Rain garden plants ohio – Native Ohio plants are the cornerstone of effective rain gardens in the Buckeye State. Discover the top 10 most suitable species, their benefits, and how plant diversity enhances rain garden performance.
Rain garden design in Ohio requires careful consideration of climate, soil, and drainage. Learn the principles of optimal sizing, location, and overflow systems to maximize rainwater management.
Rain Garden Plant Selection for Ohio: Rain Garden Plants Ohio
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/rain-garden-rocks-and-plants-ed331a6b-aeb768acecdf44c7a834ee325d6de1a4.jpg)
Native Ohio plants are crucial for rain gardens as they are adapted to the local climate and soil conditions, requiring less maintenance and providing optimal benefits. They support local wildlife, enhance biodiversity, and promote a healthy ecosystem.
Top 10 Ohio Rain Garden Plants, Rain garden plants ohio
- Swamp Milkweed (Asclepias incarnata): Attracts pollinators, supports Monarch butterflies, and tolerates wet conditions.
- Cardinal Flower (Lobelia cardinalis): Bright red blooms attract hummingbirds, and it thrives in moist soil.
- Ironweed (Vernonia spp.): Late-blooming perennial with showy purple flowers, providing nectar for insects.
- Blue Flag Iris (Iris versicolor): Showy blue-purple flowers, prefers moist to wet areas, and tolerates some shade.
- Joe-Pye Weed (Eutrochium purpureum): Tall, showy pink or purple flowers, attracts butterflies and bees, and prefers moist soil.
- Coneflower (Echinacea purpurea): Daisy-like purple flowers, attracts pollinators, and is drought-tolerant.
- Turtlehead (Chelone glabra): Unique pink or white flowers resembling turtle heads, prefers moist to wet soil, and attracts hummingbirds.
- New England Aster (Symphyotrichum novae-angliae): Showy purple or blue flowers, blooms late in the season, and attracts pollinators.
- Goldenrod (Solidago spp.): Yellow flowers, provides late-season nectar for insects, and is drought-tolerant.
- Virginia Creeper (Parthenocissus quinquefolia): Climbing vine with attractive fall foliage, provides cover for wildlife, and tolerates various soil conditions.
Plant diversity is essential for effective rain gardens. Different plants have varying root depths, nutrient requirements, and flowering times, ensuring year-round function and resilience. They create a balanced ecosystem, support a wide range of wildlife, and enhance the overall effectiveness of the rain garden in managing stormwater runoff.
