Embark on an exciting journey with the Plant Cell Labeling Quiz, where you’ll delve into the intricate world of plant cells, uncovering their remarkable structures and functions. From the sturdy cell wall to the energy-producing chloroplast, this quiz will challenge your knowledge and ignite your curiosity about the fascinating realm of plant biology.
Prepare to navigate the intricate network of organelles, including the nucleus, ribosomes, and Golgi apparatus, unraveling their roles in protein synthesis and cellular processes. Explore the dynamic world of cell division and growth, witnessing the remarkable events of mitosis and meiosis.
Plant Cell Structures and Functions

Plant cells are eukaryotic cells that have a distinct structure and function compared to other cell types. They have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole, which are essential for their survival and function.
Plant cell labeling quizzes are an excellent way to test your understanding of plant cell structures. Whether you’re a student studying biology or a professional working in the field of plant science, these quizzes can help you identify and understand the various organelles and structures found within plant cells.
From the nucleus to the chloroplasts, these quizzes cover a wide range of topics related to plant cell biology. If you’re looking for a challenging and informative way to learn more about plant cells, then be sure to check out the oro grande cement plant here . With its extensive collection of plant cell labeling quizzes, you’re sure to find the perfect quiz to test your knowledge.
The Cell Wall
The cell wall is a rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support and protection. It is made of cellulose, a complex carbohydrate that is strong and flexible. The cell wall also helps to maintain the cell’s shape and prevents it from bursting when it takes in water.
Plant cell labeling quizzes are a great way to test your knowledge of the different parts of a plant cell. One of the most common questions on these quizzes is about the function of the chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are organelles that contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that absorbs light energy from the sun.
This energy is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, a sugar that the plant uses for energy. If a weed plant turns yellow, it is a sign that the plant is not getting enough sunlight. This can be caused by a number of factors, such as being planted in too shady a spot or being covered by other plants.
To help the plant recover, you can move it to a sunnier location or thin out the plants around it. For more information on why weed plants turn yellow, visit this website .
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are organelles that contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that absorbs light energy from the sun. This energy is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, a sugar molecule that the plant uses for energy. Chloroplasts are found in the cytoplasm of plant cells and are essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants create their own food.
Vacuoles
Vacuoles are large, fluid-filled sacs that occupy most of the volume of a plant cell. They contain water, salts, and other molecules that help to maintain the cell’s shape and regulate its water balance. Vacuoles also play a role in storage and waste disposal.
Organelles and Their Interactions: Plant Cell Labeling Quiz
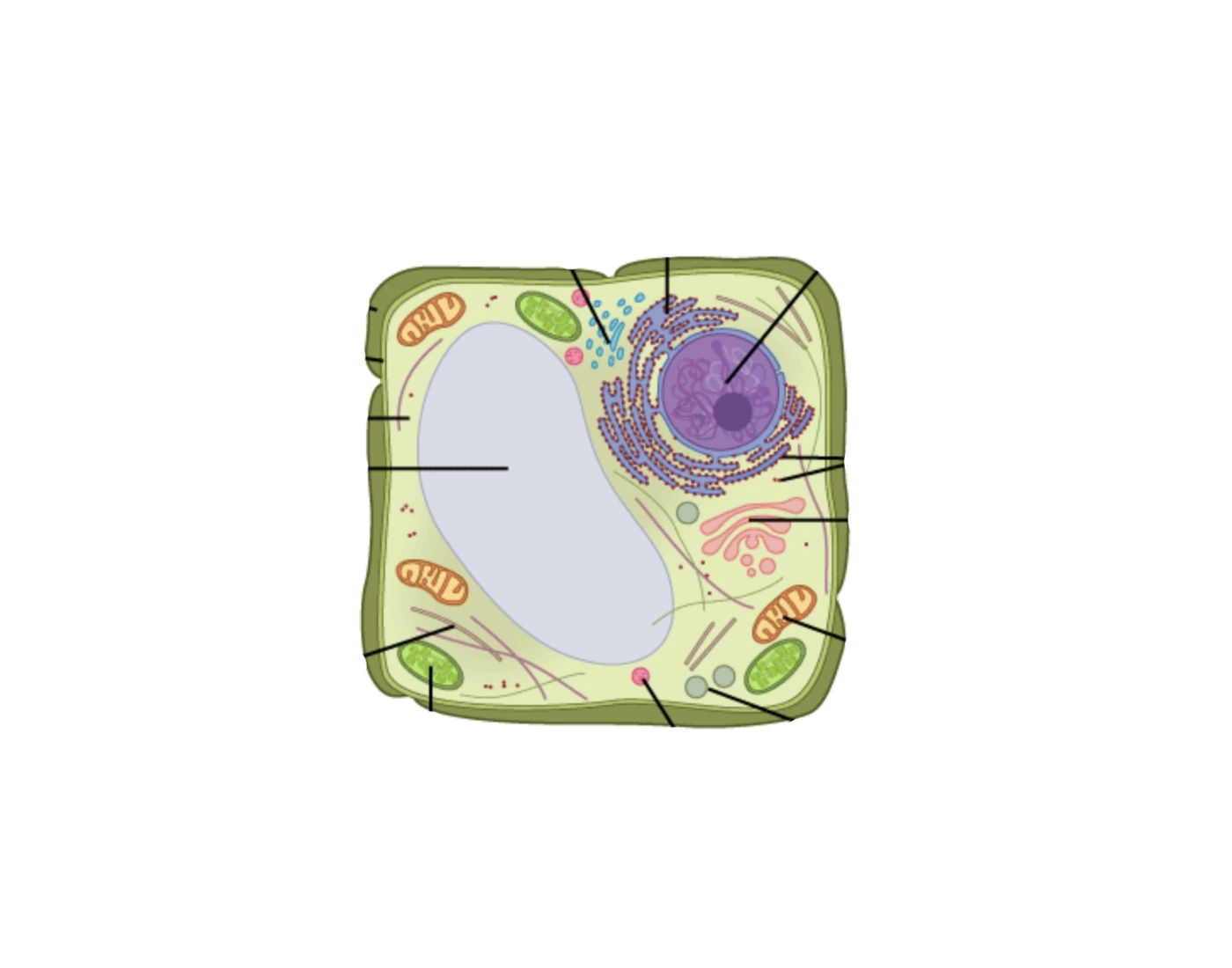
The plant cell is a complex and highly organized structure, with various organelles performing specific functions. These organelles interact with each other to maintain the cell’s overall function and survival.
Nucleus, Ribosomes, and Golgi Apparatus
The nucleus is the control center of the cell, containing the cell’s genetic material, DNA. Ribosomes are small organelles responsible for protein synthesis, while the Golgi apparatus is involved in the processing, sorting, and packaging of proteins.
