iconic mantra, inspiring countless athletes and consumers alike. Apple’s “Think Different” campaign celebrated the power of innovation and cemented the brand’s reputation for pushing boundaries.
These campaigns demonstrate the transformative power of effective ad creative. By harnessing the principles of visual impact, compelling messaging, and a resonant tone of voice, they have left an indelible mark on the advertising landscape and continue to inspire generations of marketers.
Ad Copywriting
Ad copywriting is the art of crafting persuasive and engaging text for advertisements. It’s the key to capturing attention, conveying a message, and driving conversions.
Strong ad copywriting can help you:
- Increase brand awareness
- Generate leads
- Drive sales
- Build customer relationships
Headlines
Your headline is the first thing people will see, so make it count. Keep it short, catchy, and relevant to your target audience.
Body Copy
The body copy is where you expand on your headline and provide more details about your product or service. Use clear and concise language, and highlight the benefits of your offering.
Calls-to-Action
Your call-to-action (CTA) tells people what you want them to do next, such as visit your website, download a whitepaper, or make a purchase. Make your CTA clear, concise, and easy to follow.
For descriptions on additional topics like Sabrina Wittmann, please visit the available Sabrina Wittmann.
Target Audience Research
Before you write any ad copy, it’s important to research your target audience. This will help you understand their needs, wants, and pain points, so you can tailor your copy accordingly.
Examples of Effective Ad Copywriting
Here are some examples of effective ad copywriting in different industries:
- Nike: “Just Do It”
- Apple: “Think Different”
- Coca-Cola: “Open Happiness”
- McDonald’s: “I’m Lovin’ It”
- IKEA: “The Wonderful Everyday”
Best Practices for Ad Copywriting
| Characteristic | Best Practice |
|---|---|
| Character limits | Headlines: 60 characters or less Body copy: 120 characters or less CTAs: 50 characters or less |
| Font size | Headlines: 24pt or larger Body copy: 14pt or larger CTAs: 16pt or larger |
| Formatting | Use bullet points, subheadings, and white space to make your copy easy to read |
Checklist for Ad Copywriting
- Clarity and conciseness
- Emotional appeal
- Call-to-action
- Target audience relevance
- Proofreading
AI Tools for Ad Copywriting
AI tools can help you enhance your ad copywriting, such as:
- Headline generators
- Body copy expanders
- Call-to-action optimizers
Ad Technology and Trends

Advertising technology has undergone a remarkable transformation in recent years, driven by advancements in digital technologies and the rise of data-driven marketing. These advancements have not only revolutionized the way ads are created, delivered, and measured but have also opened up new possibilities for advertisers and publishers.
Programmatic Advertising
Programmatic advertising refers to the automated buying and selling of ad inventory through software platforms. This technology enables advertisers to target specific audiences, optimize campaigns in real-time, and measure results with greater precision. Programmatic advertising has become increasingly popular due to its efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and ability to deliver highly targeted ads.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are playing a pivotal role in ad technology, enabling advertisers to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make predictions. AI-powered algorithms can optimize ad campaigns, automate tasks, and provide personalized ad experiences for consumers.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR and VR are immersive technologies that are transforming the advertising landscape. AR superimposes digital content onto the real world, while VR creates a completely virtual environment. These technologies offer advertisers new ways to engage with consumers, create memorable experiences, and drive conversions.
Addressable TV
Addressable TV is a technology that allows advertisers to deliver targeted ads to individual households based on their demographics, viewing habits, and other data points. This technology has gained traction in recent years as more consumers shift to streaming services, which offer greater opportunities for personalized advertising.
Emerging Trends
In addition to these technological advancements, several emerging trends are shaping the ad technology landscape:
The Rise of Connected TV (CTV)
CTV refers to internet-connected televisions that allow viewers to access streaming services, on-demand content, and live TV. CTV has emerged as a major advertising platform, offering advertisers the ability to reach large audiences with highly targeted ads.
The Growing Importance of Mobile Advertising
Mobile advertising continues to grow in importance as more consumers spend time on their smartphones and tablets. Mobile ads offer advertisers a unique opportunity to engage with consumers on a personal level and drive conversions.
The Convergence of Advertising and Entertainment
The lines between advertising and entertainment are becoming increasingly blurred. Advertisers are creating more immersive and engaging ad experiences that resemble entertainment content. This trend is expected to continue as consumers seek out more personalized and relevant advertising experiences.
