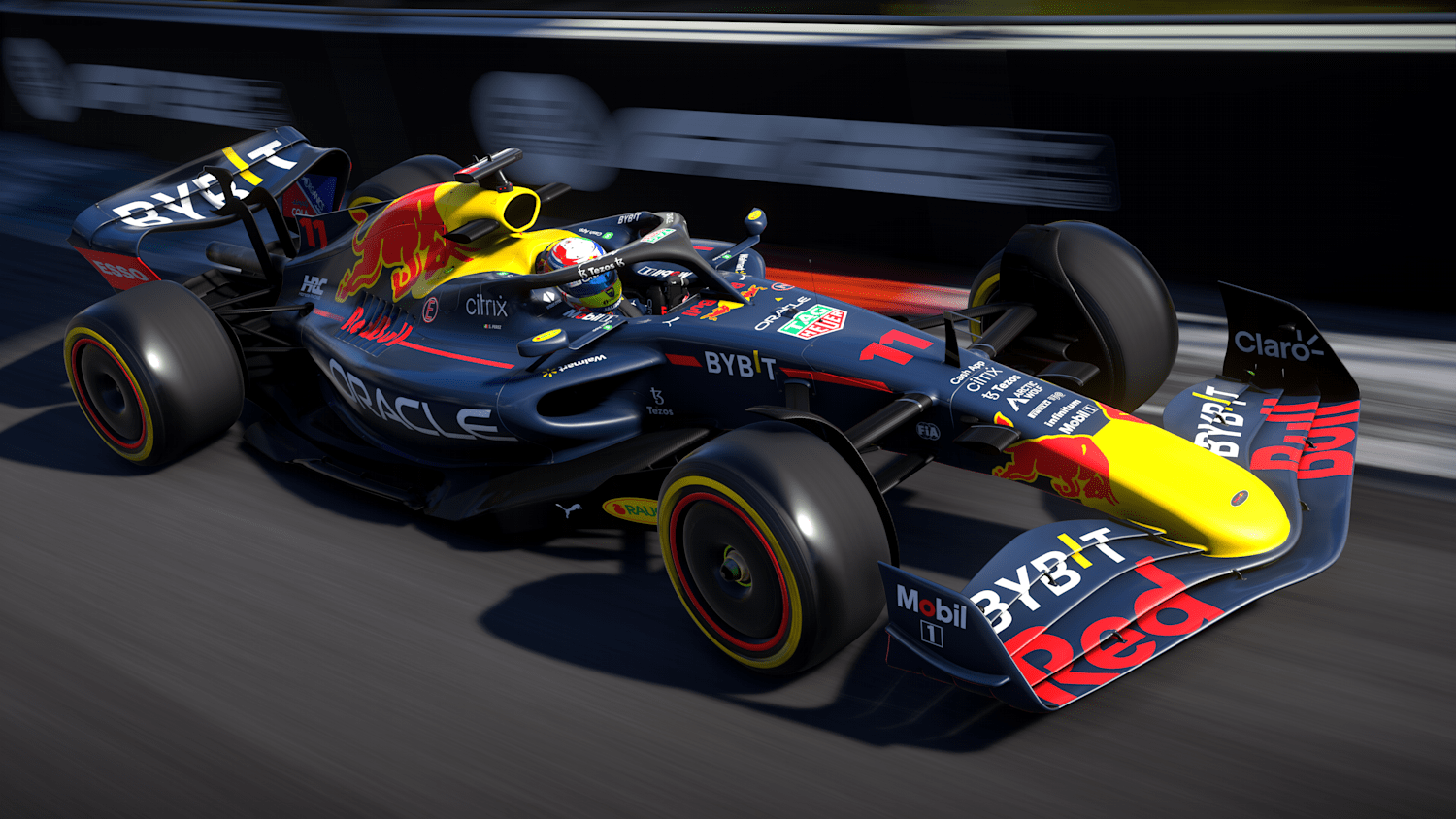
Buckle up for an adrenaline-fueled journey into the exhilarating world of Formula 1, where speed, strategy, and spectacle collide on the world’s most iconic racetracks. From the roaring engines to the checkered flag, F1 captivates millions of fans with its unparalleled blend of human skill and technological innovation.
