Exit polls, a cornerstone of election reporting, provide invaluable insights into the minds of voters as they emerge from the ballot box. These polls offer a real-time snapshot of voter preferences, shaping public opinion and influencing political discourse.
Exit polls employ rigorous methodologies to gather data, analyze it, and report the results with accuracy and transparency. They play a crucial role in predicting election outcomes, informing campaign strategies, and enhancing our understanding of the electorate.
Exit Poll Definition
Exit polls are surveys conducted among voters immediately after they have cast their ballots in an election. The purpose of exit polls is to gather information about the characteristics of the electorate, such as their demographics, voting behavior, and opinions on the candidates and issues. This information can be used to make inferences about the overall outcome of the election and to understand the factors that influenced voters’ decisions.
Exit polls are typically conducted using a random sample of voters leaving polling places. Interviewers ask voters a series of questions about their demographics, their reasons for voting for a particular candidate or party, and their opinions on the issues. The data collected from exit polls is then analyzed to identify patterns and trends in the electorate.
Exit polls are not without their limitations. One potential bias is that exit polls may overrepresent certain groups of voters, such as those who are more likely to vote early or who are more interested in politics. Additionally, exit polls can be affected by sampling error, which occurs when the sample of voters surveyed is not representative of the entire electorate.
Methodology of Exit Polls
Exit polls are conducted using various sampling techniques and data collection procedures to gather information from voters as they leave polling places on Election Day. These methods aim to provide a snapshot of the electorate’s preferences and voting patterns.
The most common sampling method used in exit polls is random sampling, where a representative sample of voters is selected from the population of all voters. This ensures that the sample accurately reflects the demographic and political characteristics of the electorate.
Data Collection Procedures
Data collection in exit polls is typically conducted through face-to-face interviews with voters as they exit polling places. Interviewers ask voters a series of questions about their candidate preferences, party affiliations, and other demographic information.
The accuracy and reliability of exit poll data depend on several factors, including the sample size, the sampling method, and the training of interviewers. Exit polls are generally considered to be accurate, but they can be subject to sampling error and other biases.
Potential for Bias
Exit polls have the potential for bias due to several factors, including:
- Sampling error: The sample may not accurately represent the population of all voters.
- Non-response bias: Some voters may decline to participate in the exit poll, which can bias the results.
- Interviewer bias: Interviewers may influence voters’ responses, either consciously or unconsciously.
Ensuring Accuracy and Reliability
To ensure the accuracy and reliability of exit poll data, several procedures are typically employed:
- Large sample sizes: Exit polls typically use large sample sizes to minimize sampling error.
- Random sampling: Random sampling methods are used to select a representative sample of voters.
- Interviewer training: Interviewers are trained to conduct interviews in a consistent and unbiased manner.
- Data weighting: Exit poll data is often weighted to adjust for demographic and political differences between the sample and the population of all voters.
Advantages of Exit Polls
Exit polls provide numerous advantages in understanding voter behavior and predicting election outcomes. These real-time surveys offer valuable insights into the electorate’s preferences and voting patterns.
One significant advantage of exit polls is their ability to predict election outcomes with remarkable accuracy. By capturing data from a representative sample of voters immediately after they cast their ballots, exit polls can provide early indications of the likely winner. Historical examples abound where exit polls have successfully predicted the outcomes of major elections, including the 2008 and 2012 presidential elections in the United States.
However, it’s crucial to acknowledge that exit polls have limitations and potential weaknesses. The accuracy and reliability of exit polls can be influenced by various factors, such as sample size, sampling bias, and response rates. Exit polls rely on a relatively small sample of voters, which may not fully represent the entire electorate. Additionally, there’s a risk of sampling bias if the sample is not truly representative of the population. Response rates can also impact the reliability of exit polls, as non-respondents may differ from respondents in their voting preferences.
