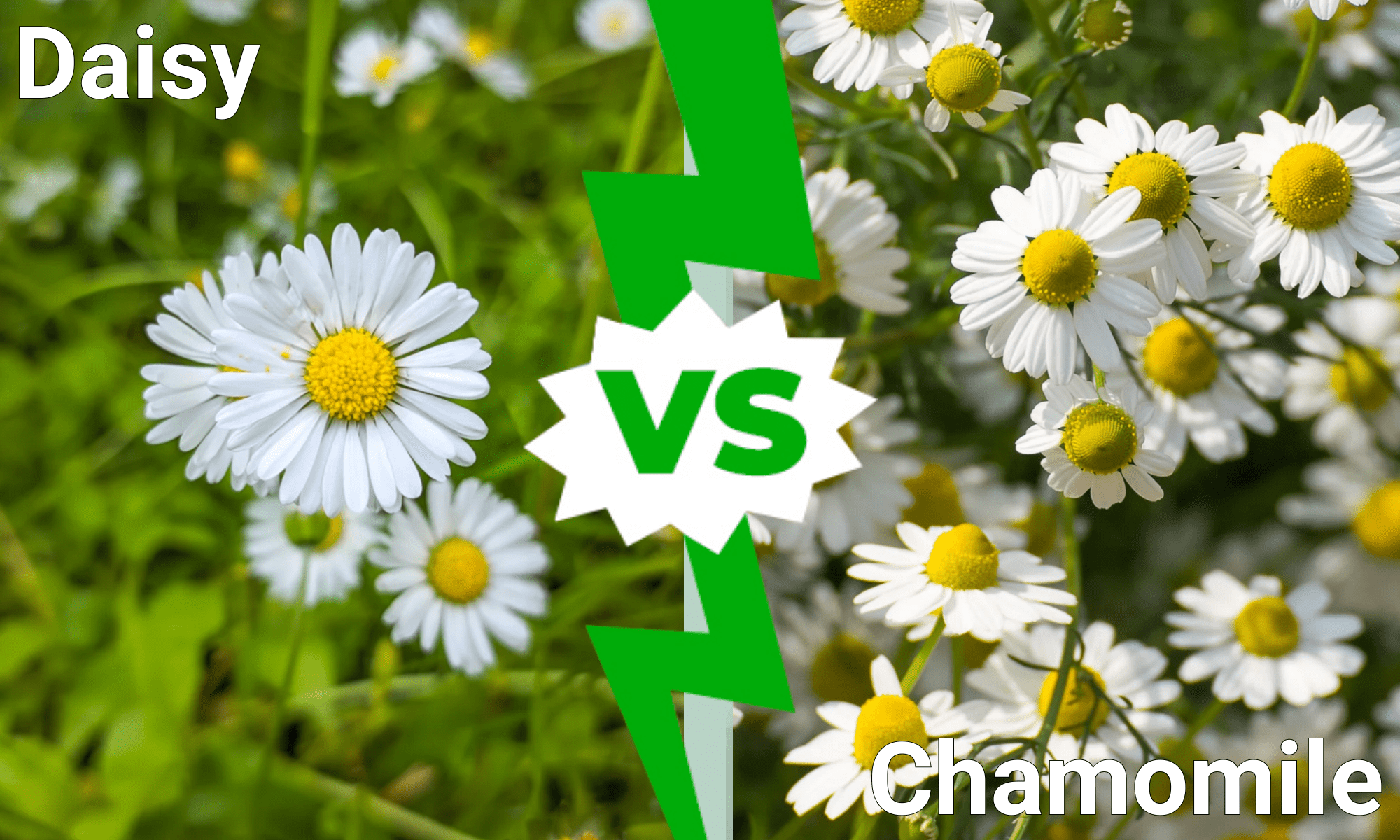
Chamomile plant vs daisy – In the realm of flora, chamomile plants and daisies share a striking resemblance, yet beneath their petals lie intriguing botanical distinctions and a wealth of medicinal properties. Embark on a journey to unravel the captivating tale of chamomile plant vs. daisy, where scientific facts intertwine with the healing power of nature.
As we delve into their taxonomic classification, we’ll uncover their unique scientific names, family lineage, and genus. A comparative table will showcase their contrasting physical attributes, from leaf shape to flower structure and root system, revealing the subtle nuances that set them apart.
