Plant cell diagram blank is an invaluable tool for educators and students alike, providing a visual representation of the intricate components that make up plant cells. This guide will delve into the essential elements of a plant cell diagram, offering insights into their functions and providing step-by-step instructions for labeling and annotating these diagrams effectively. Additionally, we will explore customization techniques to tailor the diagram to specific educational needs.
Diagram Components
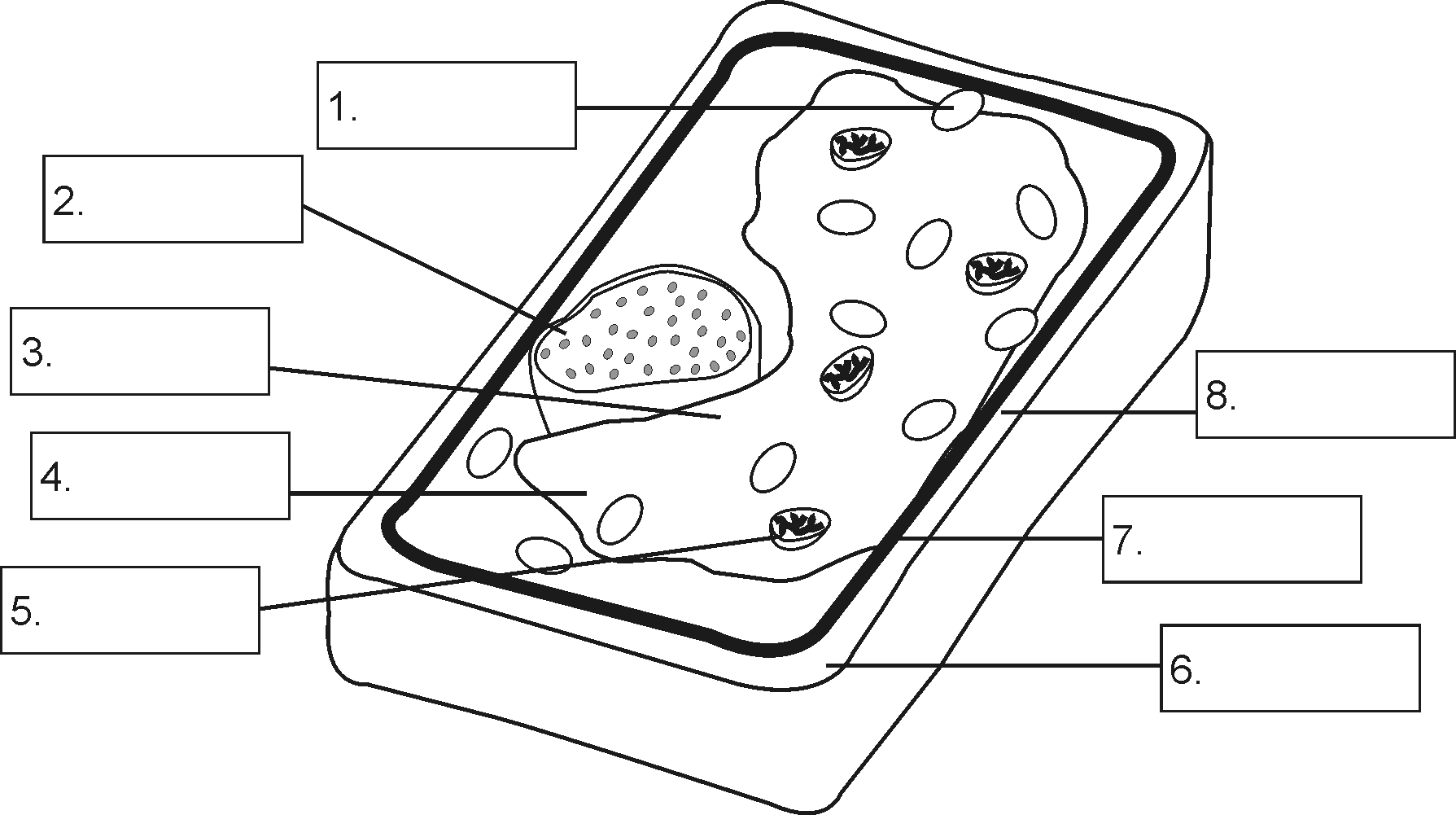
Plant cells are the fundamental building blocks of plants, responsible for their growth, development, and reproduction. A plant cell diagram provides a visual representation of the various components that make up a plant cell.
