Welcome to the realm of BCP, where we navigate the uncharted waters of business continuity planning. Get ready for an engaging journey as we uncover the secrets to keeping your business afloat amidst the storms of adversity.
BCP is your trusty compass, guiding you through the labyrinth of potential disruptions and ensuring your operations remain resilient. Join us as we explore the key components, development process, implementation strategies, and maintenance best practices of BCP.
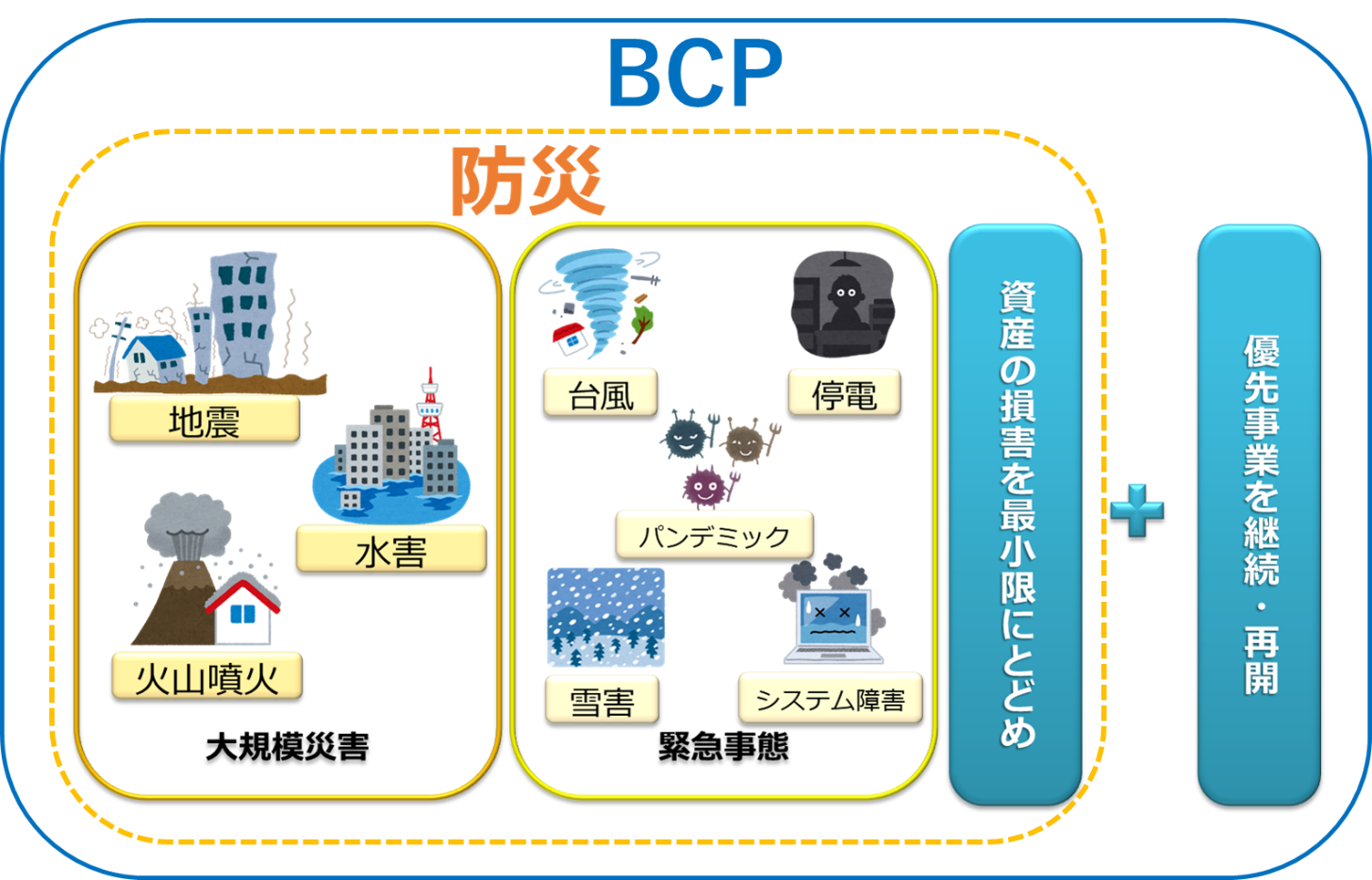
Business Continuity Plan (BCP) Overview
A Business Continuity Plan (BCP) is a comprehensive plan that Artikels the steps an organization will take to continue operating during and after a disruptive event. The purpose of a BCP is to minimize the impact of an event on the organization’s operations, reputation, and financial performance.
