Unveiling the captivating world of light green vine plants, this comprehensive guide delves into their botanical characteristics, practical applications, cultivation techniques, and fascinating lore. Prepare to be immersed in a realm of verdant beauty and scientific intrigue.
With its distinctive appearance and versatile nature, the light green vine plant has long held a place of importance in human cultures, serving both ornamental and medicinal purposes. Its delicate tendrils and vibrant foliage have adorned gardens and homes, while its therapeutic properties have been harnessed in traditional healing practices.
Botanical Description
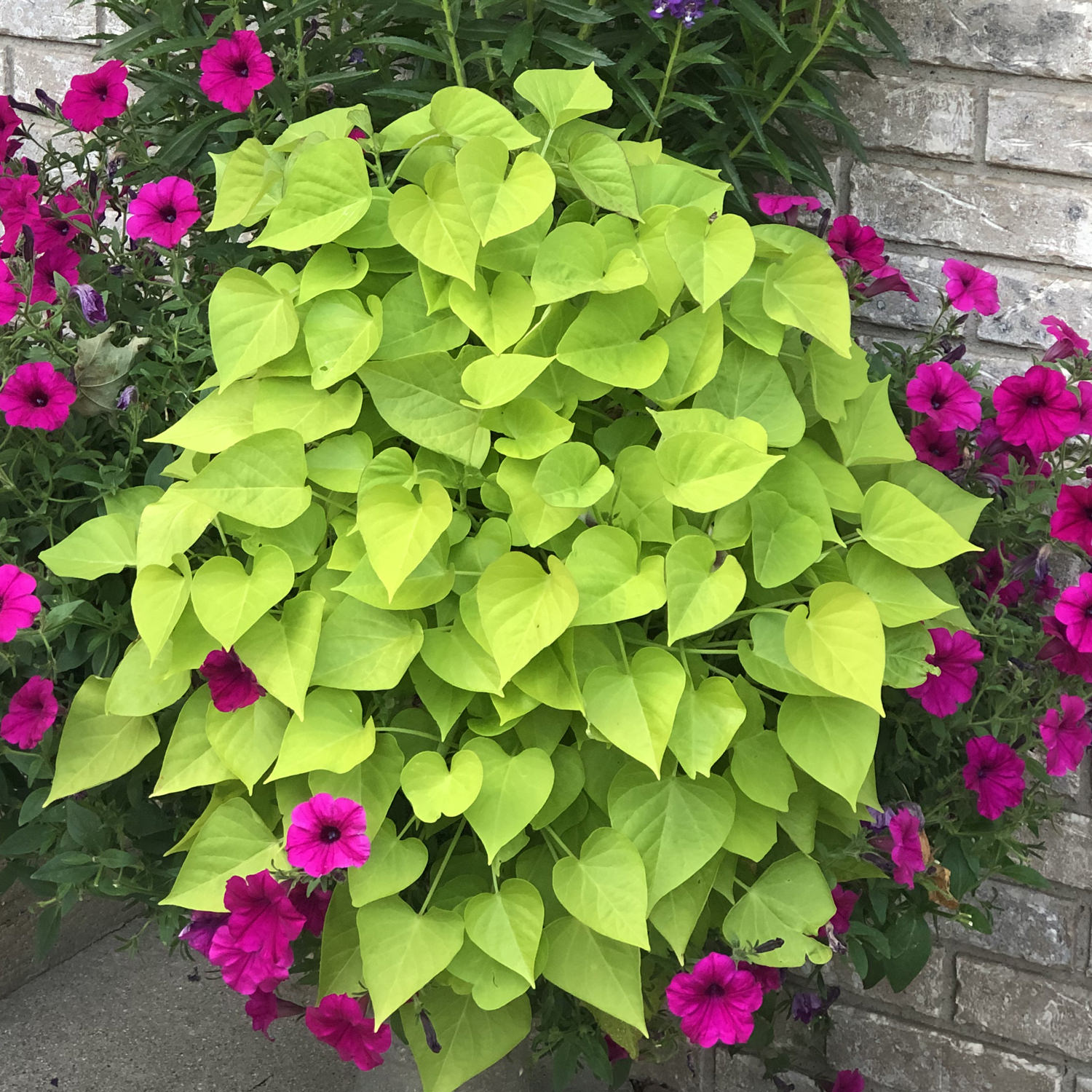

The light green vine plant, scientifically known as Cissus discolor, is a perennial evergreen vine native to tropical regions of Africa and Asia. It is characterized by its rapid growth, reaching heights of up to 10 meters (33 feet) or more.