Prepare to dive into the heart of F1, where teams of brilliant engineers, fearless drivers, and passionate fans push the limits of performance and innovation. Get ready to experience the thrill, the drama, and the unwavering pursuit of victory that defines the pinnacle of motorsport.
F1 Teams

The world of Formula One is home to a diverse range of teams, each with its unique history, strengths, and aspirations. From factory-backed powerhouses to ambitious privateer outfits, these teams represent the pinnacle of motorsport engineering and competition.
At the heart of F1, we find the factory teams, the elite squads directly supported by major automotive manufacturers. These teams, such as Mercedes-AMG Petronas Formula One Team, Scuderia Ferrari, and Oracle Red Bull Racing, possess vast resources, cutting-edge technology, and the backing of global giants.
Their relentless pursuit of performance and innovation drives the sport forward, pushing the boundaries of automotive engineering.
Customer Teams
Alongside the factory teams, customer teams play a vital role in the F1 ecosystem. These teams purchase chassis and power units from the factory teams, allowing them to compete at a lower cost while still benefiting from the expertise and technology of the larger organizations.
F1, the pinnacle of motorsports, where speed and precision reign supreme. But even in this adrenaline-fueled arena, drivers and fans alike appreciate comfort and style. Enter the Vanity Fair Beauty Back Bra , a garment that combines the support and elegance of a bra with the freedom of movement essential for the fast-paced world of F1.
Williams Racing, Alfa Romeo F1 Team ORLEN, and Haas F1 Team are notable examples of customer teams that have achieved success in F1.
Privateer Teams
At the other end of the spectrum, we have privateer teams, the underdogs of F1. These teams operate independently, relying on their own resources and ingenuity to compete against the well-funded factory and customer teams. While their chances of victory may be slim, privateer teams bring a unique spirit of passion and determination to the sport, showcasing the true essence of grassroots motorsport.
Financial Implications
Running an F1 team is an incredibly expensive endeavor. The costs of developing and maintaining cars, hiring top-tier drivers, and traveling to races around the world can easily exceed hundreds of millions of dollars per year. Teams rely on a combination of sponsorship deals, prize money, and commercial revenue streams to fund their operations.
Factors Contributing to Success
Success in F1 is a complex equation, influenced by a multitude of factors. Technical innovation, driver performance, and team management all play crucial roles. Teams must constantly strive to develop the fastest and most reliable cars, while also nurturing the talent of their drivers and fostering a positive and collaborative team environment.
F1 Drivers
Formula One drivers are the heart and soul of the sport, pushing their machines to the limit and showcasing their extraordinary skills on the world’s most iconic circuits. These elite athletes possess a unique combination of talent, dedication, and unwavering determination.
Factors that Make a Successful F1 Driver
Becoming a successful F1 driver requires a harmonious blend of several crucial factors:
- Talent:Natural ability and innate skill in handling race cars.
- Experience:Accumulated races and seasons competed, providing invaluable knowledge and racecraft.
- Fitness:Exceptional physical and mental endurance to withstand the demanding rigors of F1 racing.
- Psychological Resilience:The ability to thrive under immense pressure, overcome setbacks, and maintain focus amidst fierce competition.
Top 5 Drivers from Last Season
The 2022 season witnessed some remarkable performances from the top drivers, who showcased their exceptional abilities and strategic prowess.
- Lewis Hamilton:A seasoned veteran with unparalleled talent and unwavering determination.
- Max Verstappen:A rising star with raw speed and aggressive driving style.
- Charles Leclerc:A young prodigy known for his exceptional qualifying pace and racecraft.
- Sergio Pérez:A consistent performer with a knack for delivering under pressure.
- George Russell:A promising talent who impressed in his first season with Mercedes.
These drivers combined exceptional talent with years of experience, unwavering fitness, and remarkable psychological resilience, propelling them to the forefront of the sport.
Challenges and Opportunities for F1 Drivers
The upcoming season presents both challenges and opportunities for F1 drivers.