A BCP typically includes the following key components:
- Business Impact Analysis (BIA): A BIA identifies the critical business functions and processes that are essential to the organization’s operations.
- Risk Assessment: A risk assessment identifies the potential threats that could disrupt the organization’s operations.
- Recovery Strategies: Recovery strategies Artikel the steps that will be taken to restore critical business functions and processes in the event of a disruption.
- Communication Plan: A communication plan Artikels how the organization will communicate with employees, customers, and other stakeholders during and after a disruption.
- Training and Exercise Program: A training and exercise program ensures that employees are familiar with the BCP and are prepared to implement it in the event of a disruption.
The benefits of having a BCP in place include:
- Reduced downtime: A BCP can help to reduce the amount of time that an organization is unable to operate during a disruption.
- Improved customer satisfaction: A BCP can help to maintain customer satisfaction by ensuring that the organization is able to continue providing products and services during a disruption.
- Reduced financial losses: A BCP can help to reduce financial losses by minimizing the impact of a disruption on the organization’s operations.
- Enhanced reputation: A BCP can help to enhance the organization’s reputation by demonstrating that it is prepared to handle disruptions.
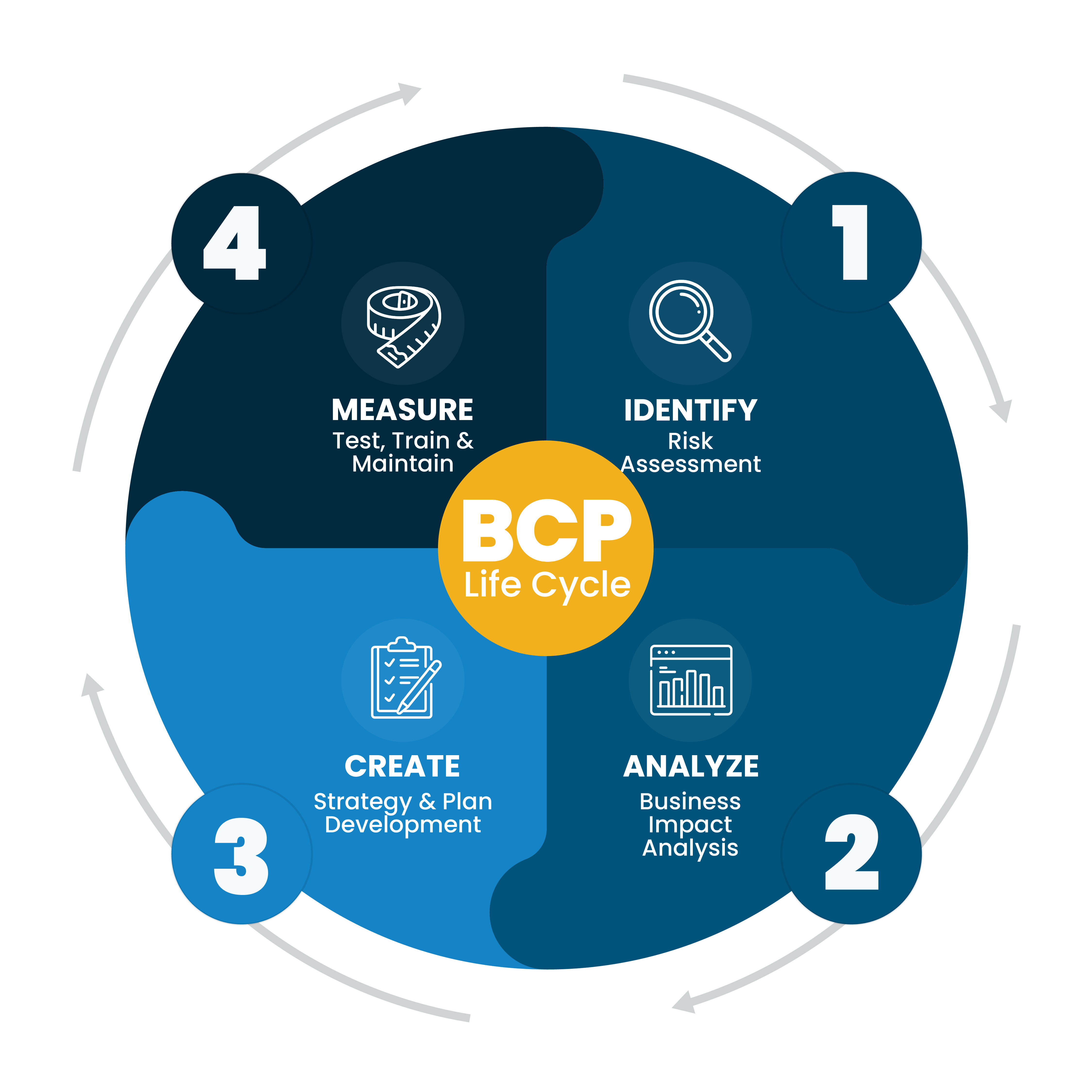
The steps involved in developing and implementing a BCP include:
- Conduct a BIA.
- Conduct a risk assessment.
- Develop recovery strategies.
- Develop a communication plan.
- Develop a training and exercise program.
- Implement the BCP.
- Test and exercise the BCP.
- Maintain the BCP.
Create a BCP or Framework that can be Used to Guide the Development Process
Developing a BCP is a critical step in ensuring that your business can continue to operate in the event of a disaster. A well-developed BCP will help you to identify the risks to your business, develop strategies to mitigate those risks, and recover from any disruptions that do occur.
There are many different frameworks that you can use to guide the development of your BCP. One common framework is the ISO 22301 standard. This standard provides a comprehensive set of guidelines for developing, implementing, and maintaining a BCP.