The Impact of Privacy Regulations on Ad Targeting
Privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, are having a significant impact on ad targeting. These regulations limit the ability of advertisers to collect and use consumer data for targeted advertising. Advertisers are adapting to these regulations by developing new methods of targeting that are compliant with privacy laws.
Ad Ethics and Regulations
Advertising plays a crucial role in shaping our perceptions and influencing our purchasing decisions. However, with great power comes great responsibility. Ethical considerations and legal regulations guide the advertising industry to ensure that ads are not only effective but also responsible and respectful.
Transparency is paramount in advertising. Misleading or deceptive practices can erode trust and damage brands. Advertisers must accurately represent their products and services, avoiding exaggerated claims or omissions of material facts.
Ethical Advertising Practices
- Truthful and accurate claims: Ads should be based on facts and not mislead consumers about the product’s benefits or features.
- Avoiding stereotyping or discrimination: Ads should not portray individuals or groups in a discriminatory or stereotypical manner.
- Respecting privacy: Advertisers should respect consumers’ privacy and obtain their consent before collecting or using their personal information.
Legal Regulations on Advertising
Notice IMT for recommendations and other broad suggestions.
Various laws and regulations govern advertising practices to protect consumers from deceptive or harmful ads. Some key regulatory bodies include:
- Federal Trade Commission (FTC): The FTC enforces truth-in-advertising laws and prohibits unfair or deceptive practices.
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA): The FDA regulates advertising for food, drugs, and cosmetics to ensure their safety and efficacy.
- Better Business Bureau (BBB): The BBB provides standards for ethical advertising and investigates complaints from consumers.
Analyze successful advertising campaigns and identify the key factors that contributed to their success
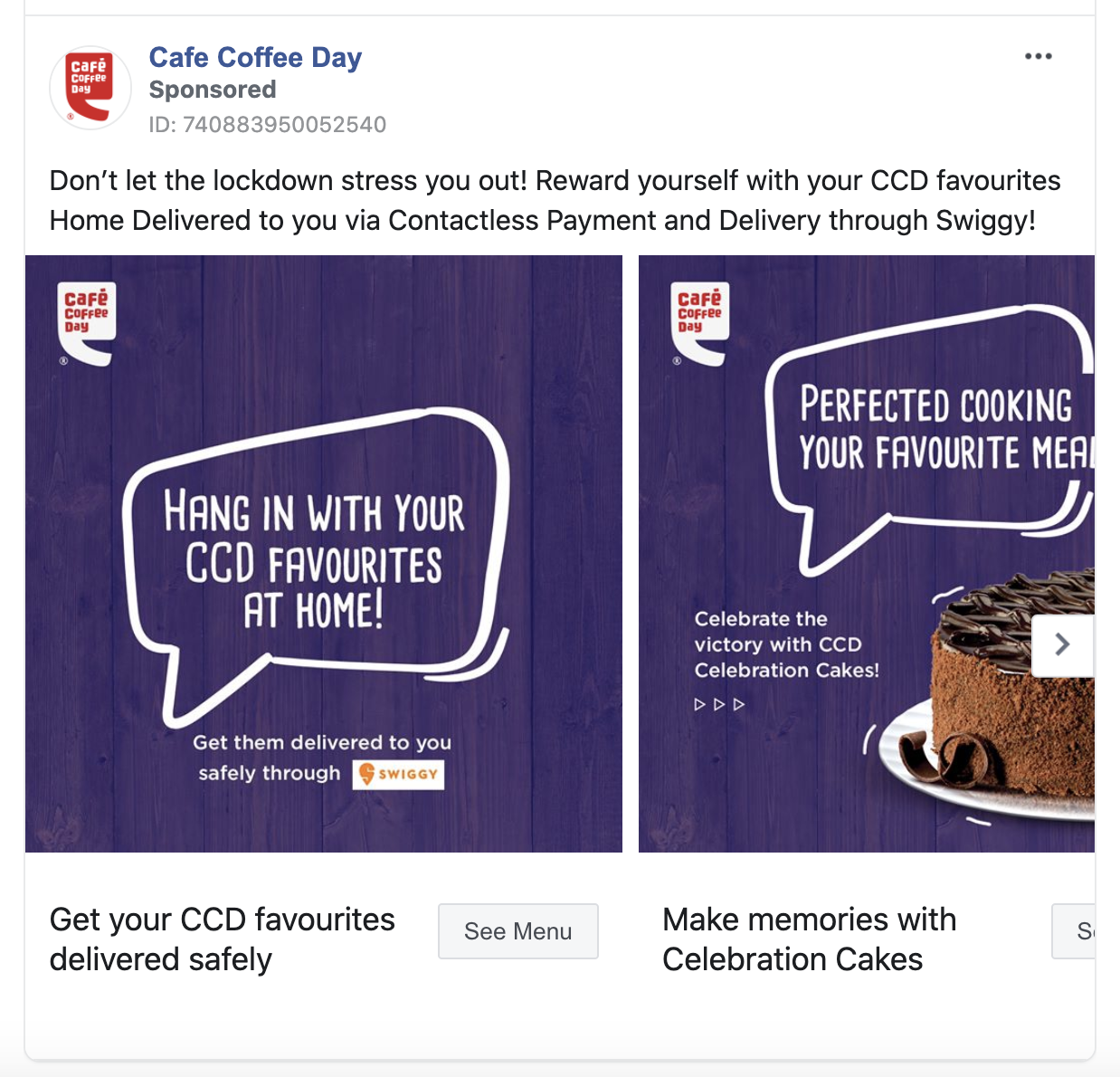
Analyzing successful advertising campaigns can provide valuable insights into the strategies and techniques that drive effective advertising. By examining case studies and identifying the key factors that contributed to their success, advertisers can gain actionable knowledge to enhance their own campaigns.