- New Car Regulations:Significant changes to car design and regulations will test drivers’ adaptability and ability to master new driving techniques.
- Increased Competition:The entry of new teams and the return of former champions will intensify the competition, demanding even greater performance from drivers.
- Sustainable Racing:The push towards sustainable racing technologies introduces new challenges and opportunities for drivers to embrace innovation and adapt to evolving regulations.
The Future of F1 and the Role of Drivers
The future of Formula One looks promising, with drivers playing a pivotal role in shaping its success.
- Ambassadors of the Sport:Drivers serve as ambassadors for F1, engaging fans and promoting the sport worldwide.
- Safety Advocates:Their relentless pursuit of safety improvements has made F1 one of the safest motorsport disciplines.
- Technological Pioneers:Drivers provide invaluable feedback for ongoing technological advancements, ensuring cars remain at the cutting edge of innovation.
As Formula One continues to evolve, the drivers will remain at the heart of the sport, captivating audiences with their skill, determination, and unwavering passion for racing.
F1 Cars
Formula One cars are the pinnacle of motorsport engineering, representing the cutting edge of automotive technology. These machines are designed to achieve极致performance and handle the extreme demands of Formula One racing.
Over the years, F1 cars have undergone significant evolution, driven by technological advancements and a relentless pursuit of speed and efficiency. Here’s a detailed look at the technical specifications, evolution, and key features of a modern F1 car:
Engine
The heart of an F1 car is its engine, a turbocharged 1.6-liter V6 hybrid power unit. This compact and efficient engine generates immense power, producing around 1,000 horsepower.
The engine is paired with an Energy Recovery System (ERS), which captures and stores energy from braking and exhaust gases. This energy can then be deployed to provide an additional boost of power, improving acceleration and overall performance.
Chassis
The chassis of an F1 car is a lightweight and incredibly strong carbon fiber monocoque. This structure provides the car with its rigidity and strength, while also acting as a safety cell to protect the driver in the event of an accident.
The chassis is designed to minimize weight and maximize aerodynamic efficiency. It features intricate aerodynamic elements, such as sidepods, bargeboards, and a rear wing, which work together to generate downforce and reduce drag.
Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics plays a crucial role in F1 car design. The shape and design of the car are meticulously engineered to generate downforce, which allows the car to maintain grip and corner at high speeds.
Downforce is created by the airflow over the car’s surfaces. The front and rear wings, along with the underbody, are designed to create a low-pressure area above the car and a high-pressure area below, resulting in a downward force that keeps the car planted on the track.
Safety Features
Safety is paramount in F1. Modern F1 cars incorporate a range of advanced safety features to protect drivers in the event of an accident.
These features include:
- Halo: A protective structure that surrounds the driver’s head, providing additional protection in the event of a rollover or side impact.
- Carbon fiber monocoque: A strong and lightweight structure that absorbs impact energy and protects the driver.
- Crash structures: Designed to absorb and dissipate energy in the event of a collision.
- Fire suppression system: Automatically activates to extinguish any fires that may occur in the car.
- Safety harness: A six-point harness that keeps the driver securely in place during high-speed maneuvers.
Evolution of F1 Cars
F1 cars have undergone a continuous evolution over the years, driven by technological advancements and the pursuit of performance.
Key milestones in F1 car evolution include:
- 1950s: The early days of F1 saw cars with large, naturally aspirated engines and limited aerodynamic features.
- 1960s: The introduction of rear wings and ground effects significantly improved downforce and cornering speeds.
- 1970s: Turbocharged engines and advanced aerodynamics pushed the limits of performance, but also led to safety concerns.
- 1980s: The introduction of carbon fiber monocoques and electronic driver aids improved safety and performance.
- 1990s: Active suspension and traction control systems further enhanced car handling and grip.
- 2000s: The introduction of hybrid power units and advanced aerodynamic devices led to a new era of efficiency and performance.
Today, F1 cars represent the pinnacle of automotive engineering, showcasing the latest technologies and innovations in the pursuit of speed, efficiency, and safety.