Plant cell diagram blank can be a useful tool for understanding the structure of a plant cell. For those looking to delve deeper into plant science, consider exploring plant nursery logan utah to discover a wide range of plant species and gain hands-on experience in plant care.
Returning to the topic of plant cell diagram blank, it’s important to note that labeling the different parts of the cell can aid in comprehension.
Nucleus, Plant cell diagram blank
The nucleus is the control center of the cell, containing the cell’s genetic material (DNA) and directing cellular activities.
In plant biology, a plant cell diagram blank serves as a foundational tool for understanding the intricate structures of plant cells. These diagrams provide a visual representation of various organelles, such as the nucleus, chloroplasts, and vacuoles. By studying these diagrams, researchers can gain insights into the cellular processes that govern plant growth and development.
Interestingly, the plant kingdom boasts a vast array of species whose names begin with the letter “k,” such as the majestic kangaroo paw and the delicate kiwifruit . These diverse species exhibit unique adaptations and ecological roles, further highlighting the complexity and beauty of the plant world.
Returning to the topic of plant cell diagram blanks, these resources continue to play a crucial role in advancing our understanding of plant biology and its implications for agriculture, ecology, and beyond.
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane forms the outermost boundary of the cell, regulating the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance that fills the cell, containing various organelles and molecules essential for cellular functions.
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are organelles responsible for photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose.
Vacuole
The vacuole is a large, fluid-filled sac that stores water, nutrients, and waste products.
Cell Wall
The cell wall is a rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane, providing support and protection.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that folds and transports proteins and other molecules.
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is a stack of flattened membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for secretion.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are organelles that generate energy for the cell through cellular respiration.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are small organelles that synthesize proteins based on the instructions encoded in DNA.
Labeling and Annotations
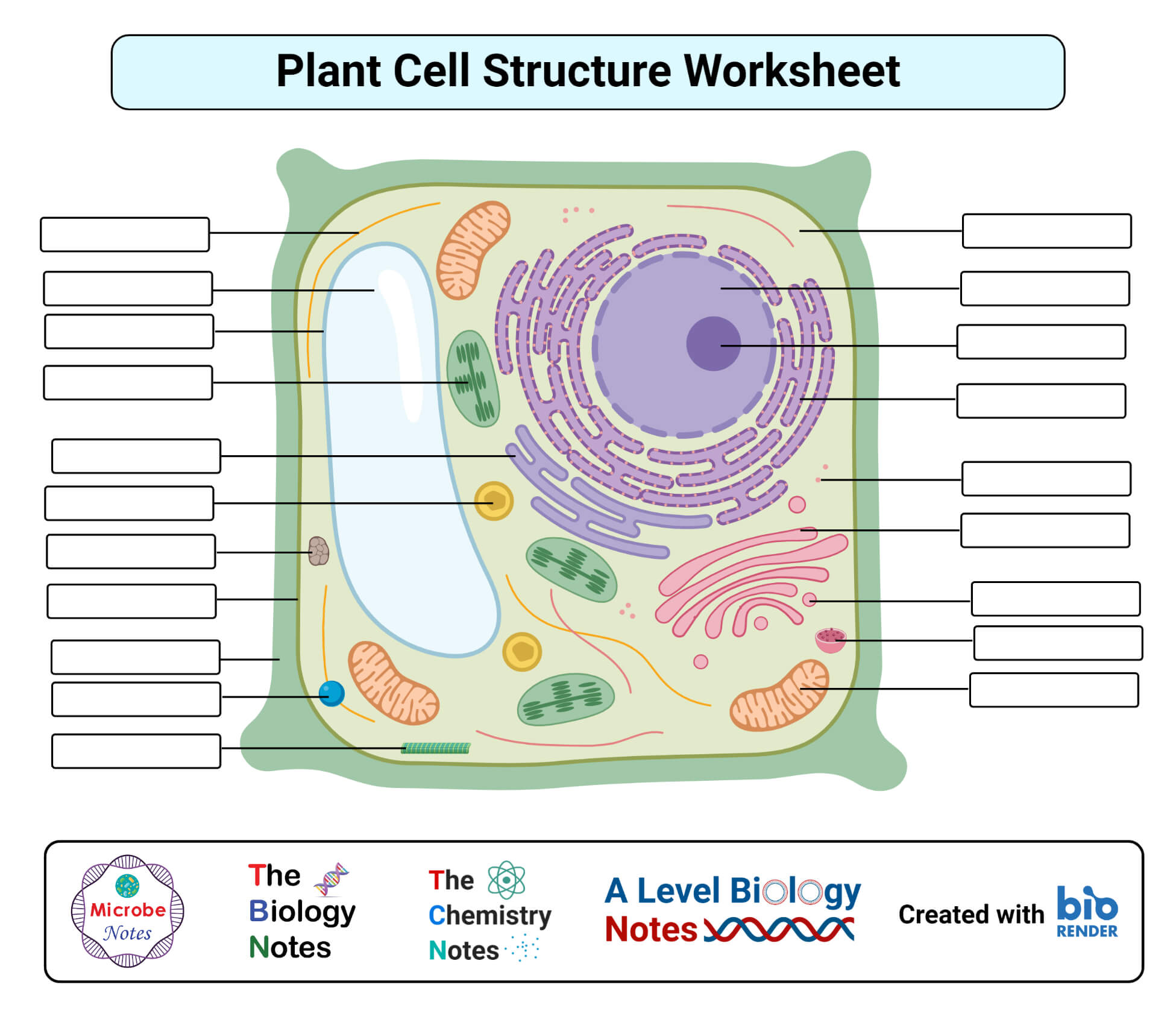