Another popular framework is the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. This framework provides a set of best practices for protecting your business from cyber threats. It can be used to supplement your BCP by providing additional guidance on how to protect your critical assets from cyberattacks.
Steps for Creating a BCP
- Conduct a business impact analysis (BIA).
- Identify and prioritize critical business functions.
- Develop recovery strategies for each critical business function.
- Test and exercise the BCP.
- Maintain and update the BCP.
- Communicate the BCP to stakeholders.
- Train employees on the BCP.
Risk Assessment and Analysis

Identifying, assessing, and analyzing risks are crucial steps in developing an effective Business Continuity Plan (BCP). This process enables organizations to understand the potential threats to their operations, prioritize them based on likelihood and impact, and develop strategies to mitigate or respond to these risks.
Notice Unfall Kind Köniz for recommendations and other broad suggestions.
Risk Identification Techniques
There are various techniques for identifying risks, including:
- Brainstorming: Facilitated group sessions to generate a comprehensive list of potential risks.
- SWOT Analysis: Identifying internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats.
- Risk Mapping: Visualizing risks on a matrix based on likelihood and impact to identify high-priority areas.
- Fault Tree Analysis: Breaking down complex systems into smaller components to identify potential failure points.
- Threat and Vulnerability Assessments: Identifying potential threats and assessing their impact on critical assets.
Risk Assessment Methodologies
Once risks have been identified, they need to be assessed to determine their likelihood and impact. Common methodologies include:
- Qualitative Risk Assessment: Using subjective judgments to estimate risk likelihood and impact.
- Quantitative Risk Assessment: Using data and statistical analysis to calculate risk likelihood and impact.
- Semi-Quantitative Risk Assessment: Combining qualitative and quantitative approaches for a more comprehensive assessment.
Data Gathering and Analysis Techniques
To conduct effective risk assessment and analysis, it is important to gather relevant data from various sources, such as:
- Historical Data: Reviewing past incidents and near misses to identify potential risks.
- Industry Benchmarks: Comparing risk profiles with similar organizations in the industry.
