Delve into the fascinating world of pea plant growth with our comprehensive pea plant growth chart. From seed to harvest, we’ll explore the intricate stages of development, environmental influences, and provide a detailed timeline with measurements to guide your cultivation journey.
Uncover the secrets of successful pea plant cultivation, empowering you to nurture thriving plants that yield bountiful harvests.
Pea Plant Growth Stages: Pea Plant Growth Chart
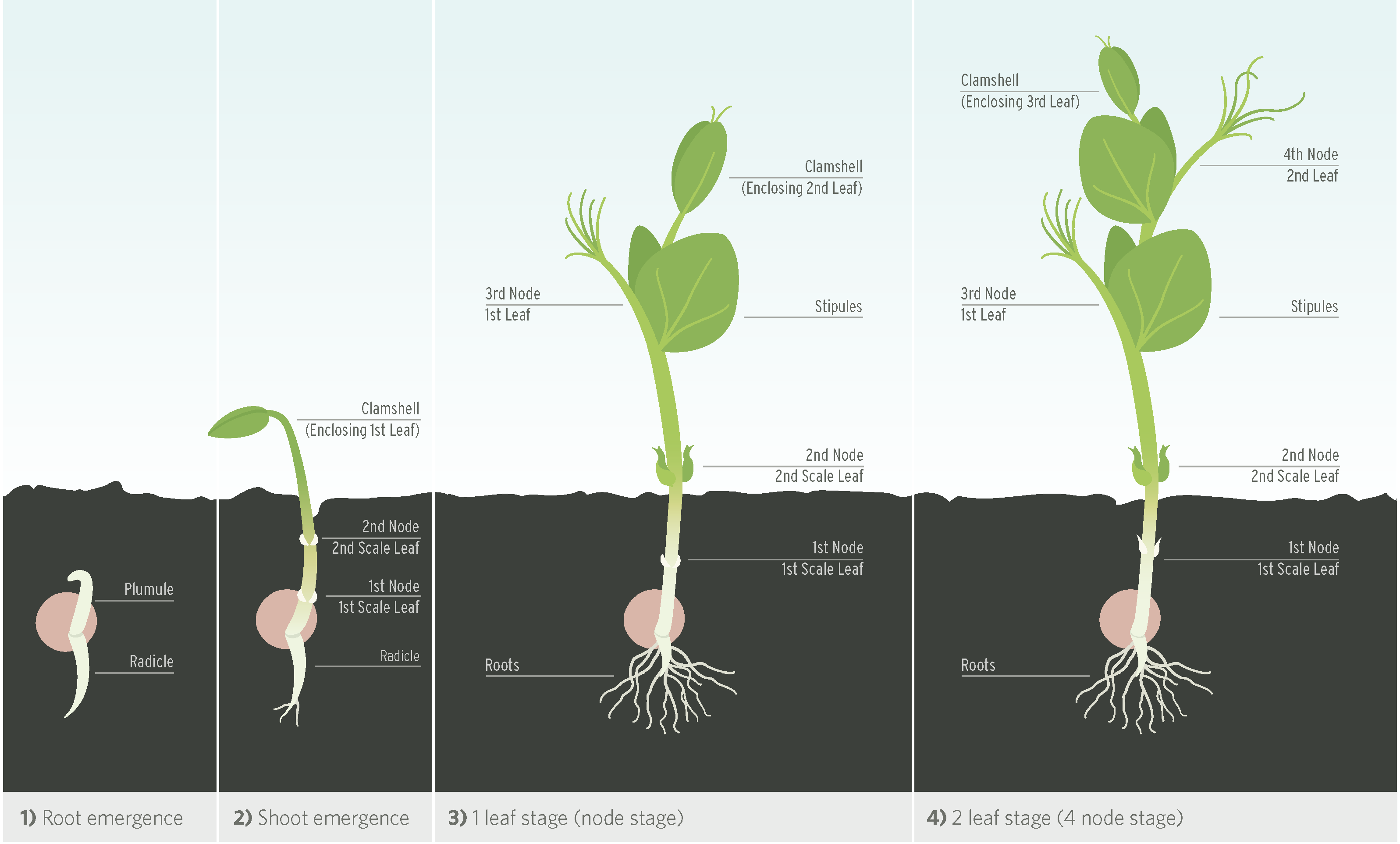
The pea plant, scientifically known as Pisum sativum, undergoes several distinct growth stages throughout its life cycle. These stages are characterized by specific morphological and physiological changes, leading to the plant’s development from a seed to a mature plant capable of producing new seeds.
