Blank plant cell diagram embarks on a scientific odyssey, unraveling the intricate structure and function of plant cells, the foundation of life on Earth. Delve into the depths of this diagram, where each organelle plays a vital role in the symphony of life.
Plant cells, distinct from their animal counterparts, possess a unique array of organelles that orchestrate their growth, energy production, and the miraculous process of photosynthesis.
Plant Cell Structure
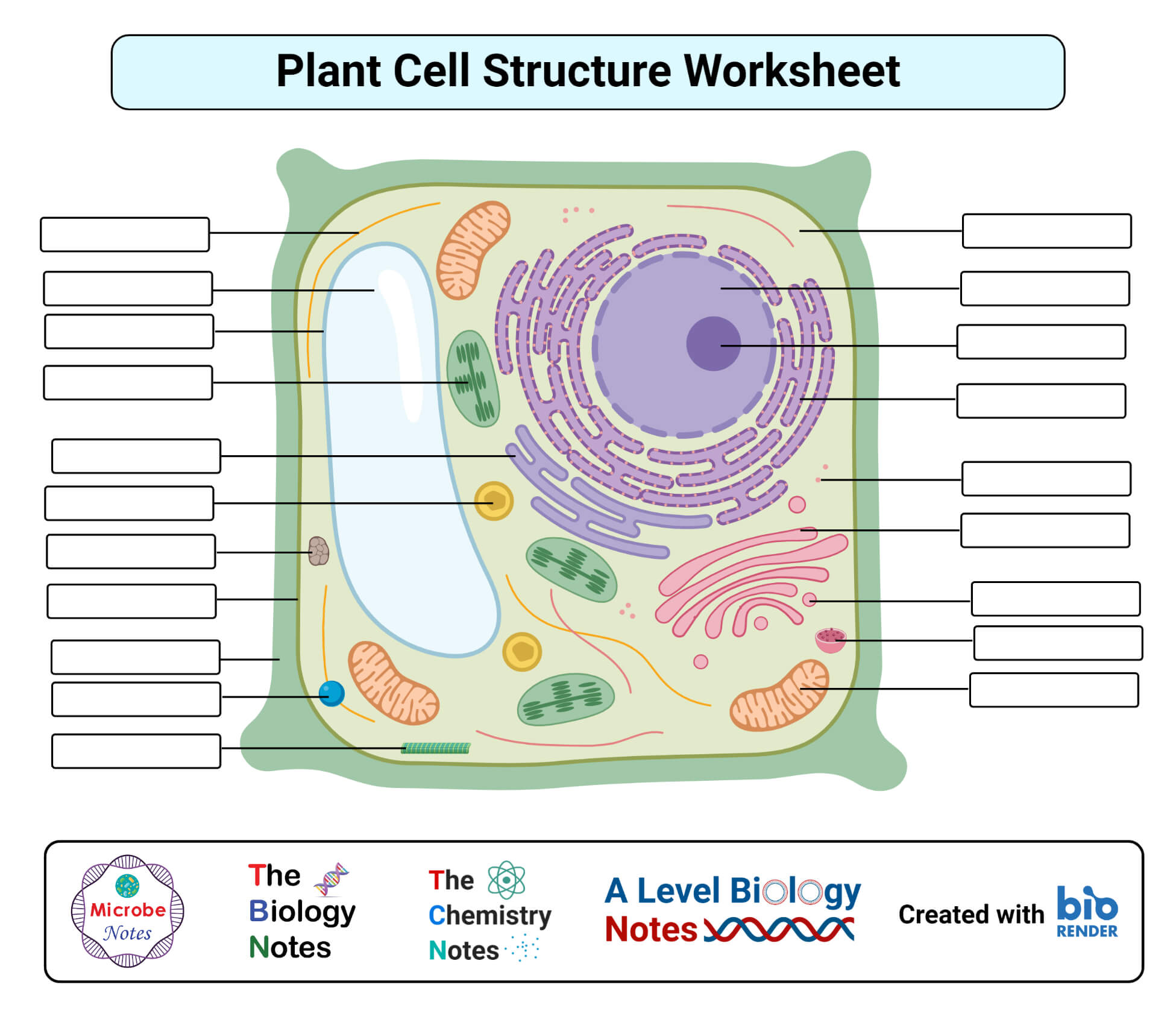
Plant cells are the basic unit of life for plants. They are similar to animal cells in many ways, but they also have some unique features that allow them to carry out photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create their own food.