The plant features slender, flexible stems that can climb or trail along surfaces. Its leaves are ovate to heart-shaped, with a distinctive light green color and a slightly crinkled texture. The leaves are arranged alternately along the stems and can reach lengths of up to 10 centimeters (4 inches).
Habitat and Growing Conditions, Light green vine plant
Light green vine plants prefer warm, humid environments with bright indirect light. They can tolerate a wide range of soil conditions but thrive in well-drained, loamy soil rich in organic matter.
These plants are relatively low-maintenance and can be grown both indoors and outdoors. When grown indoors, they should be placed in a location with plenty of natural light and provided with regular watering and occasional fertilization.
Uses and Applications: Light Green Vine Plant

Light green vine plants have a wide range of traditional and modern uses. They are commonly employed in landscaping, herbal medicine, and culinary applications.
Landscaping
Light green vine plants are popular in landscaping due to their aesthetic appeal and ability to create vertical interest. They can be trained to climb trellises, fences, or walls, adding a touch of greenery and vibrancy to outdoor spaces. Some popular light green vine plants for landscaping include:
- Hoya carnosa (wax plant)
- Epipremnum aureum (golden pothos)
- Philodendron scandens (heartleaf philodendron)
Herbal Medicine
In traditional herbal medicine, light green vine plants have been used to treat various ailments. For instance, extracts from Hoya carnosa have been traditionally employed as an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory agent. Epipremnum aureum has been used to alleviate pain and reduce swelling. However, it’s important to note that the use of these plants for medicinal purposes should be guided by a qualified healthcare professional, as some species may contain toxic substances.
Culinary Applications
Certain light green vine plants are also used in culinary preparations. The leaves of Hoya carnosa are edible and can be consumed raw or cooked. They have a slightly sour taste and are often used in salads, soups, and stir-fries. The leaves of Epipremnum aureum are also edible, but they should be cooked thoroughly to remove any potential toxins.
Benefits and Risks
Light green vine plants offer several benefits, including:
- Air purification: Some species, such as Epipremnum aureum, have been shown to remove toxins from the air, improving indoor air quality.
- Stress reduction: The presence of greenery in indoor spaces has been linked to reduced stress levels and improved mood.
- Vertical gardening: Vine plants are ideal for vertical gardening, allowing for space optimization and creating lush green walls.
However, it’s important to consider the potential risks associated with certain light green vine plants. Some species, such as Epipremnum aureum, can be toxic to pets if ingested. Additionally, the sap of some plants, such as Hoya carnosa, can cause skin irritation in some individuals.
Overall, light green vine plants offer a range of benefits and applications. Whether used for landscaping, herbal medicine, or culinary purposes, it’s essential to research specific species and use them responsibly, considering their potential benefits and risks.
Cultivation and Care
Growing and caring for a light green vine plant is a rewarding experience, adding a touch of greenery and elegance to any indoor or outdoor space. With proper care, these plants can thrive and bring years of enjoyment.
Propagation
Light green vine plants can be propagated through stem cuttings. Take a cutting from a healthy stem, ensuring it has at least two to three nodes (the points where leaves grow). Remove the lower leaves and dip the cutting in rooting hormone before planting it in moist, well-draining soil. Keep the soil consistently moist and provide bright, indirect light until the cutting develops roots.
Soil Requirements
These plants prefer well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter. A mixture of potting soil, peat moss, and perlite provides optimal drainage and aeration. Avoid using heavy, compacted soils that can suffocate the roots.
Watering Needs
Light green vine plants require regular watering, but it’s important to avoid overwatering. Allow the top inch of soil to dry out before watering again. During the growing season, water more frequently, especially during hot, dry weather. Reduce watering during the winter months when the plant is dormant.