Chamomile Plant vs. Daisy
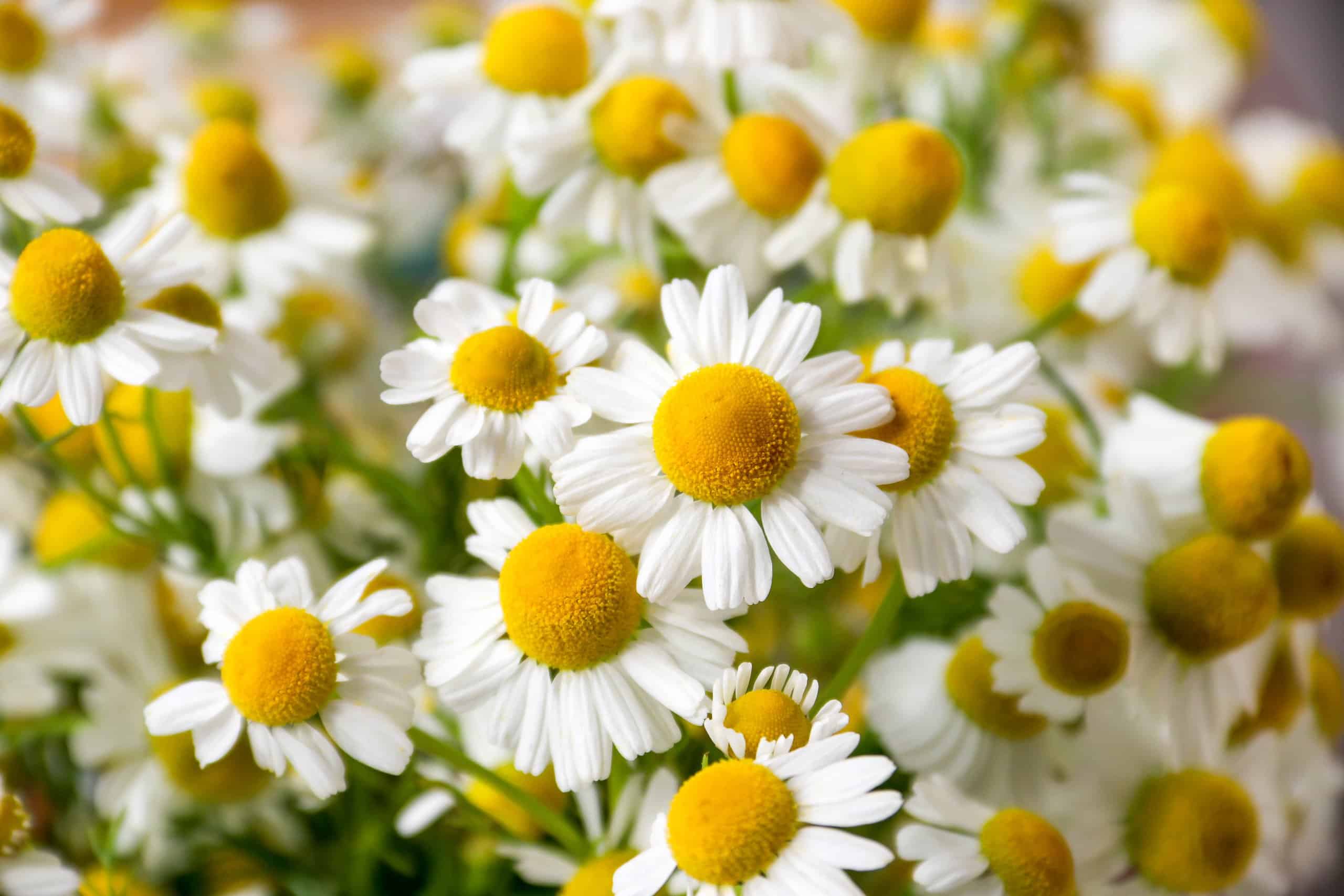

Botanical Differences
Chamomiles and daisies are both members of the Asteraceae family, which includes a wide range of flowering plants characterized by their composite flower heads. However, they belong to different genera, with chamomile belonging to the genus Matricaria and daisies belonging to the genus Bellis.
Chamomile and daisy, both members of the Asteraceae family, share a striking resemblance in their appearance. However, they differ significantly in their medicinal properties. While chamomile is widely known for its calming effects, daisy possesses antiseptic qualities. For those seeking to cultivate these charming blooms in their gardens, the rail planter box bracket provides an innovative solution.
Its sturdy design offers ample support for planter boxes, allowing for optimal growth and showcasing the delicate beauty of chamomile and daisy alike.
| Characteristic | Chamomile | Daisy |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific name | Matricaria recutita | Bellis perennis |
| Family | Asteraceae | Asteraceae |
| Genus | Matricaria | Bellis |
In terms of their physical characteristics, chamomile and daisies can be distinguished by their leaf shape, flower structure, and root system. Chamomile plants have feathery, deeply divided leaves, while daisies have simple, oval-shaped leaves. Chamomile flowers are typically white with a yellow center, while daisy flowers can vary in color from white to pink or purple and have a yellow or orange center. Additionally, chamomile plants have a taproot system, while daisies have a fibrous root system.
