Frost Guard for Plants: Embark on a journey to discover the secrets of safeguarding your beloved plants from the harsh embrace of frost. This comprehensive guide unveils the various methods, types, and considerations involved in selecting the perfect frost guard for your specific needs.
From the humble row covers to the innovative active guards, this guide equips you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and ensure the well-being of your precious greenery.
Frost Protection Mechanisms
Frost can cause severe damage to plants, leading to reduced yields or even plant death. Fortunately, there are various methods available to protect plants from frost, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
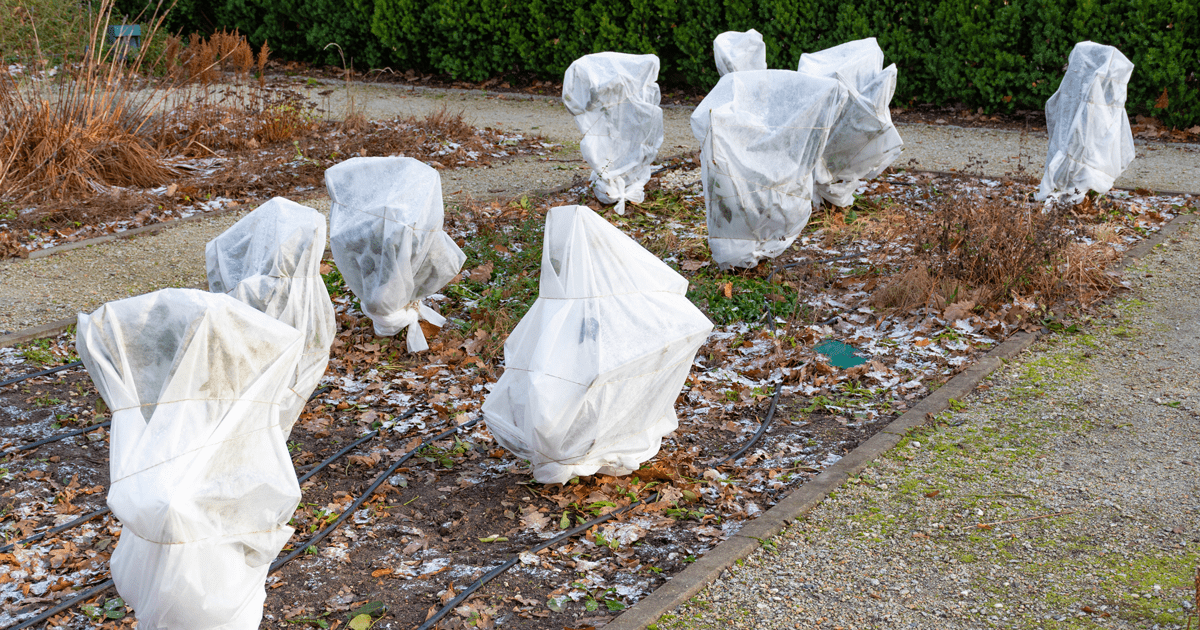
One common method of frost protection is the use of row covers. Row covers are made of a lightweight material, such as plastic or fabric, that is placed over rows of plants. The row cover creates a physical barrier between the plants and the cold air, preventing heat loss and protecting the plants from frost. Row covers are relatively inexpensive and easy to install, but they can be difficult to manage in windy conditions and may need to be removed during the day to allow for sunlight and ventilation.
Mulches
Mulches are another effective way to protect plants from frost. Mulches are materials, such as straw, hay, or compost, that are spread around the base of plants. Mulches insulate the soil, preventing heat loss and protecting the roots of plants from frost. Mulches also help to retain moisture in the soil, which can be beneficial for plants during cold weather.
Frost Blankets
Frost blankets are heavy blankets that are placed over plants to protect them from frost. Frost blankets are typically made of a thick material, such as canvas or burlap, and they provide excellent insulation against cold temperatures. Frost blankets are more expensive than row covers or mulches, but they are also more effective at protecting plants from frost.
Types of Frost Guards: Frost Guard For Plants
Frost guards are devices used to protect plants from frost damage. They come in various types, each with its own working principle and level of effectiveness.
Frost guards can be broadly classified into two categories: passive and active.
Passive Frost Guards
Passive frost guards rely on insulation or heat retention to protect plants from cold temperatures.
- Row covers: These are lightweight fabrics or plastics that are draped over plants to create a protective barrier. They trap heat from the ground and the sun, creating a warmer microclimate around the plants.
- Blankets: Similar to row covers, blankets are made of thicker materials like burlap or fleece. They provide better insulation and can withstand stronger winds.
- Mulch: Organic materials like straw, bark, or compost can be spread around the base of plants to insulate the soil and prevent heat loss.
Active Frost Guards
Active frost guards use external energy sources to generate heat and protect plants from frost.
- Heat lamps: These lamps emit infrared radiation, which is absorbed by plants and converted into heat. They are effective for small areas and can be used indoors or outdoors.
- Heaters: Electric or gas heaters can be placed near plants to raise the ambient temperature. They are more powerful than heat lamps but require a power source.
- Wind machines: These machines create a gentle breeze that helps mix the air and prevent cold air from settling around plants. They are suitable for large areas.
The cost, efficiency, and ease of use of different frost guards vary depending on the type and specific product. Passive guards are generally less expensive and easier to use, but they provide less protection compared to active guards. Active guards are more effective but require a power source and can be more expensive.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Frost Guard
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/frost-protections-GettyImages-1425333034-ad676838b2a34f5d85b2b3cf2fe952bf.jpg)
When selecting a frost guard, it’s crucial to consider factors like plant hardiness, climate conditions, and the size of the area to be protected. By understanding these variables, you can choose the most suitable type and size of frost guard for your specific needs.
Plant Hardiness
Plant hardiness refers to a plant’s ability to withstand cold temperatures. It’s determined by the plant’s genetics and is expressed in USDA hardiness zones. Choose a frost guard that is rated for the hardiness zone of your plants to ensure adequate protection.
Climate Conditions
Consider the typical climate conditions in your area when selecting a frost guard. If you live in a region with frequent frost and cold snaps, you’ll need a frost guard that provides substantial protection. In milder climates, a less heavy-duty frost guard may suffice.
Size of the Area to be Protected, Frost guard for plants
The size of the area you need to protect will influence the type and size of frost guard required. For small areas, such as individual plants or small raised beds, a portable frost guard like a blanket or cloche may be sufficient. For larger areas, consider using a more permanent frost guard, such as a greenhouse or hoop house.

