From the intricate symphony of photosynthesis to the astonishing diversity of plant life, this scientific exploration unveils the secrets of the plant kingdom, illuminating their essential role in the web of life and the very fabric of our planet.
Plants are multicellular eukaryotes that belong to the kingdom Plantae. They are the primary producers in the food chain and play a crucial role in the Earth’s ecosystem. Plants have evolved over millions of years to adapt to diverse environments, resulting in a wide range of forms and functions.
There are countless species of plants, each with unique characteristics. Here is a table summarizing some common types of plants:
| Type |
Characteristics |
| Angiosperms |
Flowering plants that produce seeds enclosed within fruits. |
| Gymnosperms |
Non-flowering plants that produce naked seeds, such as conifers and cycads. |
| Ferns |
Non-flowering plants that reproduce by spores. |
| Mosses |
Non-vascular plants that lack true roots, stems, and leaves. |
| Algae |
Simple, non-vascular plants that live in aquatic environments. |
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. It is a vital process that sustains life on Earth.
The process of photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells. Chloroplasts contain a green pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs sunlight. The sunlight energy is then used to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen is used to combine with carbon dioxide to form glucose, a sugar molecule that plants use for energy. The oxygen is released into the atmosphere.
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Photosynthesis is a complex process that involves a series of chemical reactions. However, the overall process can be summarized as follows:
- Sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll.
- Water molecules are split into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Hydrogen is used to combine with carbon dioxide to form glucose.
- Oxygen is released into the atmosphere.
Photosynthesis is essential for plant growth and development. It provides plants with the energy they need to produce food, grow, and reproduce.
Plant Classification: What Is A Title Plant
Classifying plants is essential for understanding their diversity, evolutionary relationships, and ecological roles. Over the centuries, various methods have been developed to categorize plants, each with its own advantages and limitations.
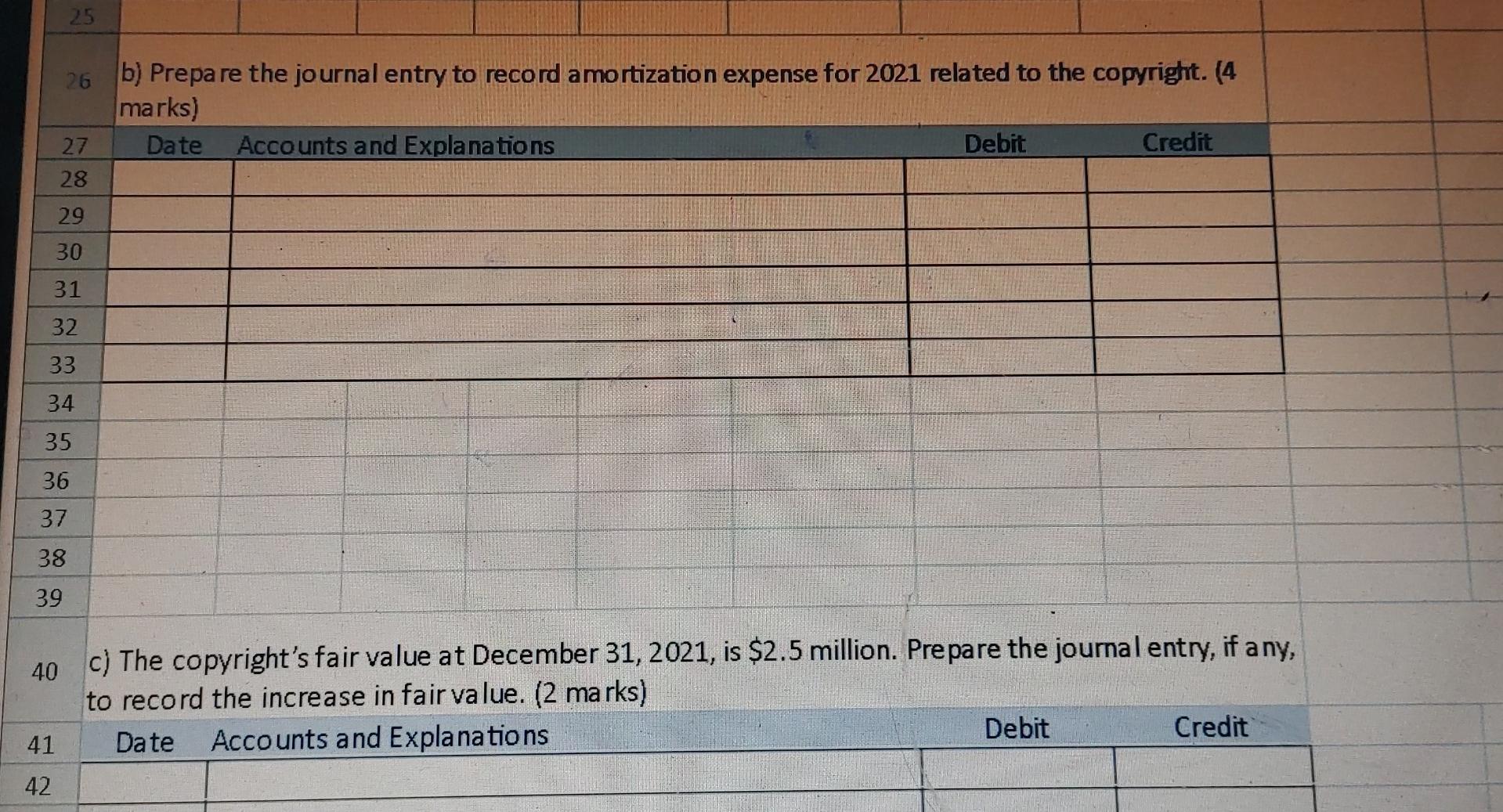
Binomial Nomenclature
Binomial nomenclature is a standardized system of naming species using two words: the genus name and the species name. This system was introduced by Carl Linnaeus in the 18th century and has become the universally accepted method of naming plants.
Major Plant Groups
Based on their shared characteristics, plants are classified into several major groups:
- Bryophytes: Non-vascular plants, including mosses, liverworts, and hornworts.