Ethical considerations also surround the use of exit polls. Some argue that exit polls can influence voter turnout, particularly in close elections. The release of early results may discourage some voters from participating if they believe their candidate is trailing. Others contend that exit polls provide valuable information to the public and can enhance voter engagement.
Summary Table: Advantages and Disadvantages of Exit Polls
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|—|—|
| Real-time insights into voter behavior | Potential for sampling bias |
| Prediction capabilities | Limited sample size |
| Identification of key issues and demographics | Response rates can impact reliability |
| Early indication of election outcomes | Ethical considerations regarding voter turnout |
Conclusion
Exit polls offer valuable insights into voter behavior and can accurately predict election outcomes. However, it’s essential to be aware of their limitations and potential biases. Careful consideration of the advantages and disadvantages of exit polls is necessary to ensure their responsible use and interpretation.
Limitations of Exit Polls
While exit polls provide valuable insights, they are not without their limitations. These polls rely on self-reporting and can be subject to sampling bias, which can impact the accuracy of the results.
Sampling bias occurs when the sample of respondents is not representative of the larger population. This can happen for several reasons, such as if the poll is conducted in a location that is not representative of the overall population or if the sample size is too small.
Accuracy Issues
- Sampling error: The sample size may not be large enough to accurately represent the population, leading to inaccurate results.
- Response bias: Respondents may be reluctant to provide honest answers, leading to biased results.
- Interviewer bias: The interviewer’s presence or behavior can influence the respondent’s answers.
Ethical Considerations

Conducting exit polls involves several ethical considerations that must be addressed to ensure the integrity and fairness of the process.
One primary concern is privacy. Exit polls collect sensitive information from individuals, including their voting preferences and personal opinions. It is crucial to protect the privacy of respondents and ensure that their data is not used for any purpose other than the intended research objectives.
Potential Biases
Another ethical consideration is the potential for biases in exit polls. These biases can arise from various factors, such as the sampling method used, the wording of questions, or the timing of the poll. It is essential to minimize these biases to ensure that the results accurately reflect the views of the population being surveyed.
Historical Significance of Exit Polls
Exit polls have a rich history, playing a crucial role in elections and public opinion research. Their evolution over time has significantly influenced the political landscape and our understanding of voter behavior.
The origins of exit polls can be traced back to the early 20th century when researchers began conducting surveys outside polling stations to gauge voter preferences. However, it was not until the 1960s that exit polls gained widespread recognition.
Impact on Election Coverage
Exit polls revolutionized election coverage, providing real-time insights into voter behavior and allowing news organizations to make early projections about the outcome. This transformed election night into a highly anticipated event, with viewers eagerly awaiting the latest results.
Shaping Political Campaigns
Exit polls also had a profound impact on political campaigns. By providing immediate feedback on voter preferences, campaigns could adjust their strategies and messaging in real-time. This led to more targeted and effective campaigning.
Influencing Public Opinion
Exit polls played a significant role in shaping public opinion about candidates and issues. By providing a glimpse into the minds of voters, exit polls influenced how the public perceived the election and the candidates involved.
– Describe techniques and methods for analyzing exit poll data, including statistical analysis and data visualization.
