Embark on an extraordinary adventure with the Plant Life Cycle Game, an immersive experience that unveils the fascinating world of plant biology. Through engaging gameplay, players embark on a quest to unravel the intricate stages of plant life, from the humble seed to the towering tree, while gaining a deep understanding of the remarkable adaptations that enable plants to thrive in diverse environments.
As you progress through the game, you’ll witness the germination of a tiny seed, marvel at the development of roots and shoots, and unravel the secrets of photosynthesis. Along the way, you’ll encounter diverse plant species, each with unique strategies for survival, showcasing the incredible diversity of the plant kingdom.
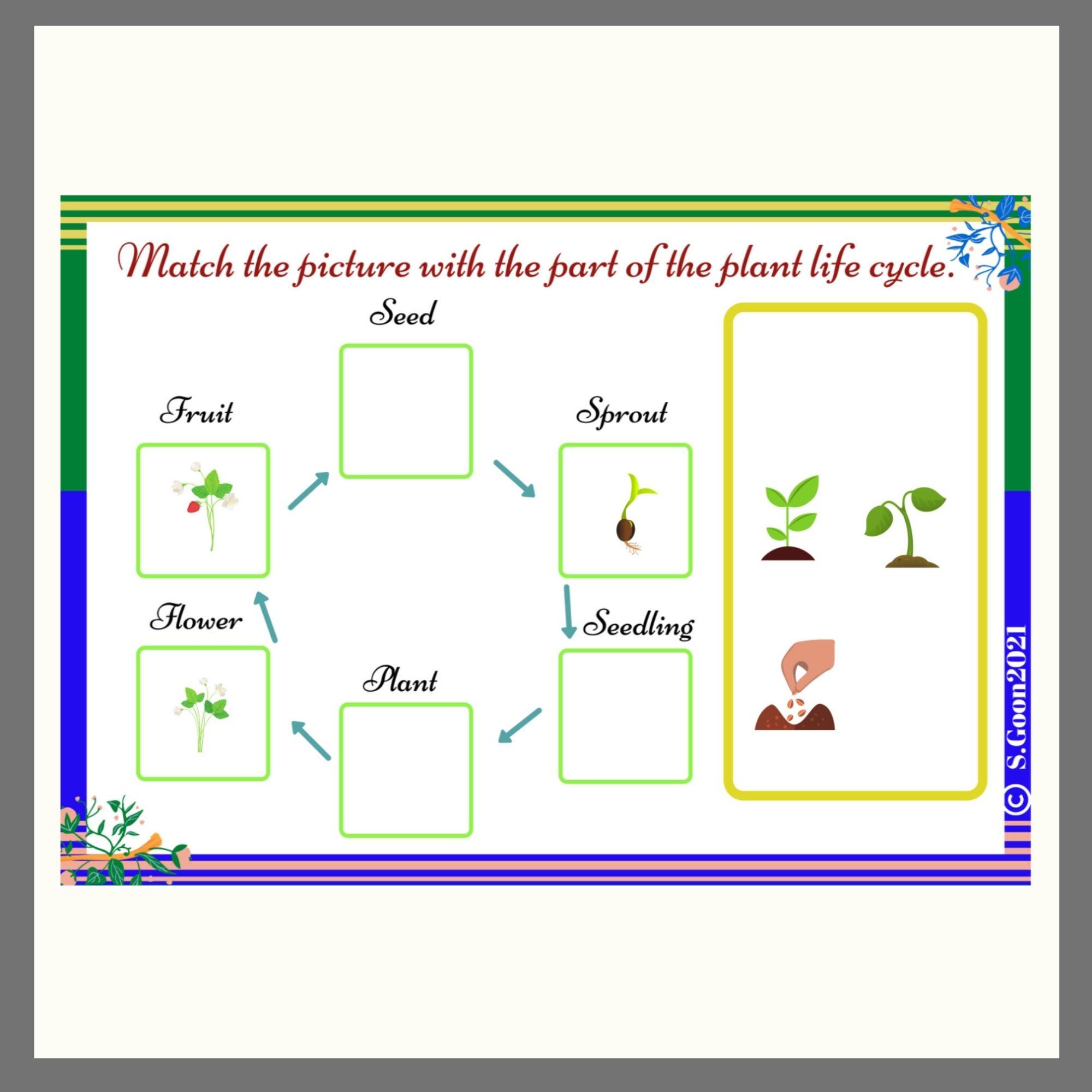
Plant Life Cycle Stages
The life cycle of a plant is a complex and fascinating process that involves several distinct stages. Each stage plays a crucial role in the development and reproduction of the plant.