- Pteridophytes: Vascular plants with no seeds, including ferns, horsetails, and club mosses.
- Gymnosperms: Seed-bearing plants with naked seeds, including conifers, cycads, and ginkgo trees.
- Angiosperms: Seed-bearing plants with enclosed seeds, including flowering plants.
Monocots vs. Dicots
Monocots and dicots are two major groups of angiosperms that differ in several key characteristics:
- Seed Structure: Monocots have one seed leaf (cotyledon), while dicots have two seed leaves (cotyledons).
- Root System: Monocots have a fibrous root system, while dicots have a taproot system.
- Leaf Veins: Monocot leaves have parallel veins, while dicot leaves have net-like veins.
- Flower Parts: Monocot flowers have parts in multiples of three, while dicot flowers have parts in multiples of four or five.
Plant Uses

Plants are not only essential for our survival but also offer a vast array of uses that have shaped human civilization. They provide us with sustenance, medicine, shelter, and a plethora of other products that enhance our lives.
Food
Plants are the primary source of nutrition for humans and animals alike. They provide us with carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients. Cereals such as wheat, rice, and corn are staple foods for billions of people worldwide. Fruits, vegetables, and legumes offer a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that are crucial for maintaining good health.
Medicine, What is a title plant
Plants have been used as medicine for centuries. Many modern pharmaceuticals are derived from plant extracts or are synthetic versions of plant compounds. Aspirin, for example, is derived from the willow tree, and digitalis, used to treat heart conditions, comes from the foxglove plant. Plants also provide essential oils and other natural remedies that are used for a variety of health purposes.
Other Uses
Beyond food and medicine, plants are used for a wide range of other purposes. They are used to produce fibers for clothing, paper, and other materials. Wood from trees is used for construction, furniture, and other products. Plants are also used to make dyes, perfumes, and cosmetics.
Importance in the Environment
Plants play a vital role in the environment. They produce oxygen through photosynthesis, which is essential for all aerobic life. Plants also help to regulate the Earth’s climate by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing water vapor into the atmosphere. They provide habitat for wildlife and help to prevent soil erosion.
Economic Value of Plants
The economic value of plants is immense. The global agricultural industry is worth trillions of dollars each year. Plants are also used to produce a wide range of industrial products, such as paper, textiles, and pharmaceuticals. The following table provides an overview of the economic value of plants in various industries:
| Industry |
Value |
| Agriculture |
$5.7 trillion |
| Forestry |
$1.6 trillion |
| Paper and pulp |
$0.8 trillion |
| Textiles |
$0.5 trillion |
| Pharmaceuticals |
$0.3 trillion |