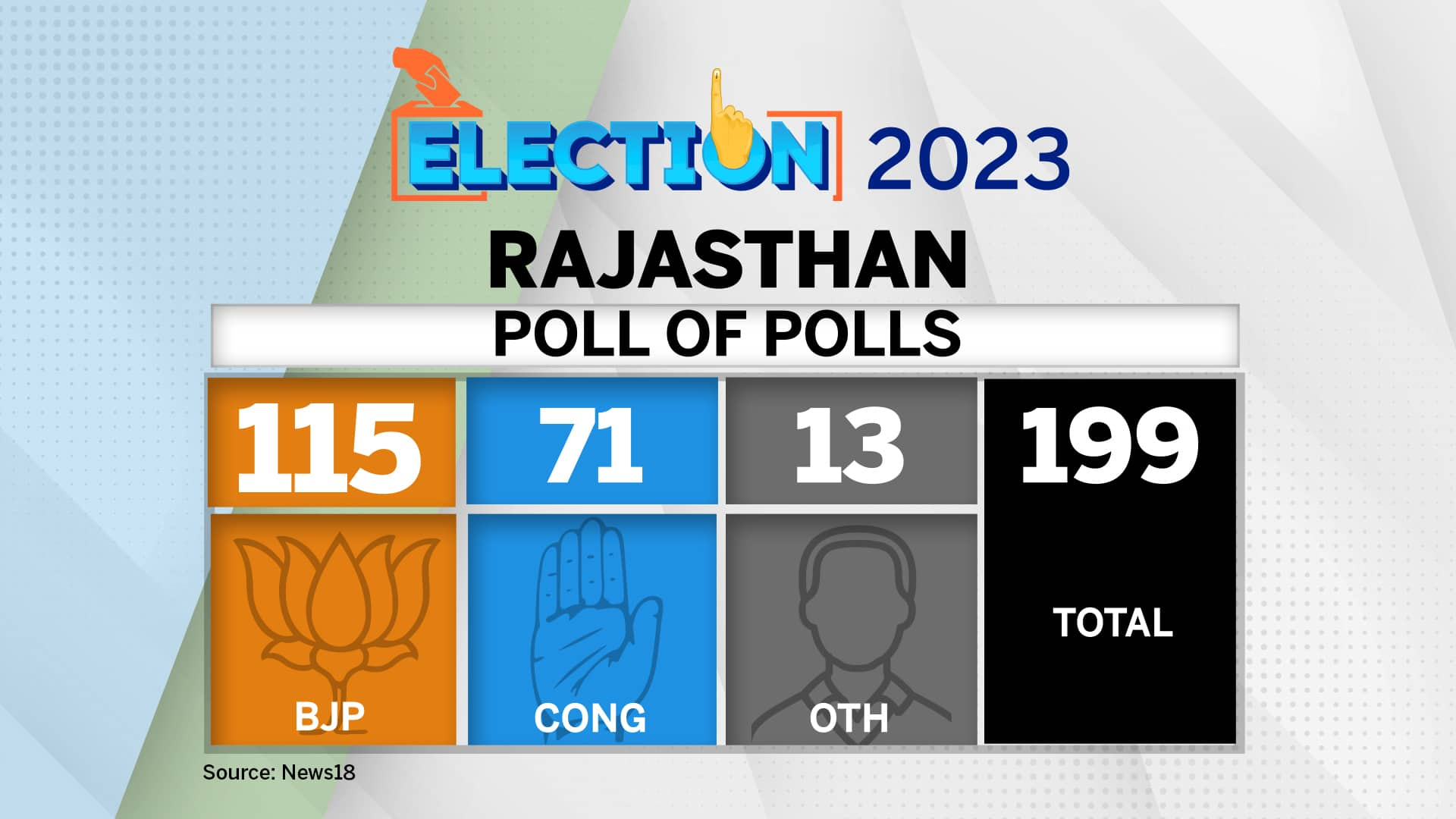
Exit poll data analysis involves applying statistical techniques and data visualization methods to extract meaningful insights from the collected data. Statistical analysis helps identify patterns, relationships, and differences within the data, while data visualization presents the results in a visually appealing and comprehensible manner.
Statistical Analysis
Common statistical tests used to analyze exit poll data include:
- Chi-square tests: Determine if there are significant differences between observed and expected frequencies, testing hypotheses about the distribution of categorical variables.
- T-tests: Compare the means of two independent groups, assessing if there are statistically significant differences between them.
- Regression analysis: Models the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables, identifying the strength and direction of their association.
These tests help researchers make inferences about the population based on the sample data, assessing the significance of observed differences and identifying potential causal relationships.
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of Mafalda Castro.