Accurate labeling and annotation are crucial for effective communication in scientific diagrams. Here’s how to label and annotate a blank plant cell diagram:
Design a Blank Diagram
- Draw a large rectangle or oval to represent the cell wall.
- Inside the cell wall, draw a smaller circle to represent the cell membrane.
- Within the cell membrane, sketch various organelles, such as the nucleus, chloroplasts, vacuole, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum.
Labeling
Use clear, concise labels to identify each structure. Place labels outside the structure they represent, using arrows or lines to connect them.
Annotations
Provide brief descriptions or explanations for each label. These annotations should be concise yet informative, providing essential information about the structure’s function or significance.
Corresponding Table
Create a table with two columns: “Label” and “Description.” Fill in the table with the corresponding labels and annotations.
Diagram Customization: Plant Cell Diagram Blank

Customizing the plant cell diagram allows for tailoring it to specific educational purposes and audiences. Educators can adjust the level of detail and complexity based on the target grade level or curriculum requirements.
For instance, a simplified diagram with fewer components and minimal annotations might be suitable for introducing basic plant cell structures to elementary students. Conversely, a more detailed diagram with additional annotations and specialized terminology could be appropriate for advanced high school biology classes.
Adding or Removing Components
Components can be added or removed to customize the diagram. For example, including specialized organelles like plastids or peroxisomes might be relevant for in-depth discussions on photosynthesis or cellular respiration.
Incorporating Additional Annotations
Incorporating additional annotations, such as arrows or text boxes, helps highlight specific features or processes. Arrows can indicate the direction of movement or flow, while text boxes can provide supplementary information or explanations.
The plant cell diagram blank provides a useful template for understanding the structure of plant cells. To cultivate plants, one requires containers, and repurposing trash cans as planters is a creative solution. Trash can planter ideas offer inspiration for transforming discarded containers into functional and stylish gardening vessels.
By utilizing these ideas, one can not only create unique plant containers but also contribute to environmental sustainability. Furthermore, the plant cell diagram blank remains an essential tool for comprehending the intricate workings of plant cells, facilitating a deeper understanding of plant biology.