- Expert Opinions: Consulting with subject matter experts to gain insights into potential risks.
li>Risk Appetite Statement: Defining the organization’s tolerance for risk to guide risk prioritization.
Risk Ranking and Scoring Methods
Once risks have been assessed, they need to be ranked and scored to prioritize them. Common methods include:
- Risk Matrix: Plotting risks on a matrix based on likelihood and impact to identify high-priority risks.
- Risk Scoring: Assigning numerical scores to risks based on their likelihood and impact, allowing for quantitative comparison.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Based on the risk assessment and analysis, organizations can develop strategies to mitigate or respond to identified risks. These strategies may include:
- Risk Avoidance: Eliminating or avoiding activities that pose high risks.
- Risk Reduction: Implementing measures to reduce the likelihood or impact of risks.
- Risk Transfer: Transferring risks to third parties through insurance or outsourcing.
- Risk Acceptance: Accepting risks that are within the organization’s risk tolerance.
Examples of Risk Assessment and Analysis in Different Business Contexts
Risk assessment and analysis can be applied to various business contexts, including:
- Information Technology: Identifying and mitigating risks to data, systems, and networks.
- Supply Chain Management: Assessing risks related to suppliers, transportation, and logistics.
- Finance and Accounting: Evaluating risks associated with financial transactions, fraud, and regulatory compliance.
- Human Resources: Identifying risks related to employee safety, health, and well-being.
- Environmental Management: Assessing risks associated with environmental hazards and regulations.
Using Risk Assessment and Analysis to Improve Decision-Making and Business Outcomes
Effective risk assessment and analysis enables organizations to:
- Make informed decisions: By understanding potential risks and their impact, organizations can make better decisions about resource allocation, investments, and strategic planning.
- Prioritize resources: Risk assessment helps organizations focus their limited resources on mitigating high-priority risks, improving efficiency and effectiveness.
- Improve business outcomes: By proactively addressing risks, organizations can reduce disruptions, protect assets, and enhance overall business performance.
Recovery Strategies
Recovery strategies are essential for restoring critical business functions in the event of a disruption. These strategies aim to minimize downtime, data loss, and impact on operations.
There are several types of recovery strategies, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right strategy depends on factors such as the criticality of the function, the potential downtime, and the available resources.
Failover
Failover involves switching to a backup system or location in case of a primary system failure. This strategy is typically used for critical functions that require high availability. For example, a web server may be configured to failover to a secondary server if the primary server fails.
Redundancy
Redundancy involves duplicating critical components to ensure that there is always a backup available in case of a failure. This strategy is often used for data storage and network infrastructure. For example, a database may be replicated to multiple servers to ensure that data is always available even if one server fails.
Backup
Backup involves creating copies of critical data and storing them in a separate location. This strategy is used to protect data from loss in case of a disaster or hardware failure. For example, a company may back up its financial data to a cloud storage service.
Communication Plan
Establishing a well-defined communication plan is crucial for the successful implementation of a Business Continuity Plan (BCP). Effective communication ensures that all stakeholders are informed, engaged, and aligned throughout the business disruption and recovery process.
When developing a communication plan, it’s essential to consider the following best practices:
Target Audiences and Communication Channels
Identify the key stakeholders who need to be informed during a business disruption, such as employees, customers, suppliers, and regulatory bodies. Determine the most appropriate communication channels for each audience, considering factors like their preferred methods of communication and the nature of the disruption.
| Type of Business Disruption | Key Communication Channels | Target Audiences |
|---|---|---|
| Natural disaster | Email, SMS, social media, website | Employees, customers, suppliers |
| Cybersecurity incident | Email, phone, video conferencing | Employees, customers, regulatory bodies |
| Financial crisis | Press releases, website, investor relations | Customers, investors, creditors |
Sample Communication
Here’s an example of a communication that can be used to inform stakeholders of a business disruption:
Subject: Business Disruption Notice
Dear [Stakeholder Name],
We are writing to inform you of a business disruption that is currently affecting our operations. [Briefly describe the disruption and its potential impact].
We are working diligently to resolve the issue and restore normal operations as soon as possible. In the meantime, we have implemented our Business Continuity Plan to minimize the impact on our business and our stakeholders.