Seed Stage
The seed stage marks the beginning of a plant’s life. A seed is a small, hard-coated structure that contains the embryo of a new plant. The embryo is surrounded by a food supply, which provides nourishment during the early stages of growth.
- Structure: A seed typically consists of an outer seed coat, an embryo, and a food supply (endosperm or cotyledons).
- Function: The seed protects the embryo from harsh environmental conditions and provides nourishment for the developing plant.
- Germination: Under favorable conditions (moisture, warmth, and oxygen), the seed absorbs water and begins to germinate. The embryo resumes growth, and a root and shoot emerge from the seed.
Plant Life Cycle Adaptations

Plants have evolved remarkable adaptations to survive in diverse environments, from arid deserts to lush rainforests. These adaptations enable plants to thrive in specific conditions, maximizing their chances of survival and reproduction.
One common adaptation is the development of specialized root systems. Plants in dry habitats, such as cacti and succulents, have shallow, wide-spreading roots that efficiently absorb moisture from the soil. In contrast, plants in wet habitats, such as mangroves and water lilies, have specialized roots that allow them to anchor in waterlogged or muddy environments.
Leaf Adaptations
- Thick, waxy leaves: Plants in arid regions have thick, waxy leaves that reduce water loss through transpiration.
- Spines or thorns: Some plants have spines or thorns to deter herbivores from eating their leaves.
- Large surface area: Plants in low-light environments have large leaves to maximize sunlight absorption.
Reproductive Adaptations
Plants have also evolved reproductive adaptations to ensure successful pollination and seed dispersal. For example, some plants produce brightly colored flowers to attract pollinators, while others release fragrant scents to lure insects.
Seed dispersal mechanisms vary widely among plants. Some plants, like dandelions, produce lightweight seeds with fluffy parachutes that can be carried by the wind. Others, like coconuts, have hard shells that can float on water for long distances.
Examples of Unique Adaptations
- Venus flytrap: This carnivorous plant has specialized leaves that trap and digest insects, providing it with additional nutrients.
- Mistletoe: This parasitic plant attaches itself to the branches of trees and obtains nutrients from its host.
- Welwitschia mirabilis: This desert plant has only two leaves that grow continuously throughout its lifetime.
Plant Life Cycle Game
To teach players about the plant life cycle, a game can be designed with engaging rules and interactive elements. This game can serve as an effective educational tool, fostering a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Game Design
The game board represents the different stages of the plant life cycle: seed, germination, seedling, maturity, and reproduction. Players take turns rolling a die and moving their game pieces around the board, landing on specific squares that trigger actions related to the corresponding stage.
For example, landing on the “seed” square may require players to plant a seed in a pot, while landing on the “maturity” square could involve caring for a fully grown plant. By completing these actions, players learn about the characteristics and requirements of each stage.
Game Rules, Plant life cycle game
- The game is played with 2-4 players.
- Each player has a game piece representing a plant.
- Players take turns rolling a die and moving their game pieces around the board.
- The first player to complete the entire life cycle wins the game.
Educational Value
The game provides a hands-on, interactive way for players to learn about the plant life cycle. By engaging in the gameplay, players develop a deeper understanding of the different stages and the factors that influence plant growth and reproduction.
Additionally, the game promotes critical thinking and problem-solving skills as players navigate the challenges and make decisions throughout the gameplay. It also fosters collaboration and communication among players as they work together to complete the life cycle.