Behold the captivating Plant Life Cycle Poster, a gateway into the intricate world of plant biology. This comprehensive guide unravels the mysteries of plant development, from the humble seed’s awakening to the majestic bloom of flowers and the fruition of fruits. Join us on an enthralling expedition where scientific precision intertwines with visual storytelling.
As we delve into the life cycle of plants, we’ll explore the remarkable processes that govern their growth and reproduction. Discover how seeds germinate and sprout, how seedlings transform into mature plants, and how environmental factors shape their destiny. With each revelation, our understanding of the plant kingdom deepens, inspiring awe and appreciation for the wonders of nature.
Seed Germination and Growth: Plant Life Cycle Poster
The journey of a plant begins with the germination of a seed. This intricate process marks the transition from a dormant seed to a thriving seedling. Water plays a pivotal role in this transformation, acting as a catalyst for metabolic reactions within the seed. Sunlight and temperature also exert significant influence, providing the energy and optimal conditions for germination to occur.
Plant life cycle posters can provide a comprehensive overview of the stages of plant development. They often include detailed illustrations of different plant parts and their functions. For example, the geum mrs bradshaw plant is known for its showy flowers and attractive foliage.
Its life cycle includes seed germination, seedling growth, flowering, and seed production. Understanding the life cycle of plants can help us appreciate the importance of plant diversity and the role plants play in the ecosystem. Plant life cycle posters can serve as valuable educational tools for students and enthusiasts alike.
Stages of Plant Growth
Once germination is complete, the plant embarks on a remarkable journey of growth and development. This process can be broadly divided into several distinct stages:
- Seedling Stage: The newly emerged plant, characterized by its delicate structure and reliance on stored nutrients within the seed.
- Vegetative Growth: A period of rapid growth and development, during which the plant establishes its root system, stem, and leaves.
- Reproductive Growth: The plant reaches maturity and begins to produce flowers and fruits, marking the transition to its reproductive phase.
Plant Structures and Functions
Plants have evolved specialized structures that enable them to perform various functions essential for their survival and growth. These structures include roots, stems, leaves, and flowers, each with distinct roles in supporting the plant’s overall biology.
Roots
- Anchor the plant firmly in the soil, providing stability and support.
- Absorb water and nutrients from the soil, which are transported to other parts of the plant.
- Store food reserves, such as starch and sugars, for later use by the plant.
Stems
- Provide structural support, allowing the plant to stand upright and withstand external forces.
- Transport water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves and vice versa.
- Contain specialized tissues that conduct photosynthesis, producing food for the plant.