F1 Races
The Formula One World Championship consists of a series of races held at circuits around the world. Each race is a unique event with its own history and characteristics.
The current F1 calendar includes 23 races, held in 20 different countries. The races are typically held on weekends, with practice and qualifying sessions on Friday and Saturday, and the race itself on Sunday.
Race Locations and History
- Australian Grand Prix(Melbourne, Australia): First held in 1985, the Australian Grand Prix is the traditional season-opening race. The race is held on the Albert Park Circuit, a street circuit located in the heart of Melbourne.
- Bahrain Grand Prix(Sakhir, Bahrain): First held in 2004, the Bahrain Grand Prix is the first race to be held in the Middle East. The race is held on the Bahrain International Circuit, a purpose-built track located in the Sakhir desert.
- Chinese Grand Prix(Shanghai, China): First held in 2004, the Chinese Grand Prix is the first race to be held in China. The race is held on the Shanghai International Circuit, a purpose-built track located on the outskirts of Shanghai.
- Emilia Romagna Grand Prix(Imola, Italy): First held in 1980, the Emilia Romagna Grand Prix is one of the most historic races on the F1 calendar. The race is held on the Autodromo Enzo e Dino Ferrari, a circuit located in the town of Imola.
- Miami Grand Prix(Miami, USA): First held in 2022, the Miami Grand Prix is the first race to be held in the United States since 1991. The race is held on the Miami International Autodrome, a street circuit located in the Miami Gardens neighborhood.
- Spanish Grand Prix(Barcelona, Spain): First held in 1951, the Spanish Grand Prix is one of the most prestigious races on the F1 calendar. The race is held on the Circuit de Barcelona-Catalunya, a purpose-built track located on the outskirts of Barcelona.
- Monaco Grand Prix(Monte Carlo, Monaco): First held in 1929, the Monaco Grand Prix is one of the most famous and glamorous races on the F1 calendar. The race is held on the Circuit de Monaco, a street circuit located in the heart of Monte Carlo.
- Canadian Grand Prix(Montreal, Canada): First held in 1967, the Canadian Grand Prix is one of the most popular races on the F1 calendar. The race is held on the Circuit Gilles Villeneuve, a street circuit located on the Ile Notre-Dame in Montreal.
Just imagine the exhilaration of watching an F1 race, the roar of the engines, the blur of colors as the cars zip past. But what about when you want to recreate that thrilling atmosphere at home? That’s where fire pit glass comes in.
If you’re wondering where you can get your hands on some, just click here to find the best deals and ignite the F1 spirit in your backyard!
- British Grand Prix(Silverstone, UK): First held in 1950, the British Grand Prix is the oldest race on the F1 calendar. The race is held on the Silverstone Circuit, a purpose-built track located in the county of Northamptonshire.
- Austrian Grand Prix(Spielberg, Austria): First held in 1970, the Austrian Grand Prix is one of the most scenic races on the F1 calendar. The race is held on the Red Bull Ring, a purpose-built track located in the Styrian mountains.
- French Grand Prix(Le Castellet, France): First held in 1906, the French Grand Prix is one of the most historic races on the F1 calendar. The race is held on the Circuit Paul Ricard, a purpose-built track located in the Provence region.
- Hungarian Grand Prix(Budapest, Hungary): First held in 1936, the Hungarian Grand Prix is one of the most technical races on the F1 calendar. The race is held on the Hungaroring, a purpose-built track located on the outskirts of Budapest.
- Belgian Grand Prix(Spa-Francorchamps, Belgium): First held in 1925, the Belgian Grand Prix is one of the most challenging races on the F1 calendar. The race is held on the Circuit de Spa-Francorchamps, a high-speed track located in the Ardennes forest.
- Dutch Grand Prix(Zandvoort, Netherlands): First held in 1952, the Dutch Grand Prix is one of the most popular races on the F1 calendar. The race is held on the Circuit Zandvoort, a purpose-built track located on the North Sea coast.