Data Visualization
Data visualization techniques present the results of exit poll analysis in a visually appealing and easily interpretable manner:
- Charts: Bar charts, pie charts, and line charts display data in a graphical format, allowing for quick comparisons and identification of trends.
- Graphs: Scatterplots and histograms depict the distribution of data points, revealing patterns and relationships between variables.
- Maps: Choropleth maps use colors or patterns to represent data values associated with geographical regions, providing insights into spatial variations.
Data visualization helps researchers communicate the findings of exit poll analysis effectively, making it accessible to a wider audience.
Limitations of Exit Poll Data
It’s important to consider the limitations of exit poll data when analyzing the results:
- Sampling error: Exit polls rely on a sample of voters, which may not perfectly represent the entire population.
- Non-response bias: Voters who choose not to participate in exit polls may have different characteristics than those who do.
- Social desirability bias: Respondents may provide answers that they believe are socially acceptable rather than their true opinions.
Researchers should account for these limitations when interpreting the results of exit poll analysis, considering the potential impact on the accuracy and generalizability of the findings.
Learn about more about the process of Pakistan vs Ireland in the field.
Exit Polls in Different Contexts
Exit polls find applications in various contexts beyond political elections. They provide valuable insights into public opinion and preferences, aiding decision-making and understanding societal trends.
Political Elections
Exit polls are extensively used in political elections to gauge voter sentiment and predict election outcomes. Advantages include providing real-time data, identifying voting patterns, and estimating candidate support. However, they can be susceptible to sampling biases and may not accurately reflect the final results. For instance, in the 2016 US presidential election, exit polls overestimated Hillary Clinton’s support, leading to surprise results.
Referendums
Exit polls play a crucial role in referendums, where voters directly decide on specific policies or constitutional changes. They help assess public sentiment and predict the likely outcome. For example, in the 2016 Brexit referendum, exit polls accurately predicted the “Leave” campaign’s victory. Ethical considerations arise when polls are conducted close to voting day, potentially influencing voter behavior.
Market Research
Exit polls are also used in market research to gather feedback on products, services, or brand perceptions. They provide insights into consumer preferences, satisfaction levels, and areas for improvement. Advantages include capturing immediate reactions and identifying trends. However, they may not represent the broader population and can be influenced by factors such as the location of the survey or the demographics of the respondents.
Future Trends
The future of exit polls involves technological advancements and methodological refinements. Online and mobile polling methods are gaining popularity, increasing accessibility and reducing costs. Data visualization techniques are being employed to present results more effectively and interactively. Additionally, there is ongoing research to address biases and improve the accuracy of exit polls.
Compare exit polls to other polling methods, such as telephone surveys and online polls, highlighting their similarities and differences.
Exit polls, telephone surveys, and online polls are all methods of collecting data from a sample of people in order to make inferences about a larger population. However, there are some key similarities and differences between these three methods.
Similarities
* All three methods involve collecting data from a sample of people.
* All three methods can be used to collect data on a wide range of topics.
* All three methods can be used to make inferences about a larger population.
Differences
* Exit polls are conducted on Election Day at polling places.
* Telephone surveys are conducted over the phone.
* Online polls are conducted online.
Exit polls have the advantage of being able to collect data from a large number of people on Election Day. This makes them a very good way to get a quick and accurate estimate of the results of an election. However, exit polls can be biased if the sample of people who are interviewed is not representative of the larger population.
Telephone surveys have the advantage of being able to collect data from a large number of people who are not necessarily located in the same place. This makes them a good way to get data from people who are difficult to reach, such as people who live in rural areas. However, telephone surveys can be biased if the sample of people who are interviewed is not representative of the larger population.
Online polls have the advantage of being able to collect data from a large number of people who are not necessarily located in the same place. They are also relatively inexpensive to conduct. However, online polls can be biased if the sample of people who participate is not representative of the larger population.