Leaves
- Carry out photosynthesis, converting sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen.
- Regulate gas exchange, allowing the plant to absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen.
- Transpire water vapor, contributing to the water cycle and cooling the plant.
Flowers
- Reproductive structures that produce seeds, ensuring the survival and propagation of the plant species.
- Attract pollinators, such as insects or birds, to facilitate cross-fertilization.
- Contain specialized tissues that protect the developing seeds and provide nutrients for their growth.
| Plant Structure | Functions |
|---|---|
| Roots | Anchoring, water and nutrient absorption, storage |
| Stems | Support, transport, photosynthesis |
| Leaves | Photosynthesis, gas exchange, transpiration |
| Flowers | Reproduction, pollination, seed production |
Life Cycle of a Plant
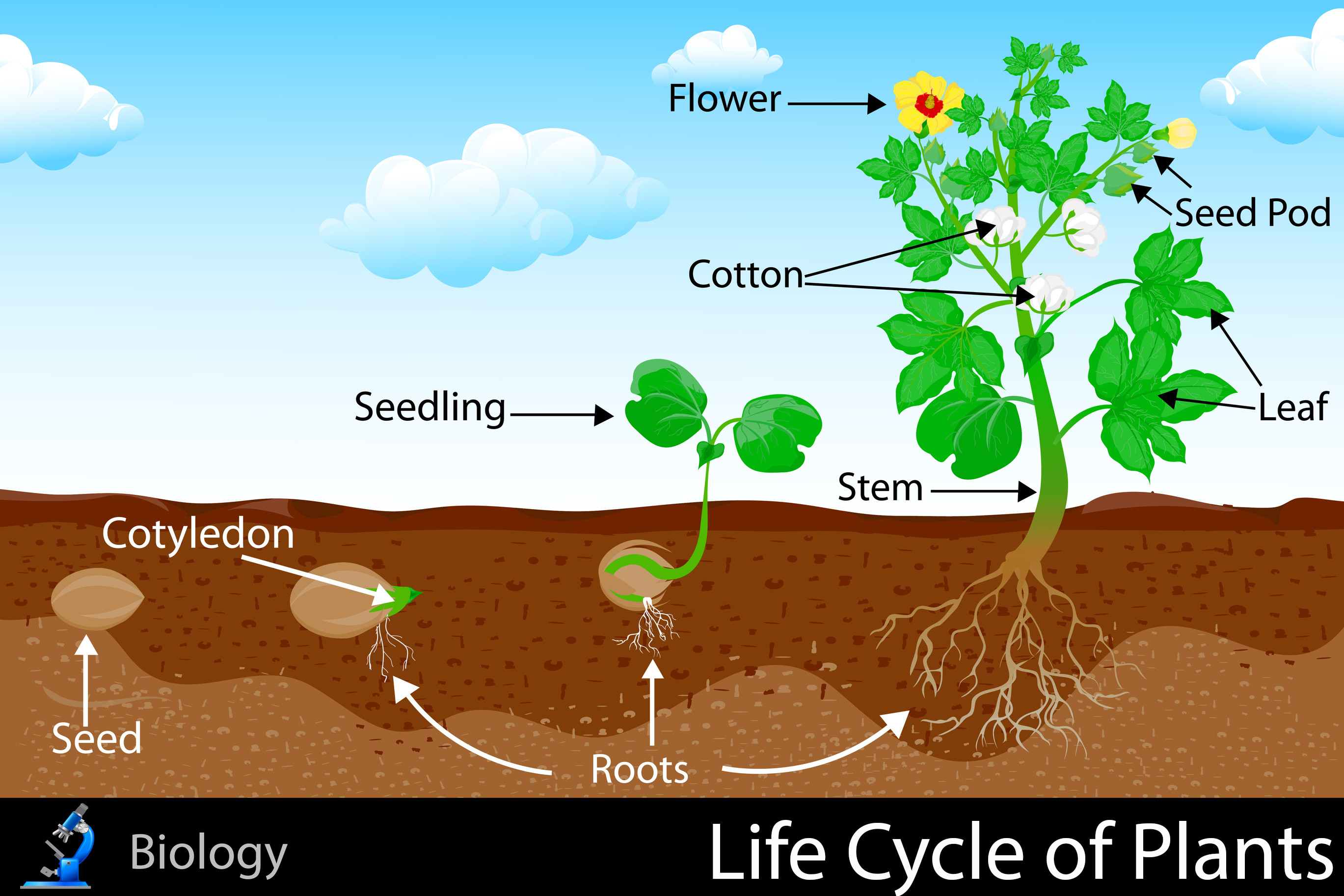
The life cycle of a plant refers to the stages of development from seed to fruit production. It involves a series of sequential events influenced by genetic and environmental factors.
Stages of a Plant’s Life Cycle
The plant life cycle consists of distinct stages:
- Germination: The seed absorbs water and begins to sprout, developing a root and a shoot.
- Seedling Stage: The young plant establishes its root system and develops leaves, gaining energy through photosynthesis.
- Vegetative Growth: The plant grows in size, producing new leaves, stems, and branches.
- Flowering: The plant produces flowers, which are reproductive structures.
- Fruit Production: After pollination and fertilization, the flowers develop into fruits, which contain seeds.
Environmental Factors Influencing the Life Cycle, Plant life cycle poster
Environmental factors significantly impact the plant’s life cycle:
- Temperature: Optimal temperatures are required for seed germination, growth, and flowering.
- Water Availability: Plants need sufficient water for photosynthesis and cellular processes.
- Sunlight: Sunlight is essential for photosynthesis, providing energy for plant growth.
- Soil Conditions: The soil’s pH, nutrient content, and drainage affect plant growth and development.
Plant life cycle posters illustrate the stages of a plant’s development from seed to maturity. They are valuable educational tools, providing insights into the intricate processes of plant growth. In a similar vein, the Seohan Auto USA Plant 2 showcases the meticulous stages of automotive manufacturing, from raw materials to finished vehicles.
Just as plant life cycle posters enhance our understanding of botanical processes, this state-of-the-art facility provides a glimpse into the precision and efficiency of modern manufacturing.
A plant life cycle poster can be an invaluable tool for understanding the stages of plant growth and development. If you’re interested in gardening in zone 3, you’ll want to focus on perennial plants that are hardy enough to withstand the cold winters.
These plants will come back year after year, so you can enjoy their beauty for seasons to come. Plant life cycle posters can help you identify the different stages of growth for your perennial plants, so you can provide them with the best possible care.