Key Factors Contributing to Successful Advertising Campaigns
- Clear Campaign Objectives: Defining specific and measurable campaign goals ensures that all efforts are aligned towards achieving desired outcomes.
- Target Audience Understanding: Thorough research and segmentation of the target audience allows advertisers to tailor messages that resonate with their specific needs and interests.
- Creative and Engaging Content: Memorable and impactful creative executions capture attention, evoke emotions, and drive engagement.
- Strategic Media Selection: Choosing the right advertising channels and platforms to reach the target audience at the right time and place.
- Effective Measurement and Evaluation: Tracking key metrics and analyzing campaign performance enables advertisers to measure ROI and optimize future campaigns.
Ad Best Practices
To craft impactful advertising campaigns, industry best practices serve as a valuable guide. These practices encompass various aspects, including target audience identification, goal setting, compelling copywriting, high-quality visuals, and performance tracking.
Optimizing ad performance across channels requires a tailored approach. Search engine marketing (SEM) benefits from -rich content and targeted campaigns. Social media marketing leverages engaging visuals and community building. Display advertising relies on visually appealing creatives and strategic placements. Email marketing fosters personalized communication and targeted messaging.
A/B Testing
A/B testing is crucial for refining ad performance. By comparing different versions of an ad, marketers can determine which elements resonate best with the target audience. This iterative approach leads to data-driven optimizations and improved campaign outcomes.
Emerging Trends in Advertising
The advertising landscape is constantly evolving, with new trends emerging to meet changing consumer behaviors and technological advancements.
Programmatic Advertising
Programmatic advertising automates the buying and selling of ad space using real-time bidding. It enables precise targeting, optimization, and increased efficiency.
Influencer Marketing
Influencer marketing leverages the credibility and reach of individuals with established followings to promote products or services. It fosters authentic connections and drives engagement.
Native Advertising
Native advertising seamlessly integrates ads into the surrounding content, creating a less intrusive and more engaging experience for users.
Ad Attribution
Ad attribution is the process of determining which marketing touchpoints contributed to a conversion. It’s crucial for measuring campaign effectiveness and optimizing future efforts.
Different attribution models assign varying degrees of credit to each touchpoint based on its position in the customer journey. Common models include:
Single-Touch Attribution
- First-click attribution: Credits the first touchpoint the customer interacted with.
- Last-click attribution: Credits the last touchpoint before the conversion.
Multi-Touch Attribution
- Linear attribution: Distributes credit equally across all touchpoints.
- Time-decay attribution: Gives more weight to touchpoints closer to the conversion.
- Position-based attribution: Gives more credit to first and last touchpoints.
Ad Fraud and Prevention
Ad fraud is a significant issue that costs advertisers billions of dollars annually. Fraudsters use sophisticated techniques to manipulate ad systems and generate fake impressions, clicks, and conversions. This can lead to wasted ad spend and inaccurate campaign performance data.
Types of Ad Fraud
- Click fraud: Fraudsters generate fake clicks on ads using bots or human farms.
- Impression fraud: Fraudsters artificially inflate the number of ad impressions by displaying ads in hidden or non-viewable areas.
