The plant cell worksheet invites us on a captivating journey into the intricate world of plant cells, unveiling their structure, processes, and the fundamental role they play in the growth and development of plants. This comprehensive guide will illuminate the key components of plant cells, the remarkable process of photosynthesis, and the intricate mechanisms of cell division.
As we delve into the depths of this worksheet, we will uncover the fascinating secrets of plant cells, shedding light on their unique adaptations and the vital functions they perform to sustain life on Earth.
Plant Cell Structure and Function: The Plant Cell Worksheet
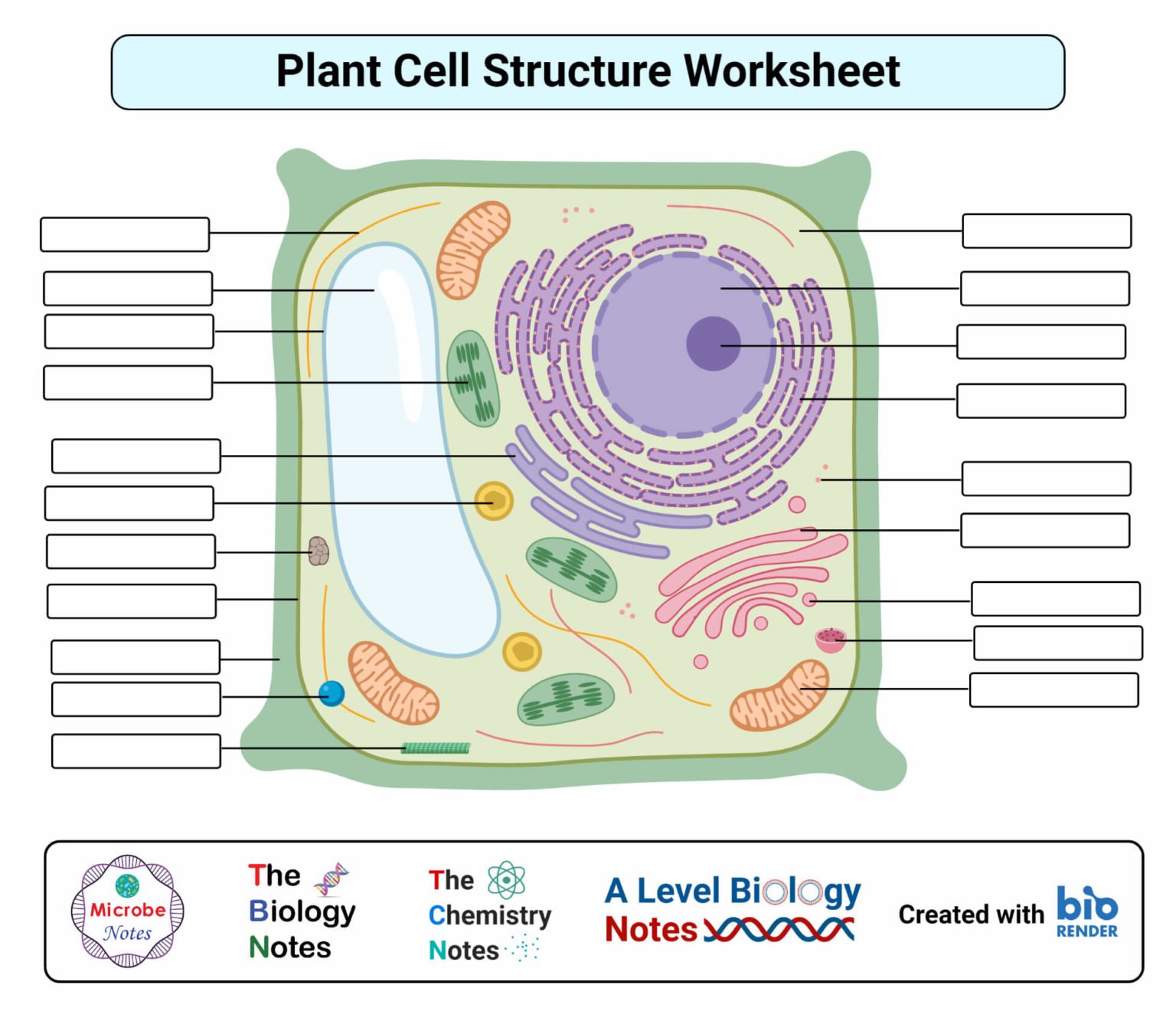
Plant cells, the fundamental units of life in plants, exhibit a remarkable level of complexity and organization. They are enclosed within a rigid cell wall, a unique feature that distinguishes them from animal cells. The cell wall, composed primarily of cellulose, provides structural support and protection to the cell.
Beneath the cell wall lies the cell membrane, a selectively permeable barrier that regulates the entry and exit of substances. It maintains the cell’s internal environment and facilitates communication with neighboring cells.