Design Considerations for Rain Gardens in Ohio
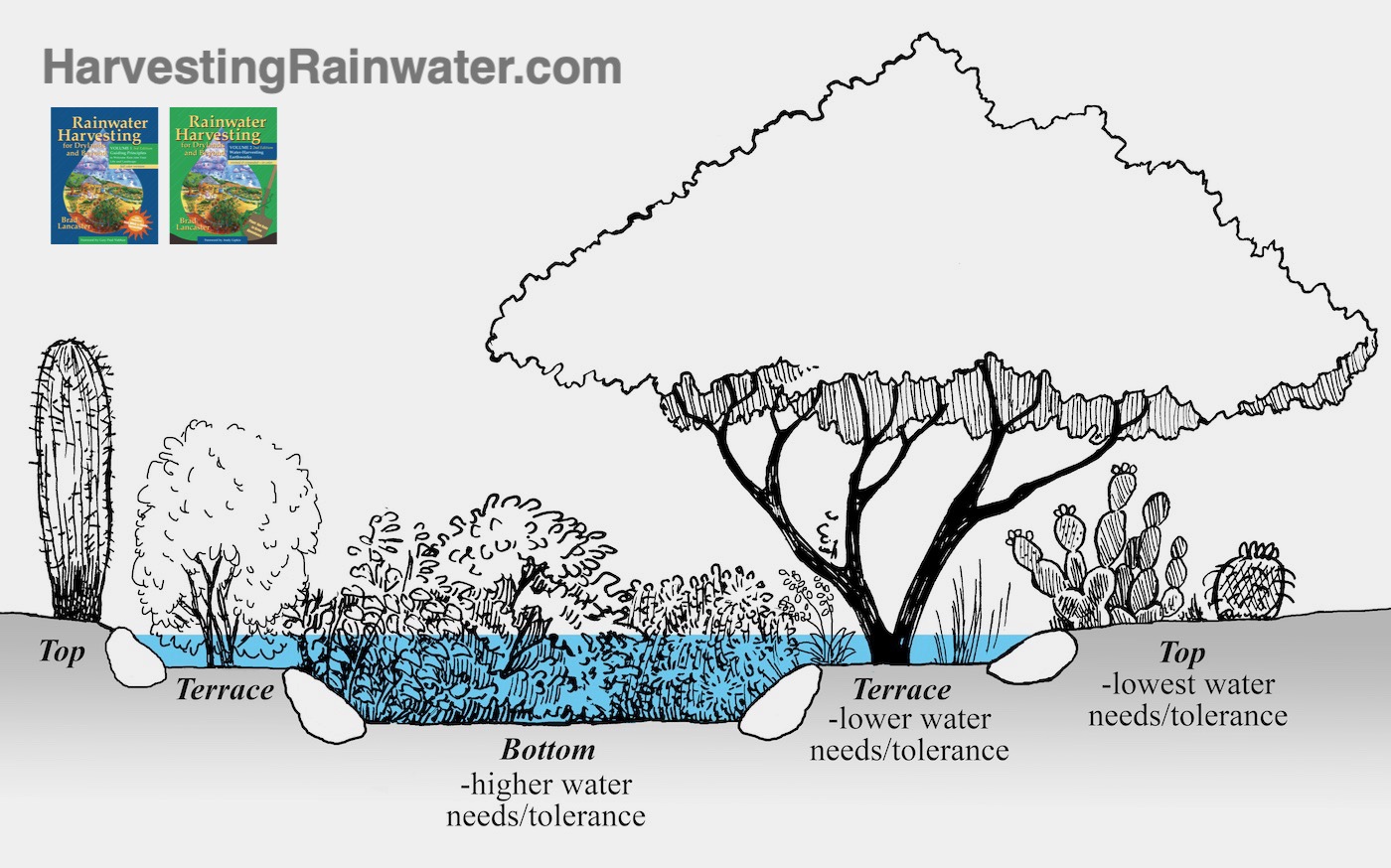
Rain gardens are designed to mimic natural ecosystems, effectively managing stormwater runoff and providing numerous environmental benefits. In Ohio’s climate, characterized by ample rainfall and varying soil conditions, specific design considerations are crucial for optimal performance.
Determining Size and Location
The size of a rain garden depends on the amount of runoff it needs to accommodate. A general rule is to create a garden that is approximately 10% of the impervious surface area contributing to the runoff. For instance, if your driveway is 1,000 square feet, your rain garden should be around 100 square feet.
The location of the rain garden is equally important. Choose an area that is low-lying and away from buildings and septic systems. Avoid placing the garden in areas with steep slopes or poor drainage. Ensure that the water has a clear path to flow into the garden without causing erosion or flooding.
Drainage and Overflow Systems
Proper drainage is essential for rain garden functionality. The soil should be well-draining, allowing water to infiltrate quickly and preventing waterlogging. If the soil is compacted or has poor drainage, consider amending it with sand or organic matter to improve permeability.
An overflow system is also crucial to prevent flooding during heavy rainfall events. This can be achieved by creating a spillway or connecting the rain garden to a nearby storm drain or swale. The overflow system should be designed to handle the excess water without causing erosion or damage to surrounding areas.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting for Rain Gardens in Ohio
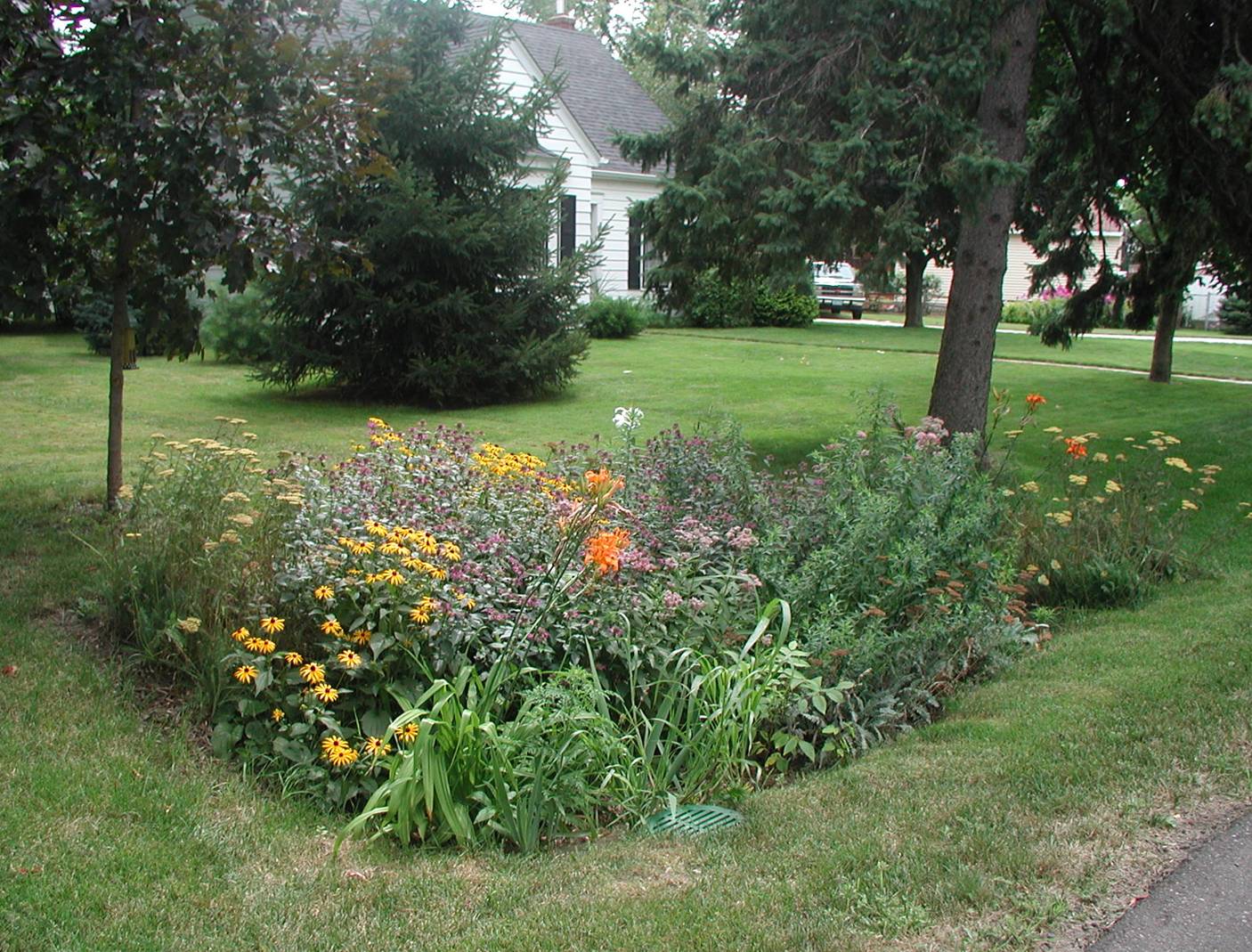

Maintaining a rain garden in Ohio requires ongoing care to ensure optimal performance. This involves proper planting techniques, regular watering, mulching, and addressing common challenges.
Planting
When planting rain garden plants, it is crucial to choose species that are native to Ohio and well-suited to the specific conditions of your site. Dig holes twice as wide as the root ball and just as deep. Place the plant in the hole and backfill with the native soil, gently firming it around the roots. Water deeply after planting.
Watering
