Parts of a bean plant – Embark on a journey into the captivating realm of bean plants, where we unravel the intricate tapestry of their anatomy. From the humble seed to the towering vine, each part of a bean plant plays a vital role in its growth and survival, contributing to its remarkable ability to thrive in diverse environments.
As we delve deeper into the fascinating world of bean plants, we will uncover the secrets behind their growth and development, explore their culinary, medicinal, and agricultural uses, and discover the nutritional value that makes them a cornerstone of a healthy diet.
Parts of a Bean Plant

A bean plant is a flowering plant that belongs to the legume family. It is cultivated for its edible seeds, which are a rich source of protein and fiber. The bean plant has several distinct parts, each with a specific function.
The main parts of a bean plant are the roots, stem, leaves, flowers, and fruits. The roots anchor the plant in the ground and absorb water and nutrients from the soil. The stem supports the plant and transports water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves. The leaves are responsible for photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
Roots
The roots of a bean plant are typically fibrous and have a taproot system. The taproot is the main root that grows vertically downward, while the fibrous roots are smaller roots that branch out from the taproot. The roots help to anchor the plant in the ground and absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
Stem
The stem of a bean plant is typically erect and has a central axis with branches. The stem supports the plant and transports water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves. The stem also contains nodes, which are points where leaves and branches attach to the stem.
Leaves
The leaves of a bean plant are typically compound, meaning that they are made up of multiple leaflets. The leaflets are typically oval or lance-shaped and have serrated edges. The leaves are responsible for photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