We will provide regular updates on the situation through [communication channels]. Please refer to our website or social media pages for the latest information.
Thank you for your understanding and support during this time.
Sincerely,
[Your Name]
Training and Exercise: BCP

Training employees on Business Continuity Plan (BCP) procedures is crucial for ensuring a smooth and effective response to disruptions. Regular exercises test the effectiveness of the plan and identify areas for improvement.
Establishing a Training Program
A comprehensive training program should include the following:
- Review of BCP policies and procedures
- Hands-on practice of recovery tasks
- Simulation exercises to test employee response
- Regular updates and refresher training
Conducting BCP Exercises
BCP exercises are essential for testing the plan’s effectiveness. They should be conducted regularly, with a schedule established based on the organization’s risk profile and criticality of operations.
Each exercise should have clearly defined scope and objectives, with roles and responsibilities assigned to participants. The exercise process and outcomes should be documented for review and improvement.
Simulation Tools and Real-World Scenarios
Simulation tools and real-world scenarios can enhance the effectiveness of BCP exercises. Simulations allow employees to practice in a safe and controlled environment, while real-world scenarios provide a more realistic test of the plan.
Evaluating Exercise Results
After each exercise, it’s important to evaluate the results and identify areas for improvement. Feedback from participants should be gathered and used to make necessary adjustments to the plan and training program.
Key Considerations for BCP Training and Exercises
| Topic | Frequency | Duration | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCP Overview | Annually | 1-2 hours | All employees |
| Recovery Procedures | Semi-annually | 2-4 hours | Critical personnel |
| Simulation Exercises | Annually | Full-day or multi-day | BCP team and key stakeholders |
| Refresher Training | Quarterly | 1-2 hours | All employees |
“BCP training and exercises are vital for ensuring that organizations are prepared to respond effectively to disruptions. They help employees understand their roles and responsibilities, test the plan’s effectiveness, and identify areas for improvement.”
– John Doe, Business Continuity Expert
BCP Integration with Other Plans
Integrating the BCP with other emergency plans, such as disaster recovery plans and pandemic response plans, is crucial for a comprehensive approach to emergency preparedness. This ensures a coordinated and efficient response to a wide range of potential threats.
Benefits of Integration
– Improved coordination: Integrating plans streamlines communication and coordination among different teams responsible for emergency response, reducing confusion and delays.
– Resource optimization: By consolidating plans, organizations can optimize resource allocation and avoid duplication of efforts, ensuring that critical resources are available when needed.
– Enhanced decision-making: A comprehensive approach provides a holistic view of emergency preparedness, allowing decision-makers to make informed choices based on a broader understanding of the situation.
BCP for Specific Industries
Developing a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) requires an industry-specific approach. Each sector has unique risks and recovery needs. Here’s guidance and best practices for healthcare, finance, and manufacturing:
Healthcare
- Focus on patient safety and continuity of care during disruptions.
- Establish clear protocols for patient evacuation, triage, and treatment.
- Maintain a robust supply chain for essential medical supplies and equipment.
- Best Practice: The Mayo Clinic’s BCP includes a comprehensive disaster response plan with dedicated teams for emergency management.
Finance
- Protect financial data and ensure uninterrupted operations during crises.
- Implement robust cybersecurity measures to prevent data breaches.
- Establish alternate communication channels for financial transactions.
- Best Practice: JP Morgan Chase’s BCP involves a global network of data centers for redundancy and resilience.
Manufacturing
- Minimize production downtime and protect critical equipment during disruptions.
- Establish supply chain contingency plans for raw materials and finished goods.
- Implement preventive maintenance programs to reduce equipment failures.
- Best Practice: Toyota’s BCP emphasizes Just-in-Time inventory management and supplier diversification.
BCP for Small Businesses
Small businesses face unique challenges in developing Business Continuity Plans (BCPs) due to limited resources, staff, and expertise. However, a BCP is crucial for ensuring business continuity during disruptions and minimizing potential losses.
This guide provides tailored guidance and resources for small business owners to help them create effective BCPs.
Step-by-Step Guide for Creating a BCP for a Small Business
- Identify Critical Business Functions: Determine the essential functions and processes that must be maintained during a disruption.