Germination
The growth cycle of a pea plant begins with germination. When a pea seed is placed in a moist environment with suitable temperature conditions, it absorbs water and initiates metabolic processes. The seed coat ruptures, and the radicle, the first root of the plant, emerges. The hypocotyl, the stem-like structure connecting the root and the shoot, then elongates, pushing the cotyledons, the first leaves of the plant, above the soil surface.
The cotyledons are initially responsible for photosynthesis, providing the seedling with nutrients until the true leaves develop. As the seedling continues to grow, the primary root system develops, anchoring the plant in the soil and absorbing water and nutrients. Lateral roots also emerge, further expanding the root system.
- Timeframe: 3-7 days
- Environmental Conditions: Warm and moist environment with temperatures between 15-25°C (59-77°F)
- Morphological Changes: Emergence of radicle, hypocotyl, and cotyledons
- Physiological Changes: Activation of metabolic processes, water absorption, and initiation of photosynthesis
Factors Affecting Pea Plant Growth

The growth and development of pea plants are significantly influenced by various environmental factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing plant growth and yield.
Light
Light is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. Pea plants require ample sunlight for optimal growth. Insufficient light can lead to stunted growth, reduced leaf size, and delayed flowering.
Studies have shown that pea plants exposed to 12-14 hours of sunlight per day exhibit optimal growth and yield.
Temperature, Pea plant growth chart
Pea plants prefer moderate temperatures between 15-25°C (59-77°F). Extreme temperatures can hinder growth. Temperatures below 10°C (50°F) can slow down growth, while temperatures above 30°C (86°F) can cause heat stress, leading to wilting and reduced yield.
In controlled experiments, pea plants grown at 20°C (68°F) showed significantly higher growth rates and yields compared to plants grown at 10°C (50°F) or 30°C (86°F).
Water
Water is crucial for plant growth, and pea plants require regular watering. However, overwatering can lead to root rot and other problems. The frequency and amount of watering depend on factors such as soil type, temperature, and humidity.
As a general rule, pea plants should be watered deeply and infrequently, allowing the soil to dry out slightly between watering.
Soil Conditions
Pea plants prefer well-drained, fertile soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0. Soil that is too acidic or alkaline can inhibit growth. Additionally, pea plants benefit from the presence of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil, which can provide essential nutrients.
Studies have demonstrated that pea plants grown in soil with a pH of 6.5 and adequate nitrogen availability exhibit higher yields compared to plants grown in less optimal soil conditions.
Pea Plant Growth Chart
Pea plants, members of the legume family, exhibit remarkable growth patterns throughout their life cycle. To monitor their development effectively, a comprehensive growth chart can be an invaluable tool. This chart provides detailed measurements for key growth parameters, including height, leaf number, and stem diameter, at different stages of the plant’s life.
Pea Plant Growth Chart
The following table presents a comprehensive growth chart for pea plants, organized into distinct growth stages:
| Growth Stage | Height (cm) | Leaf Number | Stem Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seedling | 1-3 | 2-4 | 1-2 |
| Vegetative | 5-10 | 6-8 | 2-3 |
| Flowering | 15-20 | 10-12 | 3-4 |
| Pod Formation | 25-30 | 12-14 | 4-5 |
| Maturity | 35-40 | 14-16 | 5-6 |