- Domain spoofing: Fraudsters create fake websites that mimic legitimate advertising platforms to trick advertisers into placing ads on their sites.
- Ad stacking: Fraudsters stack multiple ads on top of each other, making it difficult for users to see the real ad.
Strategies for Detecting and Preventing Ad Fraud
- Use fraud detection tools: Machine learning algorithms can analyze ad data to identify suspicious patterns and flag fraudulent activity.
- Partner with third-party vendors: Specialized vendors provide fraud detection and prevention services that can complement in-house efforts.
- Implement whitelisting and blacklisting: Create lists of trusted and untrusted websites, publishers, and devices to control where ads are displayed.
- Monitor campaign performance: Regularly review campaign metrics to identify anomalies that may indicate fraud.
Industry Regulations and Self-Regulation
Industry organizations and government agencies have implemented regulations and self-regulation initiatives to combat ad fraud. These include:
- The Digital Advertising Alliance (DAA): Establishes industry standards for ad fraud detection and prevention.
- The Better Business Bureau (BBB): Provides resources and guidance to advertisers on how to avoid ad fraud.
- The Federal Trade Commission (FTC): Enforces laws against deceptive advertising practices, including ad fraud.
Recommendations for Advertisers
- Educate yourself about ad fraud: Understand the different types of fraud and how to detect it.
- Use reputable ad networks and publishers: Partner with companies that have a proven track record of combating fraud.
- Monitor your campaigns closely: Regularly review campaign performance data to identify suspicious activity.
- Report fraudulent activity: Notify ad networks, publishers, and relevant authorities if you suspect fraud.
Future Trends in Ad Fraud
Ad fraud is constantly evolving, with fraudsters developing new techniques to evade detection. Future trends in ad fraud include:
- Increased use of artificial intelligence (AI): Fraudsters will use AI to generate fake ad traffic and mimic human behavior.
- Targeting of mobile advertising: Fraudsters will focus on mobile advertising, as it is a growing and lucrative market.
- Emergence of new ad fraud schemes: Fraudsters will continue to develop new and innovative ways to manipulate ad systems.
Ad Formats and Examples
The world of advertising is a diverse and ever-evolving landscape, with a myriad of formats to choose from. From captivating display ads to engaging video ads, from targeted social media ads to seamlessly integrated native advertising, each format offers unique advantages and opportunities for advertisers.
In this section, we’ll delve into the various ad formats, exploring their characteristics, benefits, and effectiveness. We’ll also showcase examples of successful ads in each format, providing real-world insights into how these formats can drive results.
Display Ads
Display ads are a staple of online advertising, appearing on websites, apps, and social media platforms. These ads come in a variety of sizes and shapes, from the classic banner ad to the more immersive skyscraper ad. Display ads can be static or animated, and can include text, images, and videos.
- Example: A banner ad on a news website promoting a new product launch.
- Example: A skyscraper ad on a social media platform featuring a visually stunning image of a new fashion collection.
Video Ads
Video ads have become increasingly popular in recent years, as they offer a more engaging and immersive experience for viewers. These ads can be played before, during, or after video content, and can range from short, snappy commercials to longer, more in-depth product demonstrations.
- Example: A pre-roll ad on YouTube promoting a new movie trailer.
- Example: A mid-roll ad on a streaming service featuring a behind-the-scenes look at the making of a popular TV show.
Social Media Ads
Social media ads allow businesses to target their audience on specific social media platforms, such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. These ads can be tailored to specific demographics, interests, and behaviors, making them a highly effective way to reach potential customers.
- Example: A sponsored post on Facebook promoting a new product launch, targeted to people who have expressed an interest in similar products.
- Example: A carousel ad on Instagram showcasing a range of products from a new clothing line, targeted to people who follow fashion influencers.
Native Advertising
Native advertising is a type of advertising that is designed to blend seamlessly into the surrounding content. These ads appear in the same format as the surrounding content, such as articles, blog posts, or social media updates, but are clearly labeled as sponsored or promoted content.
- Example: A sponsored article on a news website promoting a new travel destination, written in the same style as the surrounding articles.
- Example: A promoted tweet on Twitter featuring a thought leadership piece from an industry expert, clearly labeled as “Promoted Content.”
Closure: Ad

As you delve into the world of Ad, remember that the key to success lies in understanding your audience, crafting compelling messages, and leveraging the power of data to optimize your campaigns. Embrace the transformative power of Ad and unlock the potential for growth, brand recognition, and customer engagement.