Medicinal Properties and Uses
Chamomile and daisies, despite their delicate appearances, possess a wealth of medicinal properties that have been recognized for centuries. Traditional herbalists have long valued these plants for their calming, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial effects. Modern research has corroborated these traditional uses, revealing a diverse array of active compounds responsible for their therapeutic benefits.
Active Compounds and Pharmacological Effects
The medicinal properties of chamomile and daisies stem from their unique chemical compositions. Chamomile contains several active compounds, including flavonoids, terpenoids, and essential oils. The primary flavonoid, apigenin, is believed to be responsible for its sedative and anxiolytic effects. The essential oil, bisabolol, exhibits anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties.
Daisies, on the other hand, contain a range of compounds, including polyphenols, saponins, and essential oils. The polyphenols, such as chlorogenic acid, have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. The essential oil, matricin, has been shown to inhibit the growth of certain bacteria and fungi.
| Chamomile | Daisies | |
|---|---|---|
| Active Compounds | Flavonoids (apigenin) Terpenoids Essential oils (bisabolol) |
Polyphenols (chlorogenic acid) Saponins Essential oils (matricin) |
| Pharmacological Effects | Sedative Anxiolytic Anti-inflammatory Antimicrobial |
Antioxidant Anti-inflammatory Antibacterial Antifungal |
Therapeutic Applications
The medicinal properties of chamomile and daisies have led to their incorporation into various herbal remedies, teas, and supplements. Chamomile is commonly used to treat insomnia, anxiety, and digestive issues. It is also used topically to soothe skin irritations and promote wound healing.
Daisies are traditionally used to treat skin conditions, such as eczema and psoriasis. They are also used as a diuretic and to reduce inflammation.
“Chamomile tea has been shown to improve sleep quality and reduce anxiety levels in clinical trials.”
“Daisy extracts have been incorporated into skincare products for their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.”
Cultivation and Propagation: Chamomile Plant Vs Daisy

Chamomile and daisies are both relatively easy to grow and can be cultivated in a variety of climates. They prefer well-drained soil that is rich in organic matter and full sun to partial shade. Chamomile plants grow best in slightly acidic soil, while daisies prefer neutral to slightly alkaline soil.
Propagation, Chamomile plant vs daisy
Both chamomile and daisies can be propagated by seed, division, or cuttings.
Seed Sowing
Chamomile seeds should be sown in the spring after the last frost. Daisy seeds can be sown in the spring or fall. The seeds should be sown thinly and covered with a thin layer of soil. Keep the soil moist and warm until the seeds germinate.
Division
Chamomile and daisies can be divided in the spring or fall. To divide a plant, dig it up and carefully divide the roots into several smaller plants. Replant the divisions in well-drained soil and water them well.
Cuttings
Chamomile and daisies can also be propagated by cuttings. To take a cutting, cut a 4- to 6-inch stem from a healthy plant. Remove the leaves from the bottom of the stem and dip the end in rooting hormone. Plant the cutting in a pot filled with well-drained potting mix. Keep the potting mix moist and warm until the cutting roots.
Planting and Care
Once you have propagated your chamomile or daisy plants, you can plant them in your garden. Space the plants 12 to 18 inches apart. Water the plants regularly, especially during hot weather. Fertilize the plants monthly with a balanced fertilizer.
Chamomile and daisies are both relatively low-maintenance plants. However, they may be susceptible to pests and diseases. Common pests include aphids, spider mites, and whiteflies. Common diseases include powdery mildew, rust, and botrytis.

Chamomile plants and daisies share similar daisy-like flowers, but they are distinct species. Chamomile has feathery leaves and daisy has spoon-shaped leaves. While both can be grown in air plant holder ceramic , chamomile is known for its calming properties, often used in teas and herbal remedies, while daisies are primarily decorative.
Chamomile plants, with their daisy-like appearance, belong to the Asteraceae family, which also includes catsfoot, named after the furry paws of felines. While daisies and chamomile share some similarities, they are distinct species. The chamomile plant’s daisy-like flowers, often mistaken for daisies, offer calming properties.
Both daisies and chamomile are popular in gardens, with daisies known for their cheerful blooms and chamomile for its medicinal uses. Plants named after cats showcase the diverse botanical world, where even our furry feline friends inspire plant names.