Flowers
The flowers of a bean plant are typically white or purple and have a pea-like shape. The flowers are borne in clusters and are self-pollinating, meaning that they do not require insects or other animals to pollinate them. The flowers develop into fruits, which are the beans.
Fruits
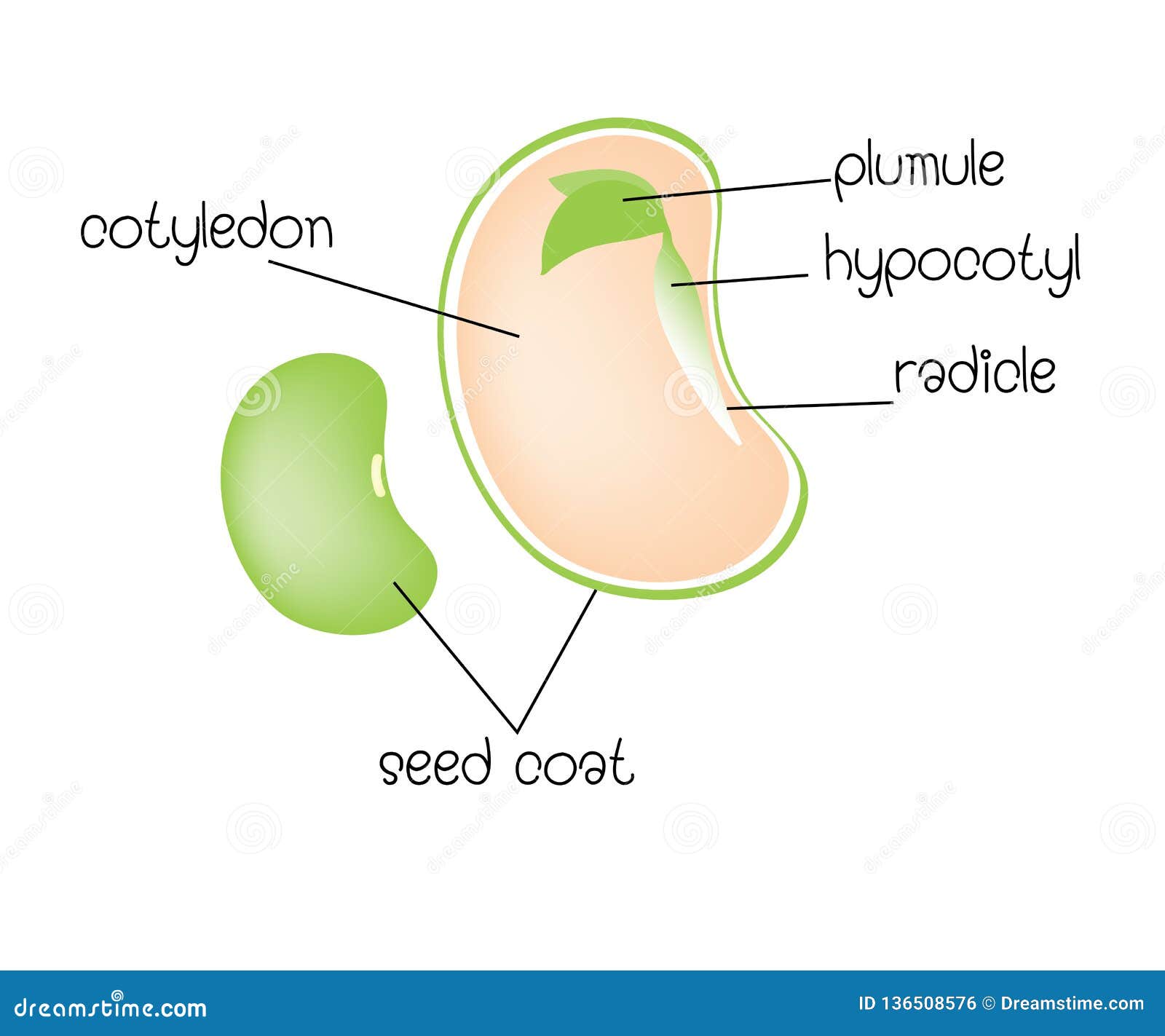
The fruits of a bean plant are typically long and slender and have a green or yellow color. The fruits are pods that contain the seeds. The seeds are the edible part of the bean plant and are a rich source of protein and fiber.
Growth and Development of a Bean Plant: Parts Of A Bean Plant
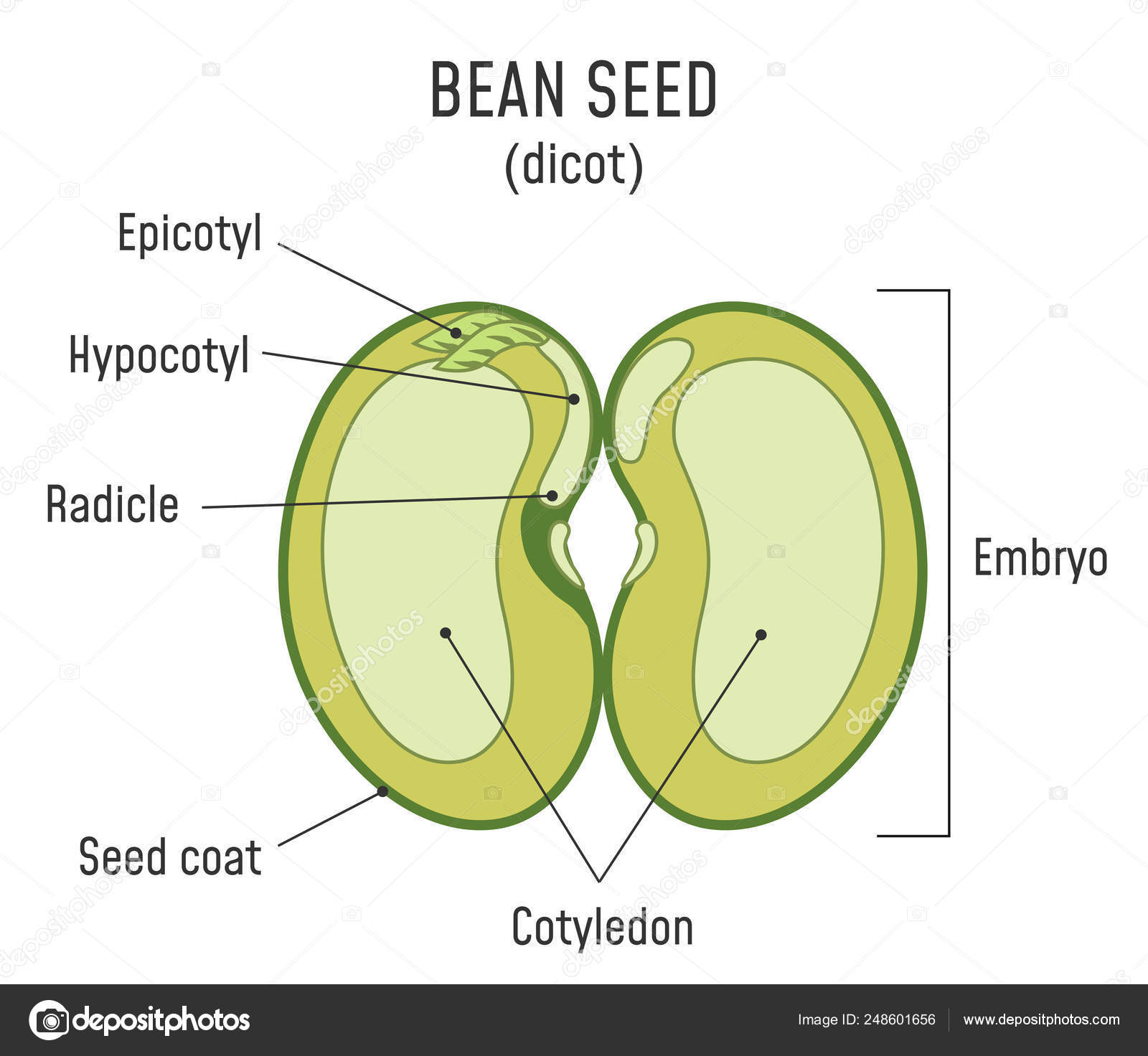
The growth and development of a bean plant is a fascinating process that involves several stages, from seed germination to maturity. Understanding these stages and the factors that influence them is crucial for successful bean cultivation.
The growth of a bean plant can be divided into three main stages: germination, vegetative growth, and reproductive growth.
Germination
Germination is the initial stage of growth, where the seed absorbs water and begins to sprout. The seed coat breaks open, and a tiny root emerges, followed by a shoot. The root anchors the plant in the soil, while the shoot grows towards the sunlight.
Vegetative Growth
During vegetative growth, the plant focuses on developing its leaves, stems, and roots. The leaves are responsible for photosynthesis, which provides the plant with energy. The stems support the plant and transport water and nutrients. The roots absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
Reproductive Growth
Reproductive growth begins when the plant produces flowers. The flowers are pollinated, and the resulting seeds are dispersed. The seeds contain the embryo of a new bean plant, and the cycle begins again.
The growth and development of bean plants are influenced by several environmental factors, including:
- Temperature: Bean plants prefer warm temperatures between 65-85°F (18-29°C).