- Italian Grand Prix(Monza, Italy): First held in 1921, the Italian Grand Prix is one of the most prestigious races on the F1 calendar. The race is held on the Autodromo Nazionale Monza, a high-speed track located on the outskirts of Milan.
- Singapore Grand Prix(Singapore): First held in 2008, the Singapore Grand Prix is the first night race on the F1 calendar. The race is held on the Marina Bay Street Circuit, a street circuit located in the heart of Singapore.
- Japanese Grand Prix(Suzuka, Japan): First held in 1976, the Japanese Grand Prix is one of the most technical races on the F1 calendar. The race is held on the Suzuka Circuit, a purpose-built track located in the Mie prefecture.
- United States Grand Prix(Austin, USA): First held in 2012, the United States Grand Prix is one of the most popular races on the F1 calendar. The race is held on the Circuit of the Americas, a purpose-built track located in the city of Austin.
- Mexico City Grand Prix(Mexico City, Mexico): First held in 1963, the Mexico City Grand Prix is one of the most passionate races on the F1 calendar. The race is held on the Autodromo Hermanos Rodriguez, a purpose-built track located in the heart of Mexico City.
- São Paulo Grand Prix(São Paulo, Brazil): First held in 1973, the São Paulo Grand Prix is one of the most iconic races on the F1 calendar. The race is held on the Autódromo José Carlos Pace, a purpose-built track located in the Interlagos neighborhood.
- Abu Dhabi Grand Prix(Abu Dhabi, UAE): First held in 2009, the Abu Dhabi Grand Prix is the season-ending race on the F1 calendar. The race is held on the Yas Marina Circuit, a purpose-built track located on Yas Island.
Types of F1 Races
In addition to the traditional Grand Prix races, there are also two other types of F1 races: sprint races and night races.
Sprint racesare shorter races that are held on Saturday afternoon, in addition to the traditional qualifying session. The results of the sprint race determine the starting grid for the main Grand Prix race on Sunday.
Night racesare races that are held at night under artificial lighting. The first night race was held in Singapore in 2008, and there are now several night races on the F1 calendar.
F1 Rules and Regulations
Formula 1 (F1) is governed by a comprehensive set of rules and regulations that ensure fair competition, safety, and technological innovation. These rules cover various aspects of the sport, including car design, driver conduct, and race procedures.
Over the years, the rules have undergone significant changes to keep pace with technological advancements and address safety concerns. Some notable changes include the introduction of hybrid engines, the halo cockpit protection system, and stricter penalties for dangerous driving.
Car Design
F1 cars are subject to strict regulations regarding their design and construction. These regulations aim to ensure that all cars are competitive and safe. Key aspects of car design include:
- Aerodynamics:The shape of the car is optimized to reduce drag and increase downforce, allowing for higher speeds and cornering abilities.
- Engine:F1 cars use hybrid engines that combine a 1.6-liter V6 turbocharged engine with an electric motor. The engines must produce a minimum of 1,000 horsepower.
- Safety features:F1 cars are equipped with numerous safety features, including the halo, a titanium structure that protects the driver’s head, and the survival cell, a carbon fiber monocoque that surrounds the driver.
Driver Conduct, F1
F1 drivers are expected to adhere to a code of conduct that promotes fair play and safety. Key regulations include:
- Respect for other drivers:Drivers must not engage in dangerous or unsportsmanlike conduct on or off the track.
- Penalties:Drivers can receive penalties for various offenses, such as exceeding track limits, causing collisions, or ignoring blue flags.
- Safety:Drivers are responsible for ensuring their own safety and the safety of other competitors.
Race Procedures
F1 races are conducted according to a set of procedures that ensure fairness and consistency. Key aspects of race procedures include:
- Qualifying:Drivers compete in qualifying sessions to determine their starting positions on the grid.
- Race start:The race begins with a standing start, where cars are lined up on the grid in order of their qualifying positions.
- Race distance:F1 races typically consist of multiple laps around a circuit, with the winner being the first driver to complete the predetermined number of laps.
- Safety car:The safety car is deployed when there is an incident on the track that requires caution. When the safety car is on the track, all cars must slow down and maintain their positions.