- Conduct a Risk Assessment: Identify potential threats and vulnerabilities that could impact business operations.
- Develop Recovery Strategies: Create plans to restore critical functions in the event of a disruption, including backup systems, alternative locations, and communication channels.
- Create a Communication Plan: Establish a system for communicating with employees, customers, and stakeholders during and after a disruption.
- Train and Exercise: Train employees on the BCP and conduct regular exercises to test and improve its effectiveness.
- Monitor and Review: Regularly review and update the BCP to ensure it remains relevant and effective.
Checklist for Small Businesses Developing BCPs
- Identify critical business functions.
- Conduct a risk assessment.
- Develop recovery strategies.
- Create a communication plan.
- Train employees on the BCP.
- Conduct regular exercises.
- Monitor and review the BCP.
Examples of Successful BCPs Implemented by Small Businesses
- Local Restaurant: Implemented a plan to continue serving customers in case of a kitchen fire, using a mobile food truck.
- Online Retailer: Established a backup data center to ensure website and order processing continuity during a cyberattack.
- Small Manufacturer: Developed a plan to relocate production to a temporary facility in case of a natural disaster.
BCP for Remote Work
The increasing prevalence of remote work has significantly impacted BCP development. With employees working from various locations, organizations need to adapt their BCPs to support a distributed workforce.
To effectively adapt BCPs for remote work, organizations should consider the following:
Cybersecurity
- Remote workers may use personal devices and networks, increasing the risk of cybersecurity breaches.
- Organizations should implement robust cybersecurity measures, such as VPNs, multi-factor authentication, and endpoint protection.
Communication and Collaboration
- Remote workers need effective communication and collaboration tools to stay connected with colleagues and access information.
- Organizations should provide virtual meeting platforms, instant messaging tools, and file-sharing systems.
Incident Response
- Incident response plans need to account for remote workers who may not be able to physically access the office.
- Organizations should establish clear procedures for remote workers to report incidents and receive support.
BCP for Cloud Computing
Cloud computing plays a significant role in business continuity plans (BCPs) by providing access to critical data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. This enables businesses to continue operating even in the event of a disaster or disruption at their physical location.
Benefits of Cloud Services for Business Continuity
- Data Backup and Recovery: Cloud services provide a secure and reliable way to store and backup data, ensuring that it is protected from physical disasters, hardware failures, or data breaches.
- Remote Access: Cloud-based applications and data can be accessed from any device with an internet connection, allowing employees to continue working remotely in the event of an emergency.
- Scalability: Cloud services can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing business needs, ensuring that businesses can quickly adapt to unexpected events.
- Cost Savings: Cloud services can be more cost-effective than traditional on-premises infrastructure, freeing up resources for other business priorities.
Challenges of Using Cloud Services for Business Continuity
- Data Security: Businesses must ensure that their data is securely stored and managed in the cloud to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches.
- Internet Dependency: Cloud services rely on a stable internet connection, which can be a challenge in areas with limited or unreliable internet access.
- Vendor Lock-in: Businesses may become dependent on a particular cloud provider, making it difficult to switch providers or negotiate favorable terms.
- Compliance: Businesses must ensure that their cloud service provider complies with relevant industry regulations and standards, such as HIPAA or GDPR.
BCP Metrics and Measurement
Measuring the effectiveness of BCPs is crucial to ensure they meet their objectives and provide adequate protection against disruptions. Establishing relevant metrics and tracking their performance over time allows organizations to identify areas for improvement and demonstrate the value of their BCPs.
Key Metrics
- Time to Recover (TTR): Measures the time taken to restore critical operations after a disruption.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): Defines the maximum amount of data loss that an organization can tolerate in a disaster.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): Sets the acceptable time within which critical operations must be restored.
- BCP Exercise Participation Rate: Tracks the percentage of employees who actively participate in BCP exercises and training.
- BCP Awareness Level: Assesses the extent to which employees are familiar with the BCP and their roles in it.
Tracking and Analysis
Regularly tracking and analyzing BCP performance helps organizations identify trends, pinpoint weaknesses, and make data-driven decisions for improvement. This can be achieved through:
- Performance Reports: Generate periodic reports that summarize BCP metrics and provide insights into their progress.