Within the cell membrane, the cytoplasm, a gel-like substance, houses various organelles, each with specialized functions. The nucleus, the control center of the cell, contains the genetic material (DNA) and directs cellular activities. Ribosomes, found in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum, are responsible for protein synthesis.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranes that folds and transports proteins. It can be smooth or rough, with ribosomes attached to its surface. The Golgi apparatus, another membranous organelle, modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for secretion or storage.
Mitochondria, often referred to as the “powerhouses of the cell,” generate energy through cellular respiration. Chloroplasts, found only in plant cells, contain chlorophyll and carry out photosynthesis, the process by which light energy is converted into chemical energy.
Plant cells also possess vacuoles, membrane-bound sacs that store various substances, including water, salts, and waste products. They contribute to maintaining cell turgor and providing structural support.
The intricate interplay of these components ensures the proper functioning and homeostasis of plant cells, enabling them to perform essential life processes such as photosynthesis, growth, and reproduction.
Plant Cell Processes
Plant cells carry out essential processes that sustain life on Earth, including photosynthesis and cellular respiration. These processes enable plants to convert light energy into chemical energy, providing the foundation for the food chains and ecosystems that support all living organisms.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a complex process that converts light energy into chemical energy, stored in the form of glucose. This process occurs in specialized organelles called chloroplasts, found in the cytoplasm of plant cells.
Photosynthesis can be divided into two main stages:
- Light-Dependent Reactions: These reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts and use light energy to produce ATP and NADPH.
- Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle): These reactions occur in the stroma of chloroplasts and use ATP and NADPH to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
The overall equation for photosynthesis is:
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are the organelles responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells. They contain a green pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy from the sun. This energy is then used to drive the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
Chloroplasts have a double membrane structure. The inner membrane surrounds a fluid-filled space called the stroma, which contains enzymes and other molecules necessary for the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis.
Experiment to Demonstrate Photosynthesis
A simple experiment can be conducted to demonstrate the process of photosynthesis:
- Place a green leaf in a beaker of water and cover it with a funnel.
- Invert a test tube filled with water over the funnel.
- Place the beaker in a sunny location.
- Observe the test tube over time.
As photosynthesis occurs, oxygen will be released from the leaf and collect in the test tube, displacing the water.
Plant Cell Division

Cell division is essential for plant growth, development, and reproduction. Plant cells undergo two main types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis.
Stages of Mitosis
Mitosis is the process by which a cell divides into two identical daughter cells. It occurs in four stages:
- Prophase: Chromosomes become visible and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase: Chromosomes align at the center of the cell.
- Anaphase: Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase: Two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes, and the cell membrane pinches in the middle, dividing the cell into two.
Stages of Meiosis
Meiosis is the process by which a cell divides into four haploid daughter cells. It occurs in two rounds of division, called meiosis I and meiosis II.
- Meiosis I: Homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through a process called crossing over. The chromosomes then separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Meiosis II: Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell. This results in four haploid daughter cells.
Differences between Mitosis and Meiosis, The plant cell worksheet
The key differences between mitosis and meiosis are:
- Number of daughter cells: Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells, while meiosis produces four haploid daughter cells.
- Synapsis: Homologous chromosomes pair up during meiosis, but not during mitosis.
- Crossing over: Genetic material is exchanged between homologous chromosomes during meiosis, but not during mitosis.
- Importance: Mitosis is important for growth and development, while meiosis is important for reproduction.
Mitosis and meiosis are essential processes for plant growth and reproduction. They ensure that cells are properly divided and that genetic material is passed on to the next generation.
The plant cell worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the fundamental components and processes within plant cells. It highlights the structure and function of organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. Interestingly, these organelles are also present in pampas grass live plants , which are known for their distinctive, feathery plumes.
Understanding the similarities and differences between plant cells in different organisms can enhance our appreciation of the diverse and fascinating world of botany.
The plant cell worksheet is an educational tool that provides information about the structure and function of plant cells. The plant cell is a highly organized structure with many different components, including the cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus.
The plant cell is also the site of photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. One of the most important parts of a plant cell is the chloroplast. Chloroplasts are organelles that contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that absorbs sunlight.
The energy from sunlight is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, a sugar that the plant can use for energy. The Honda Anna Engine Plant is a state-of-the-art facility that produces engines for Honda vehicles. The plant is located in Anna, Ohio, and employs over 2,000 people.
The plant produces a variety of engines, including the 1.5-liter Earth Dreams engine that is used in the Honda Civic and Accord. The plant cell worksheet is a valuable resource for students who are learning about plant cells.
Plant cell worksheets offer an engaging way to learn about the fundamental components of plant cells. These worksheets often include diagrams and illustrations that help students visualize the various organelles and their functions. For those who enjoy gardening, understanding plant cell biology can be further enhanced by using terra cotta wall planters . These planters provide a stylish and porous environment for plants, allowing for optimal root aeration and drainage.
By integrating practical gardening with theoretical knowledge gained from plant cell worksheets, students can develop a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of plant life.