Rain gardens rely primarily on rainfall for hydration. However, during extended dry periods, supplemental watering may be necessary. Water deeply and infrequently, allowing the soil to dry out between waterings. Avoid overwatering, as this can lead to root rot.
Mulching
Mulching around rain garden plants helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Use a 2-3 inch layer of organic mulch, such as shredded leaves, compost, or bark chips. Keep the mulch away from the base of the plants to prevent rot.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
Ohio rain gardens may face certain challenges, including:
- Standing Water: If water remains in the rain garden for more than 24 hours after a rainfall event, it may indicate poor drainage. Consider amending the soil with sand or gravel, or installing a French drain to improve drainage.
- Erosion: Heavy rainfall can cause erosion in rain gardens. Use erosion control measures such as planting groundcovers, installing rock check dams, or lining the garden with erosion control fabric.
- Pest and Disease: Rain garden plants can be susceptible to pests and diseases. Practice good garden hygiene by removing dead or diseased plant material, and use organic pest control methods whenever possible.

Rain garden plants in Ohio, like the vibrant frosty morn sedum plant , play a crucial role in capturing and filtering stormwater runoff. This resilient succulent boasts icy blue-green foliage that transforms into a captivating shade of pink in autumn.
Its ability to thrive in moist soil conditions and tolerate drought makes it an ideal choice for rain gardens, where it effectively absorbs excess water and reduces the risk of flooding.
The beauty of rain garden plants in Ohio lies in their ability to thrive in wet conditions. For those with limited space, consider choosing varieties that can also adapt to shallow pots, like plants for shallow pots . This versatility allows you to incorporate the benefits of rain garden plants into smaller spaces, effectively managing stormwater and beautifying your surroundings.
Rain garden plants in Ohio can be found at plants direct conway sc . These plants are designed to thrive in wet conditions and help filter pollutants from rainwater. By planting rain garden plants, you can help improve the water quality in your local waterways.
Rain garden plants in Ohio include native species such as black-eyed Susans, coneflowers, and swamp milkweed.