- Light: Bean plants require at least 6 hours of sunlight per day.
- Water: Bean plants need regular watering, especially during hot, dry weather.
- Soil: Bean plants grow best in well-drained soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.8.
By providing optimal growing conditions, you can help your bean plants thrive and produce a bountiful harvest.
Uses and Applications of Bean Plants

Bean plants, with their versatile and nutritious qualities, hold significant importance in culinary, medicinal, and agricultural practices worldwide. They offer a rich source of essential nutrients and serve as a valuable component in various food preparations and therapeutic applications.
Culinary Uses
Beans have been a staple food source for centuries, offering a rich source of protein, fiber, and vitamins. They are commonly used in soups, stews, salads, and side dishes. The diverse range of bean varieties, each with its unique flavor and texture, allows for culinary creativity and exploration.
Nutritional Value
Beans are an excellent source of dietary fiber, which is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system and regulating blood sugar levels. They are also a good source of protein, iron, potassium, and zinc. Regular consumption of beans has been linked to reduced risks of chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
Medicinal Applications
Traditional medicine has long recognized the therapeutic properties of bean plants. Extracts from certain bean varieties have been used to treat various ailments, including digestive disorders, inflammation, and urinary tract infections. Studies have shown that bean extracts possess antioxidant and antimicrobial properties, supporting their potential use in natural remedies.
Agricultural Uses, Parts of a bean plant
Bean plants play a vital role in agricultural systems. They are often used in crop rotation to improve soil fertility. Beans have the ability to fix nitrogen in the soil, which benefits subsequent crops. Additionally, beans are an important source of forage for livestock.