Protein synthesis is a crucial process that occurs within organelles. It involves the transcription of DNA in the nucleus to produce messenger RNA (mRNA), which carries the genetic code to the ribosomes. Ribosomes then use the mRNA to synthesize proteins, which are essential for cell growth, repair, and function.
The Golgi apparatus receives proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and further modifies them by adding carbohydrates and lipids. These modified proteins are then packaged into vesicles and transported to their specific destinations within the cell or outside the cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranes that extends throughout the cytoplasm. It plays a vital role in transporting and modifying proteins. The rough ER has ribosomes attached to its surface, where protein synthesis occurs. The smooth ER lacks ribosomes and is involved in lipid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium storage.
Cell Division and Growth
Cell division is the process by which a cell divides into two or more daughter cells. It is essential for growth, development, and reproduction. There are two main types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis.
Mitosis, Plant cell labeling quiz
Mitosis is the process by which a cell divides into two identical daughter cells. It is used for growth and development.
- Prophase: The chromosomes become visible and the nuclear membrane begins to break down.
- Metaphase: The chromosomes line up in the center of the cell.
- Anaphase: The chromosomes are separated and pulled to opposite ends of the cell.
- Telophase: Two new nuclear membranes form around the chromosomes and the cell membrane pinches in the middle, dividing the cell into two daughter cells.
Meiosis
Meiosis is the process by which a cell divides into four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. It is used for reproduction.
- Prophase I: The chromosomes become visible and the nuclear membrane begins to break down. The chromosomes then pair up with their homologues.
- Metaphase I: The chromosomes line up in the center of the cell.
- Anaphase I: The chromosomes are separated and pulled to opposite ends of the cell.
- Telophase I: Two new nuclear membranes form around the chromosomes and the cell membrane pinches in the middle, dividing the cell into two daughter cells.
- Prophase II: The chromosomes become visible and the nuclear membrane begins to break down.
- Metaphase II: The chromosomes line up in the center of the cell.
- Anaphase II: The chromosomes are separated and pulled to opposite ends of the cell.
- Telophase II: Two new nuclear membranes form around the chromosomes and the cell membrane pinches in the middle, dividing the cell into two daughter cells.
The Role of Chromosomes in Cell Division
Chromosomes are structures in the cell that contain DNA. DNA is the genetic material that is passed on from parents to offspring. During cell division, the chromosomes are duplicated and then separated into the daughter cells. This ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes.
Cell Growth and Differentiation
Cell growth is the process by which a cell increases in size. Cell differentiation is the process by which a cell becomes specialized in a particular function. Both cell growth and differentiation are essential for the development of multicellular organisms.
Cell growth is regulated by a number of factors, including the availability of nutrients, the presence of growth factors, and the cell’s own internal clock. Cell differentiation is regulated by a number of factors, including the cell’s environment, the presence of specific genes, and the cell’s own internal clock.
For an effective plant cell labeling quiz, it’s crucial to understand the distinctive features of different plant cells. One such plant that exhibits unique cellular characteristics is the elephant ear plant white . Its large, shield-shaped leaves are a testament to the remarkable diversity of plant cell structures.
Returning to the plant cell labeling quiz, a thorough understanding of these structures is essential for accurate identification and labeling of plant cells.