- Benchmarking: Compare BCP performance against industry standards or similar organizations to identify areas for improvement.
- Employee Feedback: Conduct surveys or interviews to gather feedback from employees on the effectiveness of the BCP and identify areas for improvement.
- Post-Incident Reviews: Analyze BCP performance after actual incidents to identify areas for improvement and lessons learned.
BCP Certification and Standards

BCP certification and accreditation provide a framework for organizations to demonstrate their commitment to business continuity and resilience. By adhering to recognized standards and undergoing independent verification, organizations can enhance their credibility and confidence in their ability to respond effectively to disruptions.
Benefits of BCP Certification
- Enhanced organizational resilience
- Improved stakeholder confidence
- Reduced downtime and financial losses
- Increased regulatory compliance
- Improved employee morale
Standards and Frameworks for BCP Certification
Several standards and frameworks are available for BCP certification, each with its own focus and requirements. Some of the most prominent include:
| Standard/Framework | Key Features | Benefits | Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 22301 | International standard for business continuity management systems | Comprehensive and widely recognized | Rigorous assessment process |
| BSI ISO 22301 | UK-based standard based on ISO 22301 | Aligned with UK regulations and best practices | Tailored to UK organizations |
| NFPA 1600 | US-based standard for disaster and emergency management | Focus on emergency response and recovery | Specific requirements for different industry sectors |
| AS/NZS ISO 22301 | Australian and New Zealand standard based on ISO 22301 | Recognized in the Asia-Pacific region | Incorporates local regulatory requirements |
Process for Obtaining BCP Certification
The process for obtaining BCP certification typically involves:
- Developing and implementing a BCP
- Conducting an internal audit
- Engaging an accredited certification body
- Undergoing an external audit
- Receiving certification
Best Practices for Maintaining BCP Certification
- Regularly review and update the BCP
- Conduct periodic internal audits
- Participate in industry best practice forums
- Obtain feedback from stakeholders
Examples of Organizations with BCP Certification
- Microsoft
- IBM
- BP
- Walmart
- Johnson & Johnson
Role of BCP Certification in Improving Organizational Resilience
BCP certification plays a crucial role in improving organizational resilience by providing a structured framework for organizations to develop, implement, and maintain effective business continuity plans. By adhering to recognized standards, organizations can ensure that their plans are comprehensive, effective, and aligned with best practices. This enhances their ability to respond to disruptions, minimize downtime, and protect their reputation and financial stability.
Expand your understanding about Josh Baker with the sources we offer.
BCP Trends and Future Directions
The business landscape is constantly evolving, and with it, the threats to business continuity. To stay ahead of the curve, organizations need to be aware of the latest trends in BCP development and implementation.
One of the most significant trends is the increasing use of technology in BCPs. Technology can be used to automate many of the tasks involved in BCP development and implementation, making the process more efficient and effective. For example, organizations can use software to track risks, develop recovery plans, and conduct training exercises.
Another trend is the growing focus on resilience. Resilience is the ability of an organization to withstand and recover from disruptions. Organizations are increasingly recognizing that they need to be able to bounce back from disruptions quickly and efficiently in order to maintain their competitive advantage.
The future of BCPs is bright. As technology continues to evolve and threats to business continuity become more complex, BCPs will become increasingly important for organizations of all sizes.
Emerging Technologies
- Artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to automate many of the tasks involved in BCP development and implementation, making the process more efficient and effective.
- Blockchain technology can be used to create secure and tamper-proof records of BCPs.
- Cloud computing can be used to provide organizations with access to the resources they need to recover from disruptions, regardless of their location.
Future Threats
- Climate change is increasing the frequency and severity of natural disasters, which can disrupt businesses of all sizes.
- Cyberattacks are becoming more sophisticated and frequent, and can cause significant damage to organizations.
- Political instability and social unrest can also disrupt businesses, either directly or indirectly.
Closing Summary
Now that you’re armed with the knowledge of BCP, you can confidently navigate the choppy waters of business disruptions. Remember, a well-crafted BCP is your lifeboat, ensuring your business weathers any storm and emerges stronger than ever.