Table summarizing the key similarities and differences between exit polls, telephone surveys, and online polls.
| Feature | Exit polls | Telephone surveys | Online polls |
|—|—|—|—|
| Location | Polling places | Over the phone | Online |
| Sample size | Large | Large | Large |
| Representativeness | Can be biased | Can be biased | Can be biased |
| Cost | Relatively expensive | Relatively inexpensive | Relatively inexpensive |
Designing an Exit Poll Questionnaire

Designing an effective exit poll questionnaire is crucial for collecting reliable and accurate data. Here are some guidelines to consider:
Question Types
- Open-ended questions allow respondents to provide their own answers, offering in-depth insights.
- Closed-ended questions present a limited set of response options, making data analysis easier.
- Likert scale questions measure respondents’ agreement or disagreement on a scale, providing valuable ordinal data.
Response Options
- Multiple choice allows respondents to select one or more options.
- Rank order asks respondents to rank options in order of preference.
Question Order and Flow
The order of questions should be logical and flow smoothly. Start with general questions and gradually move to more specific ones. Avoid leading questions or biasing respondents.
Avoiding Bias
- Use neutral language and avoid loaded or suggestive terms.
- Provide clear instructions and ensure all respondents understand the questions.
- Randomize the order of response options to minimize bias.
Checklist for Designing an Effective Questionnaire
- Determine the specific information you want to collect.
- Choose appropriate question types and response options.
- Consider the order and flow of questions.
- Pilot test the questionnaire to identify any issues.
- Revise and finalize the questionnaire based on feedback.
Reporting Exit Poll Results

Reporting exit poll results accurately and transparently is crucial for maintaining public trust and providing meaningful insights. Here are some best practices to follow:
Data Presentation
- Present the results in a clear and concise manner, using tables, charts, and graphs to visualize the data.
- Ensure that the data is disaggregated by relevant demographics, such as age, gender, and race, to provide a more nuanced understanding.
- Provide estimates of the margin of error associated with the results to convey the level of uncertainty in the data.
Data Interpretation
- Interpret the results cautiously, acknowledging that exit polls are only a snapshot of voter preferences at a particular point in time.
- Consider potential biases and limitations of exit polls when drawing conclusions.
- Avoid making definitive predictions based solely on exit poll data, especially in close races.
Case Studies of Exit Polls
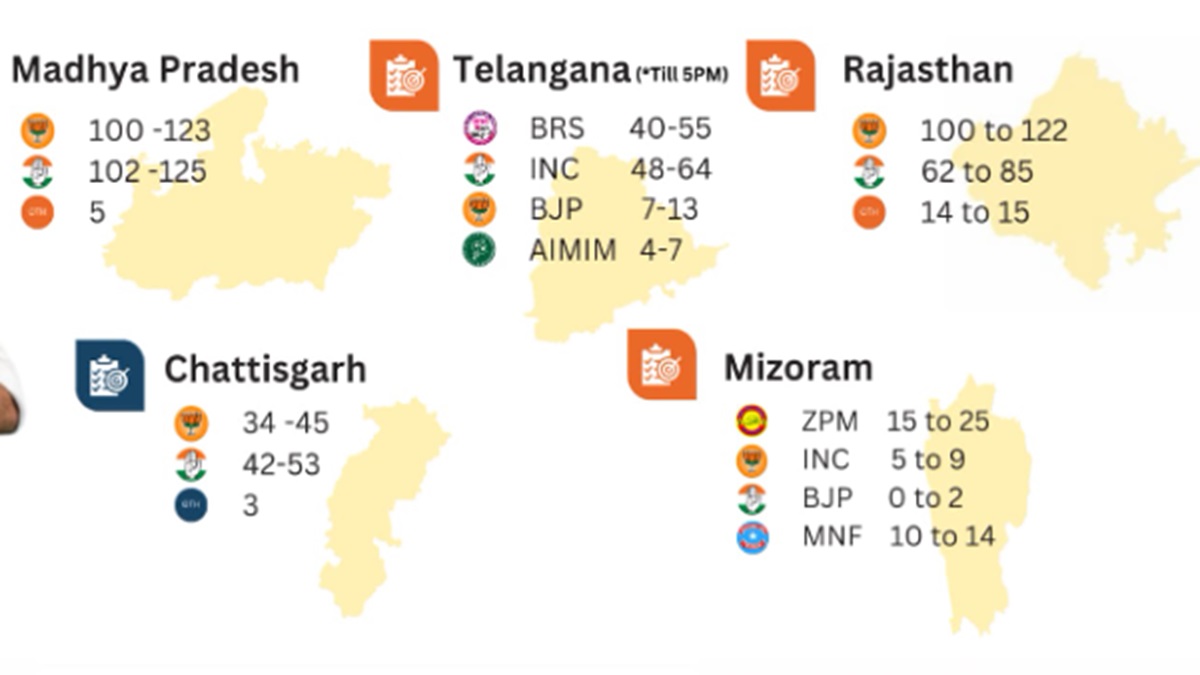
Exit polls have been used in various elections and have played a significant role in shaping public opinion and influencing election outcomes. Here are a few notable case studies:
US Presidential Election, 2016