Understanding the blank plant cell diagram is essential for studying plant biology. By studying the diagram, we can learn about the different parts of a plant cell and their functions. This knowledge can then be applied to understanding how plants grow and develop.
For example, by understanding the role of chloroplasts in photosynthesis, we can learn how plants convert sunlight into energy. This knowledge can then be used to design grandma’s garden planter that optimize plant growth and productivity. By understanding the blank plant cell diagram, we can gain a deeper understanding of the world around us and use that knowledge to improve our lives.
Cell Wall
One of the most distinctive features of plant cells is their cell wall. The cell wall is a rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support and protection. The cell wall is made up of cellulose, a tough carbohydrate that is also found in wood and paper.
A blank plant cell diagram can be useful for visualizing the different parts of a plant cell. For example, you could use it to label the cell wall, nucleus, chloroplasts, and vacuole. If you are looking for a good source of blank plant cell diagrams, you can find many free and printable options online.
You can also find more information about plant cells at drew planten raleigh nc . Plant cells are the basic unit of life for all plants. They are responsible for photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
Plant cells also contain DNA, which is the genetic material that determines the characteristics of the plant.
Chloroplasts
Another unique feature of plant cells is their chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are organelles that contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that absorbs sunlight. Chlorophyll is used to convert sunlight into energy that can be used by the cell to produce food.
In the realm of cellular biology, the blank plant cell diagram serves as a crucial tool for visualizing the intricate structures within plant cells. Understanding the organization of these organelles is essential for comprehending the fundamental processes that drive plant life.
One fascinating application of this knowledge lies in the development of agricultural machinery, such as the john deere corn planter . By mimicking the precision of plant cell division, this planter ensures optimal spacing and depth for corn seeds, maximizing yield and efficiency.
In turn, this advancement contributes to the larger field of plant science, where the blank plant cell diagram remains an indispensable tool for unraveling the mysteries of plant life.
Vacuole
Plant cells also have a large central vacuole. The vacuole is filled with water and helps to maintain the cell’s shape. The vacuole also stores nutrients and waste products.
Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells
Plant cells differ from animal cells in several ways. First, plant cells have a cell wall, while animal cells do not. Second, plant cells contain chloroplasts, while animal cells do not. Third, plant cells have a large central vacuole, while animal cells have many small vacuoles.
Cell Organelles: Blank Plant Cell Diagram

In addition to the plant cell’s basic structure, several specialized organelles perform specific functions essential for the cell’s survival and proper functioning.
Cell Wall
The cell wall is a rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support and protection to the plant cell. It is composed of cellulose, a strong and flexible carbohydrate.
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cytoplasm and regulates the passage of materials into and out of the cell.
Nucleus
The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that contains the cell’s genetic material, DNA. It is responsible for controlling cell growth, division, and protein synthesis.
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are green organelles that contain chlorophyll, a pigment that absorbs sunlight. They are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are bean-shaped organelles that are responsible for cellular respiration, the process by which cells convert glucose into energy.
Vacuoles, Blank plant cell diagram
Vacuoles are membrane-bound organelles that store water, nutrients, and waste products. They help maintain the cell’s water balance and provide support.
Cell Processes

Plant cells, the building blocks of plant life, carry out various intricate processes essential for their survival and growth. These processes include photosynthesis, energy production, and vacuole-mediated growth and development.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a vital process in plant cells that converts sunlight into chemical energy stored in glucose molecules. This process occurs within specialized organelles called chloroplasts, which contain the pigment chlorophyll.
During photosynthesis, chlorophyll molecules absorb light energy, which is used to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen atoms are then used to combine with carbon dioxide to form glucose, a sugar molecule that serves as the primary energy source for plants.
Energy Production in Mitochondria
Plant cells also contain mitochondria, organelles responsible for producing energy through cellular respiration. Cellular respiration involves the breakdown of glucose molecules in the presence of oxygen to produce ATP, the cell’s primary energy currency.
The process of cellular respiration occurs in three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm, while the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation occur within the mitochondria.
Vacuoles and Plant Cell Growth
Vacuoles are large, membrane-bound compartments found in plant cells. They play a crucial role in cell growth and development.
As plant cells grow, vacuoles expand and fill with water, creating turgor pressure against the cell wall. This turgor pressure provides structural support and rigidity to the plant, enabling it to stand upright and withstand external forces.