Plants in south dakota – Embark on a captivating journey through the vibrant plant life of South Dakota, where native species thrive amidst diverse ecosystems, playing a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. From towering trees to delicate wildflowers, discover the unique characteristics, adaptations, and ecological significance of these botanical wonders.
South Dakota’s plant communities provide sustenance, shelter, and oxygen for a myriad of wildlife species, shaping the intricate tapestry of life that defines this region. Their resilience and adaptability have allowed them to flourish in the face of harsh climatic conditions, contributing to the stability and biodiversity of the Northern Plains.
South Dakota Native Plant Species: Plants In South Dakota
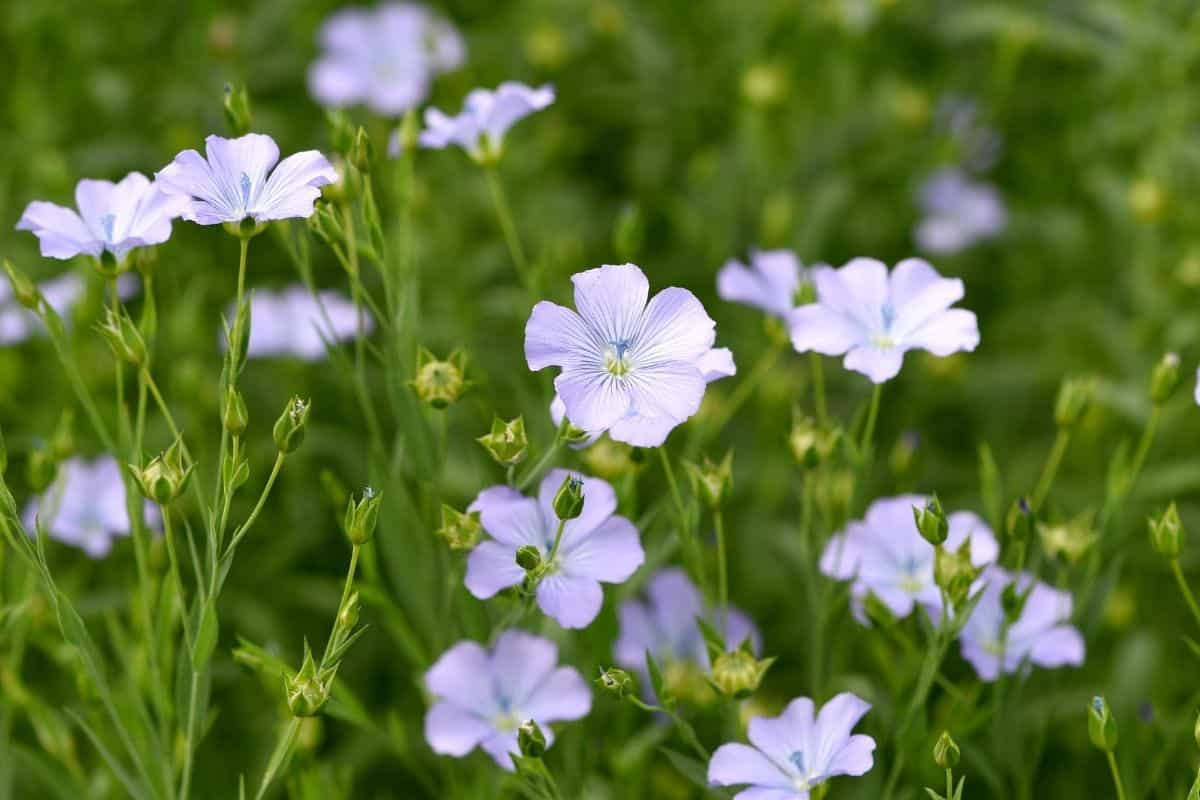

South Dakota is home to a diverse array of native plant species, each adapted to the unique climate and landscapes of the region. These plants play a crucial role in maintaining the ecological balance and biodiversity of the state.
From the rolling prairies to the rugged Black Hills, South Dakota’s native plants exhibit a wide range of characteristics and adaptations. Some species have evolved to withstand the harsh winters and extreme temperature fluctuations, while others thrive in the drier, more arid conditions of the western part of the state.