In the 2016 US presidential election, exit polls played a crucial role in predicting the outcome. The polls conducted by major news organizations, such as CNN, ABC News, and NBC News, consistently showed Hillary Clinton with a narrow lead over Donald Trump. However, on election night, Trump won the Electoral College vote, defying the predictions of the exit polls. This discrepancy was attributed to several factors, including the large number of undecided voters and the difficulty in polling certain demographic groups, such as rural voters.
Brexit Referendum, 2016
The 2016 Brexit referendum in the United Kingdom was another significant event where exit polls played a major role. The polls conducted by major broadcasters, such as the BBC and ITV, initially suggested that the “Remain” campaign was slightly ahead. However, as more results came in, it became clear that the “Leave” campaign had won. This outcome was a surprise to many, as most pre-referendum polls had predicted a narrow victory for the “Remain” campaign.
Indian General Election, 2019
In the 2019 Indian general election, exit polls played a significant role in shaping public opinion. The polls conducted by various agencies, such as India Today-Axis My India and Times Now-VMR, predicted a landslide victory for the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) led by Narendra Modi. The results of the election largely matched the predictions of the exit polls, with the BJP securing a clear majority in the Lok Sabha.
These case studies demonstrate the potential impact of exit polls on public opinion and election outcomes. However, it is important to note that exit polls are not always accurate, and they should be interpreted with caution.
Future of Exit Polls
Exit polling has evolved significantly over the years, and it is likely to continue to do so in the future. Advancements in technology and new methodologies are expected to play a major role in shaping the future of exit polling.
One of the most significant trends in the future of exit polling is the increasing use of technology. In recent years, we have seen the emergence of mobile exit polling, which allows voters to complete exit polls on their smartphones or tablets. This technology has the potential to make exit polling more convenient and accessible, and it could also lead to larger sample sizes and more accurate results.
Another trend in the future of exit polling is the development of new methodologies. One promising approach is the use of predictive analytics to identify voters who are likely to participate in exit polls. This information can be used to target outreach efforts and increase the representativeness of exit poll samples.
Potential Advancements and Trends, Exit poll
- Increased use of technology, such as mobile exit polling and online platforms
- Development of new methodologies, such as predictive analytics and data visualization techniques
- Collaboration between pollsters and researchers to improve the accuracy and reliability of exit polls
- Use of exit polls to study a wider range of political and social issues
- Integration of exit poll data with other data sources to provide a more comprehensive understanding of voter behavior
Ultimate Conclusion
As technology advances and polling techniques evolve, exit polls continue to adapt, ensuring their relevance in the ever-changing landscape of elections and public opinion research. They remain an indispensable tool for understanding voter behavior and shaping political discourse.