- Pit stops:Drivers can make pit stops to change tires, refuel, or make repairs. Pit stops are timed, and the time spent in the pits counts towards the driver’s overall race time.
A Brief History of F1
Formula One, or F1, is the pinnacle of motorsport, a global spectacle that has captivated audiences for decades. Its origins can be traced back to the early 20th century, when races were held on public roads with modified production cars.
In 1946, the Fédération Internationale de l’Automobile (FIA) established the Formula One World Championship, which standardized the rules and regulations for the sport. The early years were dominated by drivers like Juan Manuel Fangio and Alberto Ascari, and teams like Alfa Romeo and Ferrari.
F1 races can be as hot as a fireplace, but don’t worry, you can keep your cool with a beveled glass fireplace screen . It’ll protect your home from the heat and sparks while adding a touch of elegance. And when the race is over, you can relax in front of the fire, safe and sound.
The Golden Age
The 1950s and 1960s are often referred to as the “Golden Age” of F1. This era saw the emergence of legendary drivers like Stirling Moss, Jim Clark, and Jackie Stewart, and teams like Lotus, Brabham, and McLaren. The cars of this period were characterized by their sleek designs and powerful engines.
The Modern Era
The 1970s and 1980s marked the beginning of the “Modern Era” of F1. This era was dominated by teams like Ferrari, Williams, and McLaren, and drivers like Niki Lauda, Alain Prost, and Ayrton Senna. The cars of this period were more advanced and sophisticated, with the introduction of aerodynamics and turbocharged engines.
The Hybrid Era
In 2014, F1 entered the “Hybrid Era,” with the introduction of turbocharged hybrid engines. These engines combined a traditional internal combustion engine with an electric motor, resulting in increased fuel efficiency and power. The Hybrid Era has been dominated by Mercedes, with drivers like Lewis Hamilton and Nico Rosberg winning multiple championships.
Timeline of Significant Events in F1 History
- 1906: First Grand Prix race held in France
- 1946: Formula One World Championship established
- 1950: First Formula One World Championship race held at Silverstone
- 1962: Jim Clark wins his first Formula One World Championship
- 1976: Niki Lauda survives a near-fatal crash at the Nürburgring
- 1985: Ayrton Senna wins his first Formula One World Championship
- 1994: Ayrton Senna dies in a crash at the San Marino Grand Prix
- 2000: Michael Schumacher wins his first Formula One World Championship with Ferrari
- 2008: Lewis Hamilton wins his first Formula One World Championship
- 2014: Formula One enters the Hybrid Era
- 2020: Lewis Hamilton wins his seventh Formula One World Championship
F1 Technology
Formula 1 is a pinnacle of motorsport, where cutting-edge technology and engineering innovation play a pivotal role. From telemetry to data analysis and driver simulators, F1 teams employ an array of advanced technologies to enhance performance, safety, and efficiency.
Telemetry
Telemetry systems collect and transmit real-time data from various sensors on the car, including speed, acceleration, tire temperature, and fuel consumption. This data is relayed to the pit wall, allowing engineers to monitor the car’s performance, identify potential issues, and make informed decisions during the race.
Data Analysis
Advanced data analysis tools help teams extract meaningful insights from the vast amount of telemetry data. By analyzing patterns and trends, engineers can optimize car setup, improve pit stop strategies, and identify areas for performance improvement.
Driver Simulators
Driver simulators are sophisticated tools that allow drivers to practice and prepare for races in a realistic virtual environment. Simulators provide a safe and controlled environment to test different setups, race strategies, and track conditions, enabling drivers to gain valuable experience and improve their skills.
F1 Media
F1 is one of the most popular sports in the world, and as such, it is covered extensively by the media. Television, radio, and online platforms all provide coverage of F1, with each offering its own unique perspective on the sport.Television
is the most traditional way to watch F1, and it remains the most popular way for fans to experience the sport. There are a number of different television networks that broadcast F1 races, including ESPN, Sky Sports, and Fox Sports.