Table of Native Plant Species
The following table provides a comprehensive list of some of the most common and significant native plant species found in South Dakota, along with their scientific names, common names, habitats, and conservation status:
| Scientific Name | Common Name | Habitat | Conservation Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bouteloua gracilis | Blue grama grass | Prairies, grasslands | Least Concern |
| Stipa comata | Needle-and-thread grass | Prairies, grasslands | Least Concern |
| Astragalus crassicarpus | Ground plum | Prairies, grasslands | Least Concern |
| Rosa arkansana | Prairie rose | Prairies, grasslands, woodlands | Least Concern |
| Pinus ponderosa | Ponderosa pine | Black Hills, forests | Least Concern |
| Juniperus scopulorum | Rocky Mountain juniper | Black Hills, forests | Least Concern |
| Betula papyrifera | Paper birch | Riparian areas, forests | Least Concern |
| Populus tremuloides | Quaking aspen | Forests, woodlands | Least Concern |
Role of Plants in South Dakota’s Ecosystems
Plants are the foundation of South Dakota’s ecosystems, playing a vital role in maintaining the ecological balance and supporting a diverse array of wildlife. They provide essential resources such as food, shelter, and oxygen, contributing significantly to the stability and resilience of these ecosystems.
The prairies, grasslands, and forests of South Dakota are home to a wide variety of plant species, each adapted to specific environmental conditions. These plants form complex communities that interact with each other and with the animals that depend on them.
Food and Shelter for Wildlife
Plants are the primary source of food for many animals in South Dakota’s ecosystems. Herbivores, such as deer, elk, and bison, rely on grasses and other plants for sustenance. Carnivores, such as coyotes and bobcats, prey on herbivores, and their populations are indirectly supported by the availability of plant life.
In addition to providing food, plants also offer shelter for wildlife. Trees and shrubs provide nesting sites for birds, while dense vegetation can provide cover for animals seeking protection from predators or harsh weather conditions.
Oxygen Production and Carbon Sequestration
Plants play a crucial role in the cycling of oxygen and carbon in the atmosphere. Through photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, which is essential for all aerobic organisms. They also store carbon in their tissues, helping to regulate the Earth’s climate.
- Oxygen production: Plants release oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis, which is the process by which they convert sunlight into energy.
- Carbon sequestration: Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in their tissues, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change.
Soil Stabilization and Water Filtration
The root systems of plants help to stabilize soil, preventing erosion and maintaining the integrity of ecosystems. Plants also play a role in water filtration, absorbing and filtering pollutants from the soil and water.
- Soil stabilization: The root systems of plants help to hold soil in place, preventing erosion and maintaining the integrity of ecosystems.
- Water filtration: Plants absorb and filter pollutants from the soil and water, helping to improve water quality and protect aquatic ecosystems.
Plant Conservation and Restoration in South Dakota

South Dakota is home to a diverse range of plant species, many of which are unique to the state’s unique ecosystems. However, these plant populations are facing threats from habitat loss, climate change, and invasive species. Conservation and restoration efforts are underway to protect and restore these valuable plant communities.
Challenges and Successes
One of the biggest challenges to plant conservation in South Dakota is the vastness of the state. The state covers over 77,000 square miles, and much of the land is privately owned. This makes it difficult to monitor and protect plant populations across the state.
Despite the challenges, there have been a number of successes in plant conservation and restoration in South Dakota. One of the most notable successes is the restoration of the tallgrass prairie ecosystem. The tallgrass prairie once covered much of the state, but it was converted to farmland and other uses over the past century. In recent years, there has been a growing effort to restore the tallgrass prairie, and several large-scale restoration projects have been completed.
Organizations and Resources
There are a number of organizations and resources dedicated to plant conservation in South Dakota. These organizations include:
* South Dakota Department of Game, Fish and Parks
* The Nature Conservancy
* South Dakota Native Plant Society
* South Dakota State University
These organizations provide a variety of services, including:
* Monitoring plant populations
* Restoring plant communities
* Educating the public about the importance of plant conservation
Restoration Approaches, Plants in south dakota
There are a variety of different approaches that can be used to restore plant communities. The best approach for a particular site will depend on the specific conditions of the site. Some of the most common restoration approaches include:
* Seeding: Seeding is a method of planting seeds directly into the soil. This is a relatively simple and inexpensive method, but it can be less successful than other methods, especially in areas with harsh conditions.
* Plugging: Plugging is a method of planting small plugs of plants into the soil. Plugs are typically grown in a greenhouse or nursery before being planted in the field. This method is more expensive than seeding, but it is often more successful, especially in areas with harsh conditions.
* Transplanting: Transplanting is a method of moving plants from one location to another. This method is often used to move plants from areas where they are threatened to areas where they are more likely to thrive.