Frost Shield for Plants: A Guide to Protecting Your Plants from the Cold
As the cold weather approaches, it’s essential to take steps to protect your plants from the damaging effects of frost. Frost shield for plants is a vital tool for gardeners, providing a protective barrier against the cold and helping to ensure the survival of your plants during the winter months.
Understanding Frost Shield for Plants
Frost shield for plants is a protective covering or treatment that helps protect plants from damage caused by frost. Frost occurs when water vapor in the air freezes and forms ice crystals on surfaces, including plant tissues. These ice crystals can damage plant cells, leading to wilting, browning, and even death.
Frost shields for plants are essential in protecting delicate plants from the harsh effects of cold weather. They can be made from a variety of materials, such as plastic, fabric, or even burlap. One popular type of plant that benefits from frost shields is the lemon lime prayer plant ( lemon lime prayer plant ). This plant is native to tropical regions and is not tolerant of cold temperatures.
By using a frost shield, you can protect your lemon lime prayer plant from frost damage and keep it healthy and thriving.
Types of Frost Shield
There are various types of frost shield available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some common types include:
- Row covers: These are lightweight fabrics or plastic sheets that are placed over rows of plants to create a protective barrier against frost. Row covers can be made from materials such as spunbond polypropylene, polyethylene, or frost cloth.
- Floating row covers: These are similar to row covers but are supported by hoops or wires, allowing them to float above the plants. This provides better air circulation and prevents the covers from crushing the plants.
- Anti-transpirants: These are chemical solutions that are sprayed onto plant leaves to create a thin film that reduces water loss and helps prevent frost damage. Anti-transpirants can be effective in preventing frost damage, but they can also inhibit plant growth.
- Irrigation: Watering plants before a frost can help protect them by releasing heat into the air and creating a protective layer of ice around the plants. However, this method is only effective if the water does not freeze before the frost occurs.
The effectiveness of a particular frost shield depends on factors such as the type of plant, the severity of the frost, and the application method. It is important to choose the right type of frost shield for the specific situation and to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper use.
Methods of Frost Shield Application
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/frost-protections-GettyImages-1425333034-ad676838b2a34f5d85b2b3cf2fe952bf.jpg)
Frost shields can be applied to plants using various methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
One common method is covering plants with blankets, sheets, or tarps. This creates a physical barrier between the plant and the cold air, preventing heat loss. However, this method can be labor-intensive and may not be suitable for large areas or tall plants.
Spraying, Frost shield for plants
Another method is spraying plants with anti-desiccants or frost protectants. These solutions create a thin film on the plant’s surface, which reduces water loss and helps prevent cell damage caused by freezing.
Spraying is relatively easy to apply, but it may need to be repeated multiple times during a cold spell, especially if the wind or rain removes the solution.
Heating
Heating is a more direct method of frost protection. Electric heaters, heat lamps, or even campfires can be used to raise the temperature around plants and prevent frost from forming.
Heating is effective, but it can be expensive and may not be practical for large areas. Additionally, it may pose a fire hazard if not used properly.
Considerations for Frost Shield Use: Frost Shield For Plants
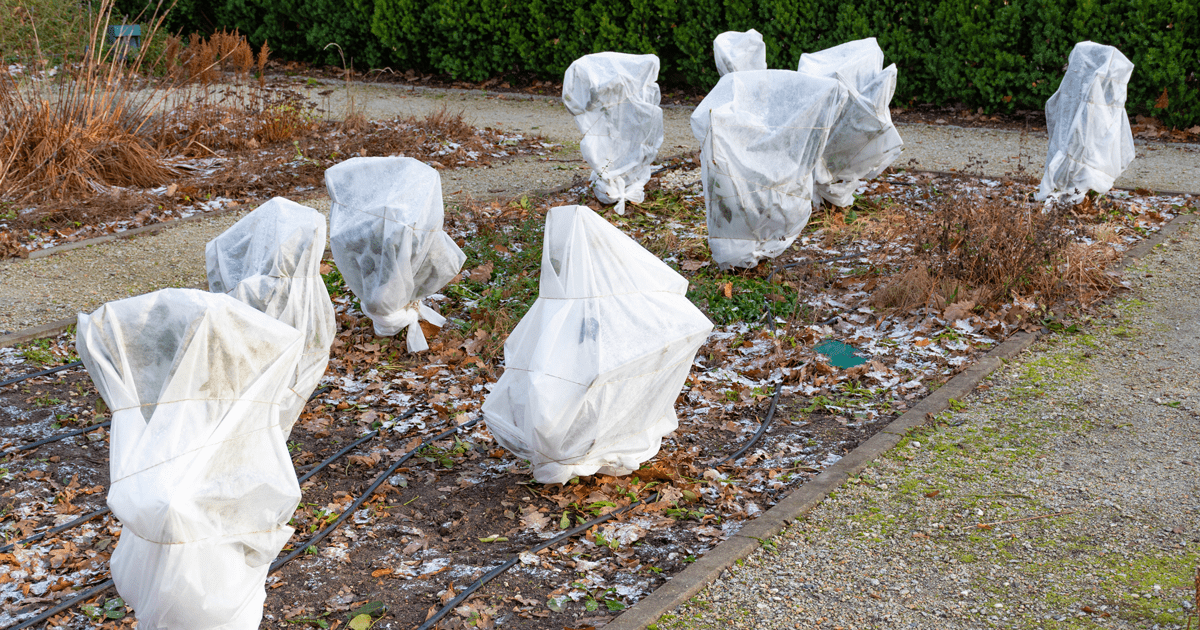

Frost shield selection and application require careful consideration to ensure effectiveness and minimize potential risks. Factors to consider include:
- Plant type: Frost tolerance varies among plant species. Some plants are more susceptible to frost damage than others. It’s essential to select a frost shield that is appropriate for the plant’s sensitivity to cold.
- Weather conditions: Frost shields are most effective in still, clear weather conditions. Wind can disperse the protective layer, reducing its effectiveness. Heavy rain or snow can also weigh down the shield, potentially damaging the plants.
- Environmental impact: Some frost shields contain chemicals that can be harmful to the environment. Choose biodegradable or organic options to minimize potential ecological damage.
Proper Application Techniques
Proper application of frost shield is crucial to avoid plant damage. Follow these guidelines:
- Apply evenly: Use a sprayer or roller to distribute the frost shield evenly over the plant’s foliage. Avoid over-application, as this can suffocate the plant.
- Cover the entire plant: Ensure that all exposed plant parts, including stems and leaves, are covered with the frost shield.
- Reapply as needed: Frost shields may need to be reapplied if they are washed away by rain or wind. Check the manufacturer’s instructions for specific reapplication guidelines.
By considering these factors and following proper application techniques, you can effectively protect your plants from frost damage and ensure their health and vitality.
Frost shields are crucial for protecting plants from the damaging effects of frost. They work by creating a microclimate around the plant, which helps to trap heat and prevent the plant from freezing. One effective way to enhance the performance of frost shields is to use them in conjunction with a planter with coco liner . Coco liners are made from natural coconut fibers, which provide excellent insulation and moisture retention.
By using a planter with coco liner, you can create an even more effective frost shield, which will help to protect your plants from even the most severe cold weather.
To protect plants from frost damage, gardeners often use frost shields. Frost shields can be made from various materials, such as fabric, plastic, or cardboard. The size of the frost shield will depend on the size of the plant. For example, a small frost shield may be sufficient for a eugenia cone plant , which typically grows to be about 2-3 feet tall.
However, a larger frost shield may be necessary for a taller plant, such as a rose bush or a small tree.