These networks provide live coverage of the races, as well as pre- and post-race analysis.Radio is another popular way to follow F1. There are a number of different radio stations that broadcast F1 races, including BBC Radio 5 Live and SiriusXM.
These stations provide live commentary of the races, as well as interviews with drivers and team principals.Online platforms are becoming increasingly popular ways to follow F1. There are a number of different websites and apps that provide live coverage of the races, as well as news and analysis.
These platforms also allow fans to interact with each other and share their thoughts on the sport.
Social Media
Social media has become an increasingly important part of F1 in recent years. Drivers, teams, and fans all use social media to share their thoughts and experiences on the sport. This has given fans a new way to interact with the sport and has helped to create a more engaged and passionate community.Social
media has also changed the way that the media covers F1. In the past, the media was the only source of information about the sport. However, today, fans can get their news and analysis from a variety of sources, including social media.
This has given fans more choice and has helped to create a more informed and engaged audience.
F1 Fan Culture
Formula 1 has a diverse and passionate fan base that transcends geographical and cultural boundaries. F1 fans are united by their shared love for the sport, but they also have their own unique motivations and ways of engaging with it.
Types of F1 Fans
There are many different types of F1 fans, each with their own reasons for following the sport. Some fans are drawn to the speed and excitement of the racing, while others appreciate the technical and strategic aspects of the sport.
Some fans follow a particular driver or team, while others simply enjoy watching the best drivers in the world compete against each other.
Ways Fans Engage with F1
Fans engage with F1 in a variety of ways. Some fans attend races in person, while others watch on TV or online. Many fans also participate in online communities, such as forums and social media groups, to discuss the sport with other fans.
F1 Commercial Rights
Formula 1’s commercial rights are owned by Formula One Group, a company controlled by Liberty Media Corporation. The rights include the exclusive right to broadcast, promote, and market the Formula 1 World Championship.
F1 generates revenue through various sources, including television rights, race hosting fees, and merchandise sales. Liberty Media has implemented several strategies to increase revenue, such as expanding into new markets, introducing new race formats, and developing digital platforms.
Revenue Streams
- Television rights: 50%
- Race hosting fees: 20%
- Merchandise sales: 15%
- Sponsorship: 10%
- Other: 5%
Commercial Rights Negotiations
Negotiations for commercial rights are typically long and complex, involving multiple stakeholders. Liberty Media has been successful in securing long-term deals with broadcasters and race organizers, ensuring a stable revenue stream for F1.
Impact of COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on F1’s commercial revenues, with race cancellations and restrictions on attendance. Liberty Media implemented cost-cutting measures and negotiated with broadcasters to mitigate the financial impact.
Future of F1 Commercial Rights
The future of F1’s commercial rights landscape is expected to be shaped by the growth of digital platforms, the increasing popularity of F1 in new markets, and the adoption of sustainable practices.
– F1 Future
The future of Formula One is uncertain, but there are a number of factors that could shape its development in the years to come. These include new technologies, changing fan demographics, and the global economy.
One of the most significant challenges facing F1 is the development of new technologies. Electric cars and autonomous driving are becoming increasingly popular, and it is possible that these technologies could eventually replace traditional F1 cars. However, there are also a number of opportunities for F1 to embrace new technologies.
For example, artificial intelligence could be used to improve the performance of F1 cars and to make the sport more accessible to fans.
Another challenge facing F1 is the changing demographics of its fans. The sport has traditionally been popular with older, male fans, but it is increasingly attracting younger and female fans. F1 needs to find ways to appeal to these new fans if it wants to continue to grow in the future.
The global economy could also have a significant impact on the future of F1. If the global economy slows down, it could lead to a decrease in sponsorship and investment in the sport. This could make it difficult for F1 teams to compete and could lead to a decline in the popularity of the sport.
Despite these challenges, there are also a number of opportunities for F1 in the years to come. The sport is becoming increasingly popular in new markets, such as Asia and South America. This could lead to a significant increase in revenue for F1 and could help the sport to continue to grow.
– Technology
New technologies are having a major impact on Formula One, and they are likely to continue to do so in the years to come. Electric cars, autonomous driving, and artificial intelligence are all technologies that could have a significant impact on the sport.
Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular, and it is possible that they could eventually replace traditional F1 cars. Electric cars are more efficient than traditional cars, and they produce zero emissions. This could make them more appealing to fans and sponsors alike.
Autonomous driving is another technology that could have a significant impact on F1. Autonomous cars are capable of driving themselves, without any input from a human driver. This could lead to a number of changes in F1, such as the elimination of drivers and the introduction of new safety features.
Artificial intelligence is a third technology that could have a significant impact on F1. Artificial intelligence can be used to improve the performance of F1 cars and to make the sport more accessible to fans.
– Fan demographics
The demographics of F1 fans are changing, and this is likely to continue in the years to come. The sport has traditionally been popular with older, male fans, but it is increasingly attracting younger and female fans.
There are a number of reasons for this change in demographics. One reason is that F1 is becoming more accessible to fans around the world. The sport is now broadcast in more countries than ever before, and it is available on a variety of platforms, including streaming services.
Another reason for the change in demographics is that F1 is becoming more exciting and competitive. The cars are faster and more powerful than ever before, and the racing is often close and unpredictable.
– Global economy
The global economy could have a significant impact on the future of F1. If the global economy slows down, it could lead to a decrease in sponsorship and investment in the sport. This could make it difficult for F1 teams to compete and could lead to a decline in the popularity of the sport.
However, the global economy could also have a positive impact on F1. If the global economy grows, it could lead to an increase in sponsorship and investment in the sport. This could help F1 teams to compete and could lead to an increase in the popularity of the sport.
– Challenges
F1 faces a number of challenges in the years to come. These challenges include the development of new technologies, the changing demographics of its fans, and the global economy.
F1 needs to find ways to adapt to these challenges if it wants to continue to grow and prosper. The sport needs to embrace new technologies, appeal to new fans, and be prepared for the challenges of the global economy.
– Opportunities
F1 also has a number of opportunities in the years to come. The sport is becoming increasingly popular in new markets, and there is a growing interest in F1 from younger and female fans.
F1 needs to seize these opportunities if it wants to continue to grow and prosper. The sport needs to invest in new technologies, promote itself to new fans, and be prepared for the challenges of the global economy.
– Recommendations
There are a number of things that F1 can do to overcome its challenges and seize its opportunities. These include:
- Investing in new technologies
- Appealing to new fans
- Preparing for the challenges of the global economy
By following these recommendations, F1 can ensure its long-term future and continue to be one of the most popular sports in the world.
F1 Controversies
F1 has had its fair share of controversies throughout its history. Some of the most notable include:
Spygate Scandal (2007)
- McLaren was found guilty of stealing confidential technical information from Ferrari.
- McLaren was fined $100 million and excluded from the Constructors’ Championship.
- The scandal led to the resignation of McLaren team principal Ron Dennis.
2021 Abu Dhabi Grand Prix
- Max Verstappen overtook Lewis Hamilton on the last lap of the race to win the championship.
- The race director’s handling of the safety car period was controversial.
- The controversy led to calls for changes to the sport’s rules and regulations.
These controversies have had a significant impact on the sport. They have damaged the reputation of F1 and led to calls for changes to the way the sport is governed.
Common Themes and Patterns
- Many F1 controversies involve allegations of cheating or unfair play.
- The controversies often lead to intense debate and division among fans.
- The controversies can have a lasting impact on the sport and its reputation.
It is important to note that these are just a few examples of the many controversies that have occurred in F1 history. The sport is constantly evolving, and new controversies are sure to arise in the future.
Final Review
As the checkered flag falls on another thrilling season of Formula 1, we can’t help but marvel at the extraordinary spectacle that unfolds on every race weekend. From the cutting-edge technology to the intense rivalries, F1 has proven time and time again why it reigns supreme as the world’s premier motorsport.
But beyond the podium celebrations and champagne showers, F1 serves as a testament to the human spirit of innovation, determination, and the relentless pursuit of excellence. It’s a sport that continues to captivate and inspire, leaving us eagerly anticipating the next chapter in its storied history.